|
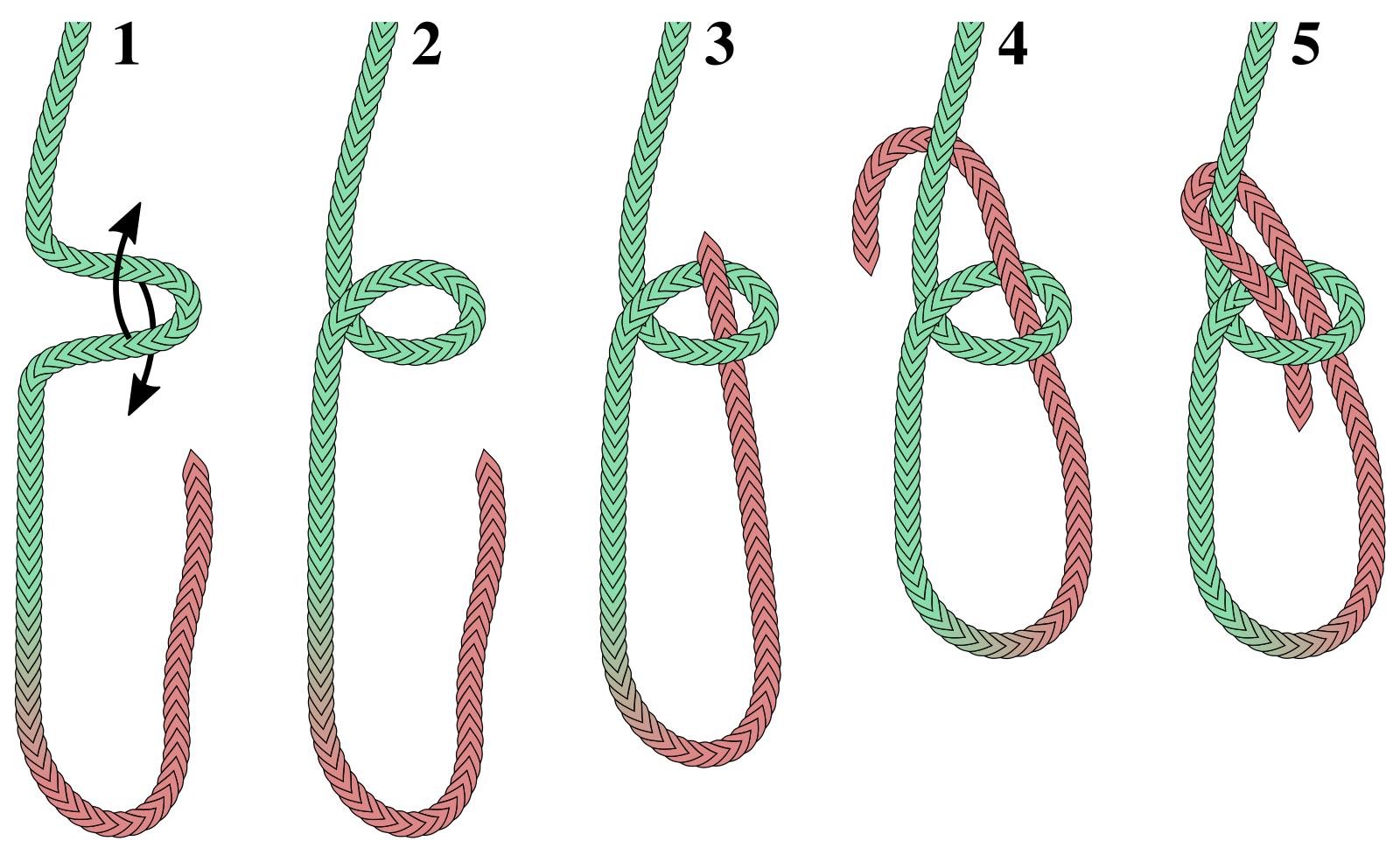
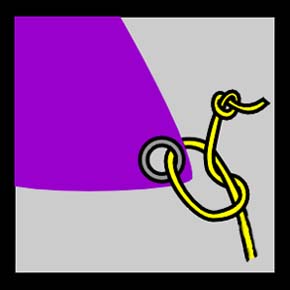
Bowline Knot Family
The bowline ( or ) is an ancient and simple knot used to form a fixed loop at the end of a rope. It has the virtues of being both easy to tie and untie; most notably, it is easy to untie after being subjected to a load. The bowline is sometimes referred to as ''King of the knots'' because of its importance. Along with the sheet bend and the clove hitch, the bowline is often considered one of the most essential knots. The common bowline shares some structural similarity with the sheet bend. Virtually all end-to-end joining knots (i.e., bends) have a corresponding loop knot. Although the bowline is generally considered a reliable knot, its main deficiencies are a tendency to work loose when not under load (or under cyclic loading), to slip when pulled sideways, and the bight portion of the knot to capsize in certain circumstances. To address these shortcomings, a number of more secure variations of the bowline have been developed for use in safety-critical applications, or by s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheet Bend
The sheet bend (also known as becket bend, weaver's knot and weaver's hitch) is a bend. It is practical for joining lines of different diameter or rigidity. It is quick and easy to tie, and is considered so essential it is the first knot given in the '' Ashley Book of Knots''. Additionally, it is one of the six knots given in the International Guild of Knot Tyers' Six Knot Challenge, along with the clove hitch, bowline, reef knot (square knot), round turn and two half-hitches, and sheepshank. The sheet bend is related in structure to the bowline; like the bowline, it has a tendency to work loose when not under load. For increased security, it is sometimes recommended that one add another turn in the smaller end, making a double sheet bend; in most cases, however, a single sheet bend should suffice. As a bend, its advantages lie in its simplicity and non-jamming properties. It is commonly taught in Scouting. Definition The term "sheet bend" derives from its use bending r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bend Knot
This is a list of bends. A bend is a knot used to join two lengths of rope. They are used in a variety of situations, including climbing, sailing, and securing loads. Bend knots are classified based on their ability to be tightened or released, their resistance to slipping, and their strength. Some common types of bend knots include the double fisherman's knot, the double overhand knot, and the double figure-eight knot. Bend knots are important because they allow two ropes to be securely joined together, enabling the combined ropes to support weight or transmit force. It is important to choose the appropriate bend knot for the specific task at hand, as some bend knots may be stronger or more secure than others. The sheet bend is the classic bend. Misuse of reef knot as a bend The common reef knot (square knot) is sometimes mistakenly tied as a bend. When used as a bend rather than a binding knot, the reef knot will capsize under sufficient tension. For this reason, the reef k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation. Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and most of these systems have undergone substantial standardization, thus exhibiting less dialect variation than the spoken language. These processes can fossilize pronunciation patterns that are no longer routinely observed in speech (e.g., "would" and "should"); they can also reflect deliberate efforts to introduce variability for the sake of national identity, as seen in Noah Webster's efforts to introduce easily noticeable differences between American and British spelling (e.g., "honor" and "honour"). Some nations (e.g. France and Spain) have established language academies in an attempt to regulate orthography officially. For most languages (including English) however, there are no such authorities and a sense of 'correct' orthography evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cringle
A cringle is an eye through which to pass a rope. In nautical settings, the word refers to a small hole anywhere along the edge or in the corner of a sail, rimmed with stranded cordage and worked into the boltrope. Typically it encloses a metal grommet Curtain grommets, used among others in shower curtains. A grommet is a ring or edge strip inserted into a hole through thin material, typically a sheet of textile fabric, sheet metal or composite of carbon fiber, wood or honeycomb. Grommets ar ... for reinforcement and to reduce wear. In this context, ''cringle'' and ''grommet'' coincide enough that the two are sometimes used interchangeably. References Sailboat components {{water-transport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Smith (explorer)
John Smith (baptized 6 January 1580 – 21 June 1631) was an English soldier, explorer, colonial governor, Admiral of New England, and author. He played an important role in the establishment of the colony at Jamestown, Virginia, the first permanent English settlement in America, in the early 17th century. He was a leader of the Virginia Colony between September 1608 and August 1609, and he led an exploration along the rivers of Virginia and the Chesapeake Bay, during which he became the first English explorer to map the Chesapeake Bay area. Later, he explored and mapped the coast of New England. He was knighted for his services to Sigismund Báthory, Prince of Transylvania, and his friend Mózes Székely. Jamestown was established on May 14, 1607. Smith trained the first settlers to work at farming and fishing, thus saving the colony from early devastation. He publicly stated, " He that will not work, shall not eat", alluding to 2 Thessalonians 3:10. Harsh weather, lack of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Points Of Sail
A point of sail is a sailing craft's direction of travel under sail in relation to the true wind direction over the surface. The principal points of sail roughly correspond to 45° segments of a circle, starting with 0° directly into the wind. For many sailing craft 45° on either side of the wind is a ''no-go'' zone, where a sail is unable to mobilize power from the wind. Sailing on a course as close to the wind as possible—approximately 45°—is termed ''beating'', a point of sail when the sails are ''close-hauled''. At 90° off the wind, a craft is on a ''beam reach''. The point of sail between beating and a beam reach is called a ''close reach''. At 135° off the wind, a craft is on a ''broad reach''. At 180° off the wind (sailing in the same direction as the wind), a craft is ''running downwind''. A given point of sail (beating, close reach, beam reach, broad reach, and running downwind) is defined in reference to the true wind—the wind felt by a stationary observe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Take Aback
A take is a single continuous recorded performance. The term is used in film and music to denote and track the stages of production. Film In cinematography, a take refers to each filmed "version" of a particular shot or "setup". Takes of each shot are generally numbered starting with "take one" and the number of each successive take is increased (with the director calling for "take two" or "take eighteen") until the filming of the shot is completed. Film takes are often designated with the aid of a clapperboard. It is also referred to as the slate. The number of each take is written or attached to the clapperboard, which is filmed briefly prior to or at the beginning of the actual take. Only those takes which are vetted by the continuity person and/or script supervisor are printed and are sent to the film editor. Single-takes A single-take or one-take occurs when the entire scene is shot satisfactorily the first time, whether by necessity (as with certain expensive special e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow (ship)
The bow () is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern. Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the forward-most part of the bow above the waterline. Function A ship's bow should be designed to enable the hull to pass efficiently through the water. Bow shapes vary according to the speed of the boat, the seas or waterways being navigated, and the vessel's function. Where sea conditions are likely to promote pitching, it is useful if the bow provides reserve buoyancy; a flared bow (a raked stem with flared topsides) is ideal to reduce the amount of water shipped over the bow. Ideally, the bow should reduce the resistance and should be tall enough to prevent water from regularly washing over the top of it. Large commercial barges on inland waterways rarely meet big waves and may have remarkably little freeboard at the bow, whereas fast military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may be made from a combination of woven materials—including canvas or polyester cloth, laminated membranes or bonded filaments—usually in a three- or four-sided shape. A sail provides propulsive force via a combination of lift and drag, depending on its angle of attack—its angle with respect to the apparent wind. Apparent wind is the air velocity experienced on the moving craft and is the combined effect of the true wind velocity with the velocity of the sailing craft. Angle of attack is often constrained by the sailing craft's orientation to the wind or point of sail. On points of sail where it is possible to align the leading edge of the sail with the apparent wind, the sail may act as an airfoil, generating propulsive force as air p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Rig
Square rig is a generic type of sail and rigging arrangement in which the primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spars which are perpendicular, or square, to the keel of the vessel and to the masts. These spars are called ''yards'' and their tips, outside the lifts, are called the ''yardarms.'' A ship mainly rigged so is called a square-rigger. The square rig is aerodynamically the most efficient running rig (i.e., sailing downwind), and stayed popular on ocean-going sailing ships until the end of the Age of Sail. The last commercial sailing ships, windjammers, were usually square-rigged four-masted barques. History The oldest archaeological evidence of use of a square-rig on a vessel is an image on a clay disk from Mesopotamia from 5000 BC. Single sail square rigs were used by the ancient Egyptians, the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Romans, and the Celts. Later the Scandinavians, the Germanic peoples, and the Slavs adopted the single square-rigged sail, with it be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Sail
The Age of Sail is a period that lasted at the latest from the mid-16th (or mid- 15th) to the mid- 19th centuries, in which the dominance of sailing ships in global trade and warfare culminated, particularly marked by the introduction of naval artillery, and ultimately reached its highest extent at the advent of the analogue Age of Steam. Enabled by the advances of the related Age of Navigation, it is identified as a distinctive element of the early modern period and the Age of Discovery. Especially in context of the latter, it refers to a more particular Eurocentric Age of Sail, while generally the Age of Sail is the culminating period of a long intercontinental history of sailing. Periodization Like most periodic eras, the definition is inexact but instead serves as a general description. The term is used differently for warships and merchant vessels. Sailing ships are an ancient technology, making far-reaching trade like the ancient spice trade possible. With the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhand Knot
The overhand knot is one of the most fundamental knots, and it forms the basis of many others, including the simple noose, overhand loop, angler's loop, reef knot, fisherman's knot, Half hitch, and water knot. The overhand knot is a stopper, especially when used alone, and hence it is very secure, to the point of jamming badly. It should be used if the knot is intended to be permanent. It is often used to prevent the end of a rope from unraveling. An overhand knot becomes a trefoil knot, a true knot in the mathematical sense, by joining the ends. It can also be adjusted, faired, or mis-tied as a half hitch Tying There are a number of ways to tie the Overhand knot. * Thumb method – create a loop and push the working end through the loop with your thumb. * Overhand method – create a bight, by twisting the hand over at the wrist and sticking your hand in the hole, pinch the working end with your fingers and pull through the loop. Heraldry In heraldry, the overhand knot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |