|
CREB1
CAMP responsive element binding protein 1, also known as CREB-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CREB1'' gene. This protein binds the cAMP response element, a DNA nucleotide sequence present in many viral and cellular promoters. The binding of CREB1 stimulates transcription. This protein is a CREB transcription factor that is a member of the leucine zipper family of DNA-binding proteins. This protein binds as a homodimer to the cAMP-responsive element, an octameric palindrome. The protein is phosphorylated by several protein kinases, and induces transcription of genes in response to hormonal stimulation of the cAMP pathway. Alternate splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. See also *CREB Interactions CREB1 has been shown to interact with: * CEBPB, * CREB binding protein, * FHL2, * FHL3, * FHL5. * HTATIP, * P53 p53, also known as tumor protein p53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CREB
CREB-TF (CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein) is a cellular transcription factor. It binds to certain DNA sequences called cAMP response elements (CRE), thereby increasing or decreasing the transcription of the genes. CREB was first described in 1987 as a cAMP-responsive transcription factor regulating the somatostatin gene. Genes whose transcription is regulated by CREB include: '' c-fos'', BDNF, tyrosine hydroxylase, numerous neuropeptides (such as somatostatin, enkephalin, VGF, corticotropin-releasing hormone), and genes involved in the mammalian circadian clock (PER1, PER2). CREB is closely related in structure and function to CREM ( cAMP response element modulator) and ATF-1 ( activating transcription factor-1) proteins. CREB proteins are expressed in many animals, including humans. CREB has a well-documented role in neuronal plasticity and long-term memory formation in the brain and has been shown to be integral in the formation of spatial memory. CREB down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RPS6KA5
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RPS6KA5'' gene. This kinase, together with RPS6KA4, are thought to mediate the phosphorylation of histone H3, linked to the expression of immediate early genes. Interactions RPS6KA5 has been shown to interact with CREB1 CAMP responsive element binding protein 1, also known as CREB-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CREB1'' gene. This protein binds the cAMP response element, a DNA nucleotide sequence present in many viral and cellular promoters. T .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * EC 2.7.11 {{Gene-14-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTATIP
Histone acetyltransferase KAT5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''KAT5'' gene. It is also commonly identified as TIP60. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the MYST family of histone acetyl transferases (HATs) and was originally isolated as an HIV-1 TAT-interactive protein. HATs play important roles in regulating chromatin remodeling, transcription and other nuclear processes by acetylating histone and nonhistone proteins. This protein is a histone acetylase that has a role in DNA repair and apoptosis and is thought to play an important role in signal transduction. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. Structure The structure of KAT5 includes an Acetyl-CoA, acetyl CoA binding domain and a zinc finger in the MYST domain, and a CHROMO domain. Excess acetyl CoA is necessary for acetylation of histones. The zinc finger domain has been shown to aid in the acetylation process as well. The CHROMO domain aids in KAT5 ability to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FHL5
Four and a half LIM domains protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FHL5'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is coordinately expressed with activator of cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM). It is associated with CREM and confers a powerful transcriptional activation function. CREM acts as a transcription factor essential for the differentiation of spermatids into mature spermatozoa. There are multiple polyadenylation sites found in this gene. Interactions FHL5 has been shown to interact with CREB1 and CAMP responsive element modulator cAMP responsive element modulator is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CREM gene, and it belongs to the cAMP-responsive element binding protein family. It has multiple isoforms, which act either as repressors or activators. CREB family .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-6-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FHL3
Four and a half LIM domains protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FHL3'' gene. LIM proteins are defined by the possession of a highly conserved double zinc finger motif called the LIM domain. Function FHL3 plays a role in myogenesis, and also stimulates the development of neural crest by enhancing BMP signaling.Intracellular enhancement of BMP signaling by LIM-domain protein FHL3 controls spatiotemporal emergence of the neural crest driven by WNT signaling Mansour Alkobtawi, Patrick Pla, Anne H. Monsoro-Burq bioRxiv 711192; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/711192 Interactions FHL3 has been shown to interact with: * CREB1, * CTBP2, * FHL2, * ITGA7 Alpha-7 integrin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ITGA7'' gene. Alpha-7 integrin is critical for modulating cell-matrix interactions. Alpha-7 integrin is highly expressed in cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle and smooth muscle cells, an ... and * KLF3. References Further reading * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FHL2
Four and a half LIM domains protein 2 also known as FHL-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FHL2'' gene. LIM proteins contain a highly conserved double zinc finger motif called the LIM domain. Function FHL-2 is thought to have a role in the assembly of extracellular membranes and may function as a link between presenilin-2 and an intracellular signaling pathway. Family The Four-and-a-half LIM (FHL)-only protein subfamily is one of the members of the LIM-only protein family. Protein members within the group might be originated from a common ancestor and share a high degree of similarity in their amino acid sequence. These proteins are defined by the presence of the four and a half cysteine-rich LIM homeodomain with the half-domain always located in its N-terminus. The name LIM was derived from the first letter of the transcription factors LIN-11, ISL-1 and MEC-3, from which the domain was originally characterized. No direct interactions between LIM domain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CEBPB
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CEBPB'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this intronless gene is a bZIP transcription factor that can bind as a homodimer to certain DNA regulatory regions. It can also form heterodimers with the related proteins CEBP-alpha, CEBP-delta, and CEBP-gamma. The encoded protein is important in the regulation of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses and has been shown to bind to the IL-1 response element in the IL-6 gene, as well as to regulatory regions of several acute-phase and cytokine genes. In addition, the encoded protein can bind the promoter and upstream element and stimulate the expression of the collagen type I gene. CEBP-beta is critical for normal macrophage functioning, an important immune cell sub-type; mice unable to express CEBP-beta have macrophages that cannot differentiate (specialize) and thus are unable to perform all their biological functions—inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the normal development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. Estrogen, oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
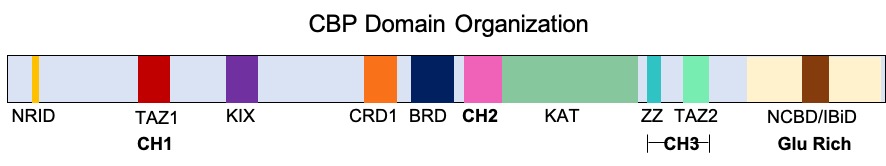
CREB Binding Protein
CREB-binding protein, also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, (where CREB is cAMP response element-binding protein) is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions. For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies including colorectal cancer as w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments (exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions of genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different proteins enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternate Splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of the observed splice variants are due to spli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |