|
CUBIC TCP
CUBIC is a network congestion avoidance algorithm for TCP which can achieve high bandwidth connections over networks more quickly and reliably in the face of high latency than earlier algorithms. It helps optimize long fat networks. In 2006, the first CUBIC implementation was released in Linux kernel 2.6.13. Since kernel version 2.6.19, CUBIC replaces BIC-TCP as the default TCP congestion control algorithm in the Linux kernel. MacOS adopted TCP CUBIC with the OS X Yosemite release in 2014, while the previous release OS X Mavericks still used TCP New Reno. Microsoft adopted it by default in Windows 10.1709 Fall Creators Update (2017), and Windows Server 2016 1709 update. Characteristics CUBIC is a less aggressive and more systematic derivative of BIC TCP, in which the window size is a cubic function of time since the last congestion event, with the inflection point set to the window size prior to the event. Because it is a cubic function, there are two components t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Congestion
Network congestion in data networking and queueing theory is the reduced quality of service that occurs when a network node or link is carrying more data than it can handle. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections. A consequence of congestion is that an incremental increase in offered load leads either only to a small increase or even a decrease in network throughput. Network protocols that use aggressive retransmissions to compensate for packet loss due to congestion can increase congestion, even after the initial load has been reduced to a level that would not normally have induced network congestion. Such networks exhibit two stable states under the same level of load. The stable state with low throughput is known as congestive collapse. Networks use congestion control and congestion avoidance techniques to try to avoid collapse. These include: exponential backoff in protocols such as CSMA/CA in 802.11 and the similar CSMA/C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
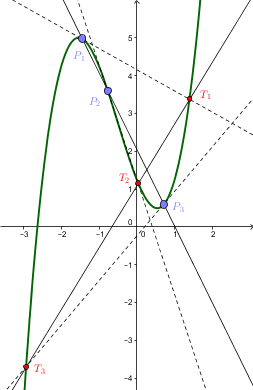
Cubic Function
In mathematics, a cubic function is a function of the form f(x)=ax^3+bx^2+cx+d, that is, a polynomial function of degree three. In many texts, the ''coefficients'' , , , and are supposed to be real numbers, and the function is considered as a real function that maps real numbers to real numbers or as a complex function that maps complex numbers to complex numbers. In other cases, the coefficients may be complex numbers, and the function is a complex function that has the set of the complex numbers as its codomain, even when the domain is restricted to the real numbers. Setting produces a cubic equation of the form :ax^3+bx^2+cx+d=0, whose solutions are called roots of the function. The derivative of a cubic function is a quadratic function. A cubic function with real coefficients has either one or three real roots ( which may not be distinct); all odd-degree polynomials with real coefficients have at least one real root. The graph of a cubic function always has a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound TCP
Compound TCP (CTCP) is a Microsoft algorithm that was introduced as part of the Windows Vista and Window Server 2008 TCP stack. It is designed to aggressively adjust the sender's congestion window to optimise TCP for connections with large bandwidth-delay products while trying not to harm fairness (as can occur with HSTCP). It is also available for Linux, as well as for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 via a hotfix. Principles of operation Like FAST TCP and TCP Vegas, Compound TCP uses estimates of queuing delay as a measure of congestion; if the queuing delay is small, it assumes that no links on its path are congested, and rapidly increases its rate. Unlike them, it does not seek to maintain a constant number of packets queued. Compound TCP maintains two congestion windows: a regular AIMD window and a delay-based window. The size of the actual sliding window used is the sum of these two windows. The AIMD window is increased the same way that TCP Reno increases it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCTP
The Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) is a computer networking communications protocol in the transport layer of the Internet protocol suite. Originally intended for Signaling System 7 (SS7) message transport in telecommunication, the protocol provides the message-oriented feature of the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), while ensuring reliable, in-sequence transport of messages with TCP congestion control, congestion control like the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Unlike UDP and TCP, the protocol supports multihoming and redundant paths to increase resilience and reliability. SCTP is standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in . The SCTP reference implementation was released as part of FreeBSD version 7, and has since been widely ported to other platforms. Formal oversight The IETF Signaling Transport (SIGTRAN) working group defined the protocol (number 132) in October 2000, and the IETF Transport Area (TSVWG) working group maintains it. defines t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TCP Congestion Avoidance Algorithm
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) uses a congestion control algorithm that includes various aspects of an additive increase/multiplicative decrease (AIMD) scheme, along with other schemes including slow start and a congestion window (CWND), to achieve congestion avoidance. The TCP congestion-avoidance algorithm is the primary basis for congestion control in the Internet. Per the end-to-end principle, congestion control is largely a function of internet hosts, not the network itself. There are several variations and versions of the algorithm implemented in protocol stacks of operating systems of computers that connect to the Internet. To avoid congestive collapse, TCP uses a multi-faceted congestion-control strategy. For each connection, TCP maintains a CWND, limiting the total number of unacknowledged packets that may be in transit end-to-end. This is somewhat analogous to TCP's sliding window used for flow control. Additive increase/multiplicative decrease The ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TCP BBR
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) uses a congestion control algorithm that includes various aspects of an additive increase/multiplicative decrease (AIMD) scheme, along with other schemes including slow start and a congestion window (CWND), to achieve congestion avoidance. The TCP congestion-avoidance algorithm is the primary basis for congestion control in the Internet. Per the end-to-end principle, congestion control is largely a function of internet hosts, not the network itself. There are several variations and versions of the algorithm implemented in protocol stacks of operating systems of computers that connect to the Internet. To avoid congestive collapse, TCP uses a multi-faceted congestion-control strategy. For each connection, TCP maintains a CWND, limiting the total number of unacknowledged packets that may be in transit end-to-end. This is somewhat analogous to TCP's sliding window used for flow control. Additive increase/multiplicative decrease The additive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairness Measure
Fairness measures or metrics are used in network engineering to determine whether users or applications are receiving a fair share of system resources. There are several mathematical and conceptual definitions of fairness. Transmission Control Protocol fairness Congestion control mechanisms for new network transmission protocols or peer-to-peer applications must interact well with Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). TCP fairness requires that a new protocol receive a no larger share of the network than a comparable TCP flow. This is important as TCP is the dominant transport protocol on the Internet, and if new protocols acquire unfair capacity they tend to cause problems such as congestion collapse. This was the case with the first versions of RealMedia's streaming protocol: it was based on UDP and was widely blocked at organizational firewalls until a TCP-based version was developed. TCP throughput unfairness over WiFi is a critical problem and needs further investigations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round-trip Delay Time
In telecommunications, round-trip delay (RTD) or round-trip time (RTT) is the amount of time it takes for a signal to be sent ''plus'' the amount of time it takes for acknowledgement of that signal having been received. This time delay includes propagation times for the paths between the two communication endpoints. In the context of computer networks, the signal is typically a data packet. RTT is commonly used interchangeably with ping time, which can be determined with the ping command. However, ping time may differ from experienced RTT with other protocols since the payload and priority associated with ICMP messages used by ping may differ from that of other traffic. End-to-end delay is the length of time it takes for a signal to travel in one direction and is often approximated as half the RTT. Protocol design RTT is a measure of the amount of time taken for an entire message to be sent to a destination and for a reply to be sent back to the sender. The time to send the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflection Point
In differential calculus and differential geometry, an inflection point, point of inflection, flex, or inflection (rarely inflexion) is a point on a smooth plane curve at which the curvature changes sign. In particular, in the case of the graph of a function, it is a point where the function changes from being concave (concave downward) to convex (concave upward), or vice versa. For the graph of a function of differentiability class (its first derivative , and its second derivative , exist and are continuous), the condition can also be used to find an inflection point since a point of must be passed to change from a positive value (concave upward) to a negative value (concave downward) or vice versa as is continuous; an inflection point of the curve is where and changes its sign at the point (from positive to negative or from negative to positive). A point where the second derivative vanishes but does not change its sign is sometimes called a point of undulation or und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 10 Version History
Windows 10 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. Microsoft described Windows 10 as an " operating system as a service" that would receive ongoing updates to its features and functionality, augmented with the ability for enterprise environments to receive non-critical updates at a slower pace or use long-term support milestones that will only receive critical updates, such as security patches, over their five-year lifespan of mainstream support. It was released in July 2015. Channels Windows 10 Insider Preview builds are delivered to Insiders in three different channels (previously "rings"). Insiders in the Dev Channel (previously ''Fast ring'') receive updates prior to those in the Beta Channel (previously ''Slow ring''), but might experience more bugs and other issues. Insiders in the Release Preview Channel (previously ''Release Preview ring'') do not receive updates until the version is almost available to the public, but are compara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Control Protocol
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the main communications protocol, protocols of the Internet protocol suite. It originated in the initial network implementation in which it complemented the Internet Protocol (IP). Therefore, the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP. TCP provides reliability (computer networking), reliable, ordered, and error detection and correction, error-checked delivery of a reliable byte stream, stream of octet (computing), octets (bytes) between applications running on hosts communicating via an IP network. Major internet applications such as the World Wide Web, email, remote administration, and file transfer rely on TCP, which is part of the transport layer of the TCP/IP suite. Transport Layer Security, SSL/TLS often runs on top of TCP. TCP is Connection-oriented communication, connection-oriented, meaning that sender and receiver firstly need to establish a connection based on agreed parameters; they do this through three-way Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OS X Mavericks
OS X Mavericks (version 10.9) is the 10th major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. OS X Mavericks was announced on June 10, 2013, at WWDC 2013, and was released on October 22, 2013, worldwide. It was also the last version to use a mostly skeuomorphic design; the next release, OS X Yosemite, featured a redesign of the user interface appearance. It was also the first version of macOS to be offered only on the App Store, rather than on a physical disk. The update emphasized battery life, Finder improvements, other improvements for power users, and increased iCloud integration, as well as bringing more of Apple's iOS apps to OS X. Mavericks was named after the surfing location in Northern California. It also removed some of the skeuomorphic designs from OS X Mountain Lion, and it is the final version of macOS that features the Lucida Grande typeface as the standard system font since Mac OS X Public Beta in 2000. Mav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |