|
100 (number)
100 or one hundred (Roman numerals, Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 (number), 99 and preceding 101 (number), 101. In mathematics 100 is the square of 10 (number), 10 (in scientific notation it is written as 102). The standard SI prefix for a hundred is "Hecto-, hecto-". 100 is the basis of percentages ( meaning "by the hundred" in Latin), with 100% being a full amount. 100 is a Harshad number in decimal, and also in base-four, a base in-which it is also a self-descriptive number. 100 is the sum of the first nine prime numbers, from 2 through 23 (number), 23. It is also divisible by the number of primes below it, 25 (number), 25. 100 cannot be expressed as the difference between any integer and the total of coprimes below it, making it a noncototient. 100 has a Carmichael function, reduced totient of 20, and an Euler totient of 40. A totient value of 100 is obtained from four numbers: 101 (number), 101, 125 (number), 125, 202 (number), 202, and 250 (number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
99 (number)
99 (ninety-nine) is the natural number In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive in ... following 98 and preceding 100. In mathematics 99 is: *a composite number; a square-prime, of the form (''p''2, q). It is the 11th composite number of this form and the third of the form (32, q). It has an aliquot sum of 57, within an aliquot sequence of two composite numbers (99, 57, 23, 1,0), to the Prime in the 23-aliquot tree. *a Kaprekar number *a lucky number *a palindromic number in base ten *the ninth repdigit *the sum of the cubes of three consecutive integers: 99 = 23 + 33 + 43. *the sum of the sums of the divisors of the first 11 positive integers. * ".99" is frequently used as a price ender in pricing. See also * 99 (other) References External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
25 (number)
25 (twenty-five) is the natural number following 24 and preceding 26. In mathematics It is a square number, being 52 = 5 × 5, and hence the third non-unitary square prime of the form ''p''2. It is one of two two-digit numbers whose square and higher powers of the number also ends in the same last two digits, e.g., 252 = 625; the other is 76. 25 has an even aliquot sum of 6, which is itself the first even and perfect number root of an aliquot sequence; not ending in ( 1 and 0). It is the smallest square that is also a sum of two (non-zero) squares: 25 = 32 + 42. Hence, it often appears in illustrations of the Pythagorean theorem. 25 is the sum of the five consecutive single-digit odd natural numbers 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9. 25 is a centered octagonal number, a centered square number, a centered octahedral number, and an automorphic number. 25 percent (%) is equal to . It is the smallest decimal Friedman number as it can be expressed by its own digits: 52. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
23 (number)
23 (twenty-three) is the natural number following 22 and preceding 24. It is a prime number. In mathematics Twenty-three is the ninth prime number, the smallest odd prime that is not a twin prime. It is, however, a cousin prime with 19, and a sexy prime with 17 and 29; while also being the largest member of the first prime sextuplet ( 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23). Twenty-three is also the next to last member of the first Cunningham chain of the first kind ( 2, 5, 11, 23, 47), and the sum of the prime factors of the second set of consecutive discrete semiprimes, ( 21, 22). 23 is the smallest odd prime to be a highly cototient number, as the solution to x-\phi(x) for the integers 95, 119, 143, and 529. * 23 is the second Smarandache–Wellin prime in base ten, as it is the concatenation of the decimal representations of the first two primes (2 and 3) and is itself also prime, and a happy number. * The sum of the first nine primes up to 23 is a square: 2 + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a Product (mathematics), product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, or , involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorization, factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order. The property of being prime is called primality. A simple but slow primality test, method of checking the primality of a given number , called trial division, tests whether is a multiple of any integer between 2 and . Faster algorithms include the Miller–Rabin primality test, which is fast but has a small chance of error ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-descriptive Number
In mathematics, a self-descriptive number is an integer ''m'' in a given base ''b'' that is ''b'' digits long, and each digit ''d'' at position ''n'' (the most significant digit being at position 0 and the least significant at position ''b''−1) counts how many instances of digit ''n'' are in ''m''. Example For example, in base 10, the number 6210001000 is self-descriptive because of the following reasons: In base 10, the number has 10 digits, indicating its base; It contains 6 at position 0, indicating that there are six 0s in 6210001000; It contains 2 at position 1, indicating that there are two 1s in 6210001000; It contains 1 at position 2, indicating that there is one 2 in 6210001000; It contains 0 at position 3, indicating that there is no 3 in 6210001000; It contains 0 at position 4, indicating that there is no 4 in 6210001000; It contains 0 at position 5, indicating that there is no 5 in 6210001000; It contains 1 at position 6, indicating that there is one 6 in 62100010 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
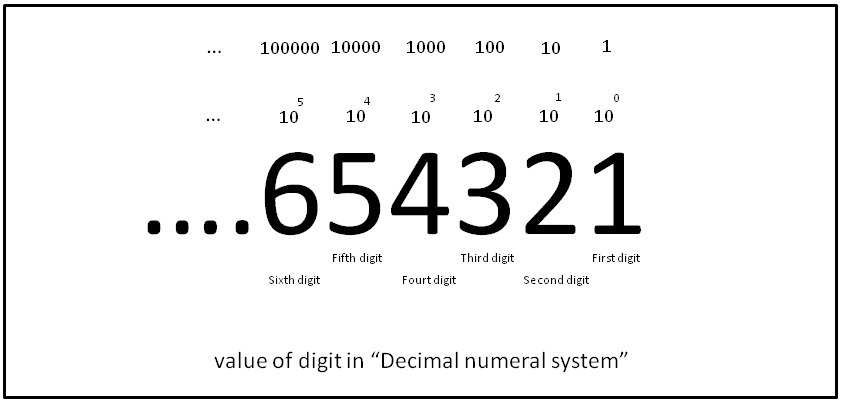
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harshad Number
In mathematics, a harshad number (or Niven number) in a given radix, number base is an integer that is divisible by the digit sum, sum of its digits when written in that base. Harshad numbers in base are also known as -harshad (or -Niven) numbers. Because being a Harshad number is determined based on the base the number is expressed in, a number can be a Harshad number many times over. So-called Trans-Harshad numbers are Harshad numbers in every base. Harshad numbers were defined by D. R. Kaprekar, a mathematician from India. The word "harshad" comes from the Sanskrit ' (joy) + ' (give), meaning joy-giver. The term "Niven number" arose from a paper delivered by Ivan M. Niven at a conference on number theory in 1977. Definition Stated mathematically, let be a positive integer with digits when written in base , and let the digits be a_i (i = 0, 1, \ldots, m-1). (It follows that a_i must be either zero or a positive integer up to .) can be expressed as :X=\sum_^ a_i n^i. is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percentage
In mathematics, a percentage () is a number or ratio expressed as a fraction (mathematics), fraction of 100. It is often Denotation, denoted using the ''percent sign'' (%), although the abbreviations ''pct.'', ''pct'', and sometimes ''pc'' are also used. A percentage is a dimensionless quantity, dimensionless number (pure number), primarily used for expressing proportions, but percent is nonetheless a unit of measurement in its orthography and usage. Examples For example, 45% (read as "forty-five percent") is equal to the fraction , or 0.45. Percentages are often used to express a proportionate part of a total. (Similarly, one can also express a number as a fraction of 1,000, using the term "per mille" or the symbol "".) Example 1 If 50% of the total number of students in the class are male, that means that 50 out of every 100 students are male. If there are 500 students, then 250 of them are male. Example 2 An increase of $0.15 on a price of $2.50 is an increase by a fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hecto-
''Hecto'' (symbol: h) is a decimal unit prefix in the metric system denoting a factor of one hundred. It was adopted as a multiplier in 1795, and comes from the Greek , meaning "hundred". In 19th century English it was sometimes spelled "hecato", in line with a puristic opinion by Thomas Young. Its unit symbol as an SI prefix in the International System of Units (SI) is the lower case letter h. The prefix is rarely used in general, but has certain specific applications: * hectopascal (hPa), in meteorology, for atmospheric pressure, the modern equivalent of the traditional millibar. * hectolitre (hl or hL), in agriculture, for liquids (notably milk and alcoholic beverages) and bulk commodities (e.g., grain). * hectogram (hg), in agronomy, for quantities of animal feed (hectogram/animal) and for measures of agricultural productivity (hectogram/hectare); also used in Italy abbreviated as , and in Canada, New Zealand and Sweden simply as 100 g, for retail sale of cold cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SI Prefix
The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI (from French ), is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. It is the only system of measurement with official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI system is coordinated by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, which is abbreviated BIPM from . The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units, which can always be represented as products of powers of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Notation
Scientific notation is a way of expressing numbers that are too large or too small to be conveniently written in decimal form, since to do so would require writing out an inconveniently long string of digits. It may be referred to as scientific form or standard index form, or standard form in the United Kingdom. This base ten notation is commonly used by scientists, mathematicians, and engineers, in part because it can simplify certain arithmetic operations. On scientific calculators, it is usually known as "SCI" display mode. In scientific notation, nonzero numbers are written in the form or ''m'' times ten raised to the power of ''n'', where ''n'' is an integer, and the coefficient ''m'' is a nonzero real number (usually between 1 and 10 in absolute value, and nearly always written as a terminating decimal). The integer ''n'' is called the exponent and the real number ''m'' is called the '' significand'' or ''mantissa''. The term "mantissa" can be ambiguous where loga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |