|
Auxins
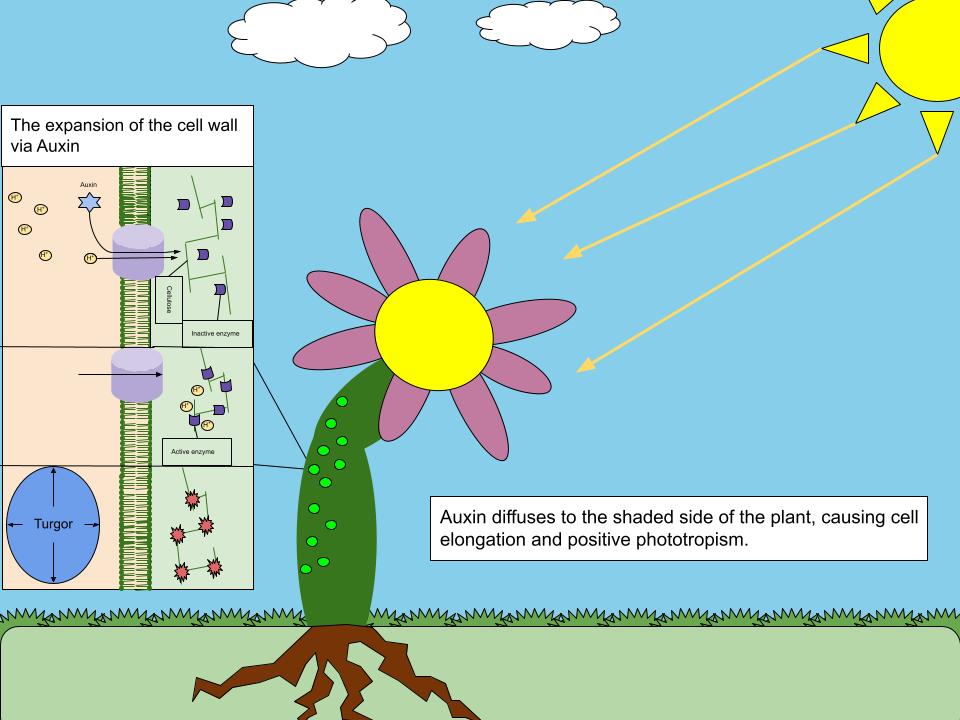
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Ancient Greek, Greek word ( – 'to grow/increase'). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both metabolism a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word ( – 'to grow/increase'). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both metabolism and transp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Hormone
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of Organ (anatomy), organ size, pathogen defense, Stress (biology), stress tolerance and Reproduction, reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Frits Warmolt Went, Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in vascular plant, vascular plants ("higher plants"). Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungus, fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytohormones
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of organ size, pathogen defense, stress tolerance and reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in vascular plants ("higher plants"). Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristics The word hormone is derived from Greek, meaning ''set in motion''. Plant hormones a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indole-3-butyric Acid
Indole-3-butyric acid (1''H''-indole-3-butanoic acid, IBA) is a white to light-yellow crystalline solid, with the molecular formula C12H13NO2. It melts at 125°C in atmospheric pressure and decomposes before boiling. IBA is a plant hormone in the auxin family and is an ingredient in many commercial horticultural plant rooting products. Plant hormone Since IBA is not completely soluble in water, it is typically dissolved in 75% aqueous ethanol (aqua vitae) for use in plant rooting, making a solution of between 10,000 and 50,000 ppm. This alcohol solution is then diluted with distilled water to the desired concentration. IBA is also available as a alkali metal salt, which is soluble in water. The solution should be kept in a cool, dark place for best results. This compound had been thought to be strictly synthetic; however, it was reported that the compound was isolated from leaves and seeds of maize and other species. In maize, IBA has been shown to be biosynthesized in vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indole-3-acetic Acid
Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA, 3-IAA) is the most common naturally occurring plant hormone of the auxin class. It is the best known of the auxins, and has been the subject of extensive studies by plant physiologists. IAA is a derivative of indole, containing a carboxymethyl substituent. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents. Biosynthesis IAA is predominantly produced in cells of the apex ( bud) and very young leaves of a plant. Plants can synthesize IAA by several independent biosynthetic pathways. Four of them start from tryptophan, but there is also a biosynthetic pathway independent of tryptophan. Plants mainly produce IAA from tryptophan through indole-3-pyruvic acid. IAA is also produced from tryptophan through indole-3-acetaldoxime in ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. In rats, IAA is a product of both endogenous and colonic microbial metabolism from dietary tryptophan along with tryptophol. This was first observed in rats infected by '' Trypanosoma br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokinin
Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in Cell (biology), cell growth and cellular differentiation, differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf plant senescence, senescence. There are two types of cytokinins: adenine-type cytokinins represented by kinetin, zeatin, and 6-benzylaminopurine, and phenylurea-type cytokinins like diphenylurea and thidiazuron (TDZ). Most adenine-type cytokinins are synthesized in roots. Cambium (botany), Cambium and other actively dividing tissues also synthesize cytokinins. No phenylurea cytokinins have been found in plants. Cytokinins participate in local and long-distance signalling, with the same transport mechanism as purines and nucleosides. Typically, cytokinins are transported in the xylem. Cytokinins act in concert with auxin, another plant growth hormone. The two are complementary, having generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Auxin Transport
Polar auxin transport is the regulated transport of the plant hormone auxin in plants. It is an active process, the hormone is transported in cell-to-cell manner and one of the main features of the transport is its asymmetry and directionality ( polarity). The polar auxin transport functions to coordinate plant development; the following spatial auxin distribution underpins most of plant growth responses to its environment and plant growth and developmental changes in general. In other words, the flow and relative concentrations of auxin informs each plant cell where it is located and therefore what it should do or become. Chemiosmotic model Polar auxin transport (PAT) is directional and active flow of auxin molecules through the plant tissues. The flow of auxin molecules through the neighboring cells is driven by carriers (''type of membrane transport protein'') in the cell-to-cell fashion (from one cell to other cell and then to the next one) and the direction of the flow i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicamba
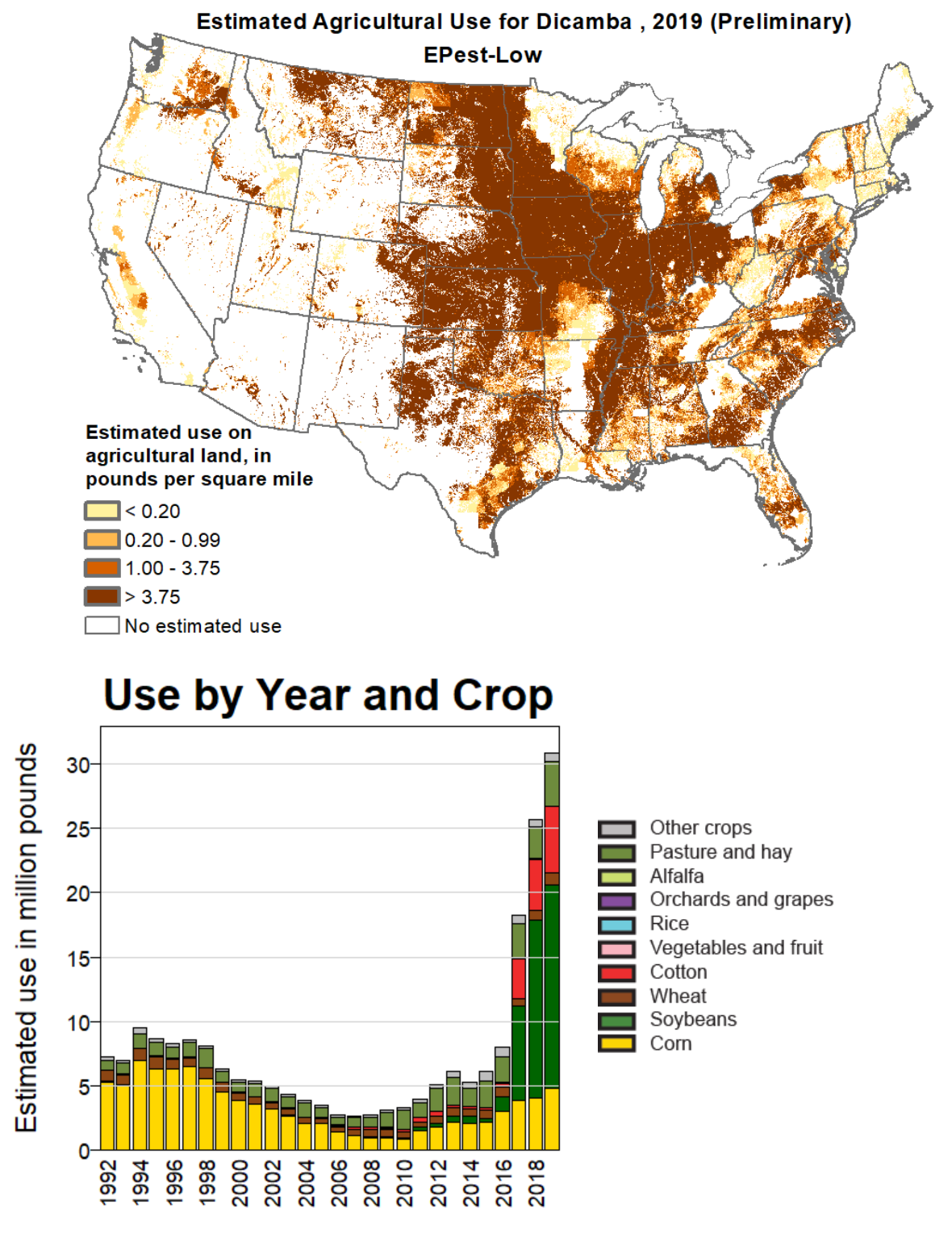
Dicamba (3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid) is a selective systemic herbicide first registered in 1967. Brand names for formulations of this herbicide include Dianat, Banvel, Diablo, Oracle and Vanquish. This chemical compound is a chlorinated derivative of ''o''-anisic acid. It has been described as a "widely used, low-cost, environmentally friendly herbicide that does not persist in soils and shows little or no toxicity to wildlife and humans." Despite its success in improving crop yields, dicamba has attracted controversy. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), dicamba's primary ecological risk is for non-target terrestrial plants from exposure through spray drift, whereby dicamba inadvertently migrates to non-targeted neighboring areas, damaging those plants. In 2016, dicamba was approved for use in the United States over GMO dicamba-resistant crops created by Monsanto. Dicamba came under significant scrutiny due to its tendency to sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Chloroindole-3-acetic Acid
4-Chloroindole-3-acetic acid (4-Cl-IAA) is an organic compound that functions as a plant hormone. Synopsis It is a member of the class of compounds known as auxins and a chlorinated analogue of the more common indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) auxin. 4-Cl-IAA is found in the seeds of a variety of plants, particularly legumes such as peas and broad beans. In one study it is written that the substance is "mainly found in reproductive structures" and "is thought to be restricted to members of the leguminous tribe '' Fabeae'', specifically "the genera '' Vicia'', ''Pisum'', ''Lathyrus'', ''Lens'', and '' Vavilovia''". In Pisum sativum, 4-Cl-IAA biosynthesis diverges from IAA biosynthesis when the amino acid tryptophan is chlorinated to form 4-chlorotryptophan (4-Cl-Trp); the biosynthesis of 4-Cl-IAA then precedes parallel to that of IAA. Engvild hypothesized in 1996 that 4-Cl-IAA may be a "death hormone" that maturing seeds use to trigger death of the parent plant by mobilizing nutrients to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-Naphthaleneacetic Acid
1-Naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) is an organic compound with the formula C10H7CH2CO2H. This colorless solid is soluble in organic solvents. It features a carboxylmethyl group (CH2CO2H) linked to the "1-position" of naphthalene. Use and regulation NAA is a synthetic plant hormone in the auxin family and is an ingredient in many commercial horticultural products; it is a rooting agent and used for the vegetative propagation of plants from stem and leaf cuttings. It is also used for plant tissue culture. The hormone NAA does not occur naturally, and, like all auxins, is toxic to plants at high concentrations. In the United States, under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), products containing NAA require registration with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) as pesticides. Use and analysis NAA is widely used in agriculture for various purposes. It is considered to be only slightly toxic but when at higher concentrations it can be toxic to animals. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |