|
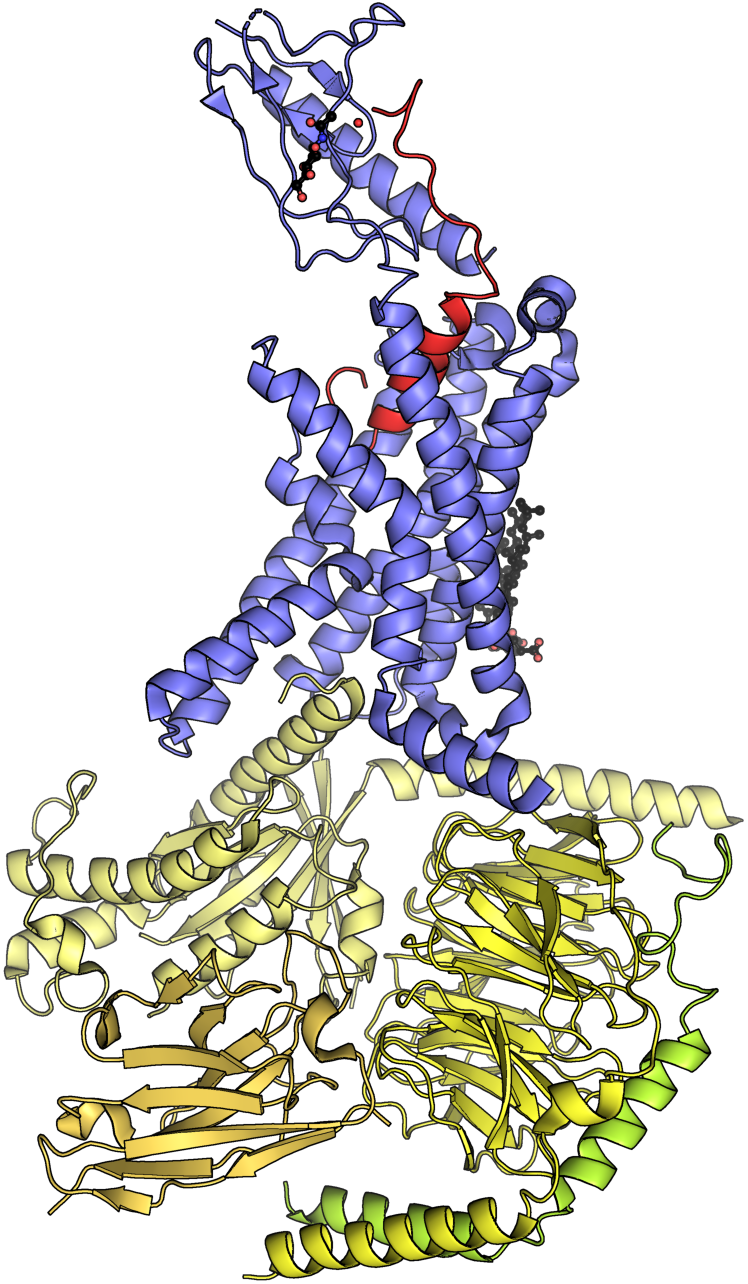
CALCRL
Calcitonin receptor-like (CALCRL), also known as the calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR), is a human protein; it is a receptor for calcitonin gene-related peptide. Function The protein encoded by the CALCRL gene is a G protein-coupled receptor related to the calcitonin receptor. CALCRL is linked to one of three single transmembrane domain receptor activity-modifying proteins (RAMPs) that are essential for functional activity. The association of CALCRL with different RAMP proteins produces different receptors: * with RAMP1: produces a CGRP receptor * with RAMP2: produces an adrenomedullin (AM) receptor, designated AM1 * with RAMP3: produces a dual CGRP/AM receptor designated AM2 These receptors are linked to the G protein Gs, which activates adenylate cyclase and activation results in the generation of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). CGRP receptors are found throughout the body, suggesting that the protein may modulate a variety of physiological fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a neuropeptide that belongs to the calcitonin family. Human CGRP consists of two Protein isoform, isoforms, CGRP alpha (α-CGRP, also known as CGRP I) and CGRP beta (β-CGRP, also known as CGRP II). α-CGRP is a 37-amino acid neuropeptide formed by alternative splicing of the calcitonin/CGRP gene located on chromosome 11. β-CGRP is less studied. In humans, β-CGRP differs from α-CGRP by three amino acids and is encoded in a separate, nearby gene. The CGRP family includes calcitonin (CT), adrenomedullin (AM), and amylin (AMY). Function CGRP is produced in both peripheral and central neurons. It is a potent peptide vasodilator and can function in the transmission of nociception. In the spinal cord, the function and expression of CGRP may differ depending on the location of synthesis. CGRP is derived mainly from the cell bodies of motor neurons when synthesized in the Ventral horn of spinal cord, ventral horn of the spinal cord and may c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CGRP
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a neuropeptide that belongs to the calcitonin family. Human CGRP consists of two isoforms, CGRP alpha (α-CGRP, also known as CGRP I) and CGRP beta (β-CGRP, also known as CGRP II). α-CGRP is a 37-amino acid neuropeptide formed by alternative splicing of the calcitonin/CGRP gene located on chromosome 11. β-CGRP is less studied. In humans, β-CGRP differs from α-CGRP by three amino acids and is encoded in a separate, nearby gene. The CGRP family includes calcitonin (CT), adrenomedullin (AM), and amylin (AMY). Function CGRP is produced in both peripheral and central neurons. It is a potent peptide vasodilator and can function in the transmission of nociception. In the spinal cord, the function and expression of CGRP may differ depending on the location of synthesis. CGRP is derived mainly from the cell bodies of motor neurons when synthesized in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and may contribute to the regeneration of nervous t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenomedullin
Adrenomedullin (ADM) is a peptide hormone that plays an important role in various physiological processes throughout the human body. Initially discovered in 1993 from a pheochromocytoma, a tumor of the adrenal medulla, this 52-amino acid peptide is now recognized for its diverse effects, including vasodilation, regulation of blood pressure, and maintenance of the vascular system. ADM is widely expressed in tissues and also found in the circulation, exerting its influence on the cardiovascular, lymphatic, and endocrine systems, as well as demonstrating anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective properties. In humans ADM is encoded by the ''ADM'' gene. A similar peptide named adreomedullin2 was reported in rats in 2004 which exhibits a similar function. Structure The human ADM gene is localized to a single locus on Chromosome 11 with 4 exons and 3 introns. The ADM gene initially codes for a 185-amino acid precursor peptide, that can be differentially excised to form a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Activity-modifying Protein
Receptor activity-modifying proteins (RAMPs) are a class of protein that interact with and modulate the activities of several Class B G protein-coupled receptors including the receptors for secretin, calcitonin (CT), glucagon, and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). There are three distinct types of RAMPs in mammals (though more in fish), designated RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3, each encoded by a separate gene. Function Currently, the function of RAMPs is divided into classes of activities. When associated with the Calcitonin receptor (CTR) or Calcitonin receptor-like (CALCRL) (below), RAMPs can change the selectivity of the receptor for a specific hormone. In the cases of the other receptors mentioned, however, there is no evidence that they can do this, but instead function to regulate trafficking of receptors from the ER / golgi to the membrane. These functions appear to be ones where there is redundancy, as neither RAMP1 nor RAMP3 knockout mice (KO) have grossly abn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAMP1
Receptor activity modifying protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAMP1'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAMP family of single-transmembrane-domain proteins, called receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying proteins (RAMPs). RAMPs are type I transmembrane proteins with an extracellular N terminus and a cytoplasmic C terminus. RAMPs are required to transport calcitonin-receptor-like receptor (CALCRL) to the plasma membrane. CALCRL, a receptor with seven transmembrane domains, can function as either a calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor or an adrenomedullin receptor, depending on which members of the RAMP family are expressed. In combination with the RAMP1 protein, CALCRL functions as the CGRP receptor. The RAMP1 protein is involved in the terminal glycosylation, maturation, and presentation of the CGRP receptor to the cell surface. The RAMP1 protein can also interact with the calcitonin receptor (CT) protein, where heter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAMP2
Receptor activity modifying protein 2, also known as RAMP2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''RAMP2'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAMP family of single-transmembrane-domain proteins, called receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying proteins (RAMPs). RAMPs are type I transmembrane proteins with an extracellular N-terminus and a cytoplasmic C-terminus. RAMPs are required to transport calcitonin-receptor-like receptor (CRLR) to the plasma membrane. CRLR, a receptor with seven transmembrane domains, can function as either a calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor or an adrenomedullin receptor, depending on which members of the RAMP family are expressed. In the presence of this (RAMP2) protein, CRLR functions as an adrenomedullin Adrenomedullin (ADM) is a peptide hormone that plays an important role in various physiological processes throughout the human body. Initially discovered in 1993 from a pheochromocytoma, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAMP3
Receptor activity modifying protein 3, also known as RAMP3, is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAMP family of single-transmembrane-domain proteins, called receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying proteins (RAMPs). RAMPs are type I transmembrane proteins with an extracellular N terminus and a cytoplasmic C terminus. RAMPs are required to transport calcitonin-receptor-like receptor (CRLR) to the plasma membrane. CRLR, a receptor with seven transmembrane domains, can function as either a calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor or an adrenomedullin receptor, depending on which members of the RAMP family are expressed. In humans and other mammals, there are 3 RAMPS, while in fish there are more, with sub-variants. In the presence of this (RAMP3) protein, CRLR functions as an adrenomedullin Adrenomedullin (ADM) is a peptide hormone that plays an important role in various physiological processes throughout the human body. Initially discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide Receptor Antagonist
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonists, commonly known as gepants, are a class of drugs that act as antagonists of the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRPR). Several monoclonal antibodies that bind to the CGRP receptor or peptide have been approved for prevention of migraine. Nerve activation triggers the release of CGRP and other neuropeptides, leading to inflammation, pain, and swelling. Three small molecule CGRPR antagonists are approved in the U.S. as antimigraine agents. Drugs of this class have also been investigated for use in osteoarthritis. Examples Non-peptide small molecules * Ubrogepant is approved for acute treatment of migraines * Rimegepant (BMS-927711) is approved for acute and preventative treatment of migraines * Atogepant (AGN-241689) is approved for preventative treatment of migraines * Zavegepant (BHV- 3500) is a nasal spray approved for acute treatment of migraines. * Telcagepant (MK-0974), reached phase III clinical trial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Cells
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an excitable cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually gained new gene modules which enabled cells to create post-synaptic scaffolds and ion ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidocaine typically begins working within several minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours. Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area. It is often used mixed with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine) to prolong its local effects and to decrease bleeding. If injected intravenously, it may cause cerebral effects such as confusion, changes in vision, numbness, tingling, and vomiting. It can cause low blood pressure and an irregular heart rate. There are concerns that injecting it into a joint can cause problems with the cartilage. It appears to be generally safe for use in pregnancy. A lower dose may be required in those with liver problems. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botox
Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin (commonly called botox), is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neuromuscular junction, thus causing flaccid paralysis. The toxin causes the disease botulism. The toxin is also used commercially for medical and cosmetic purposes. Botulinum toxin is an acetylcholine release inhibitor and a neuromuscular blocking agent. The seven main types of botulinum toxin are named types A to G (A, B, C1, C2, D, E, F and G). New types are occasionally found. Types A and B are capable of causing disease in humans, and are also used commercially and medically. Types C–G are less common; types E and F can cause disease in humans, while the other types cause disease in other animals. Botulinum toxins are among the most potent toxins known to science. Intoxication can occur naturally as a result of either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |