|
Borsh Castle
Borsh Castle ( sq, Kalaja e Borshit) also known as Sopot Castle ( sq, Kalaja e Sopotit) from the hill it is located, is a ruined castle near the village Borsh, Albania, near the coast of the Ionian Sea. Inside the castle is the 17th-century Hajji Bendo Mosque from Ottoman times. History The castle dates to Antiquity, and its fortifications follow the trace of an acropolis, with four subsequent phases of reconstruction, ranging from the early Byzantine period to the late Middle Ages. The name "Sopot" is of Slavic origin. In medieval Greek documents, the castle is named ''Sopoton'' or ''Sopotos'', from which its name in other languages derives; its harbour is mentioned in Greek portolans with the name ''Gazopolis''. The site is first mentioned in the early 13th century, when archbishop Demetrios Chomatenos wrote of the " archonship of ''Sopotos''" ( gr, ἀρχοντία Σοπωτοῡ, ''archontia Sopotou''), part of the region of Vagenetia. In 1258, the Despot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borsh
Borsh is a maritime village, in the Albanian Riviera, in the former Lukovë municipality, Vlorë County, Albania, At the 2015 local government reform it became part of the municipality Himarë. The village is inhabited by Albanians,Kallivretakis, Leonidas (1995).Η ελληνική κοινότητα της Αλβανίας υπό το πρίσμα της ιστορικής γεωγραφίας και δημογραφίας [The Greek Community of Albania in terms of historical geography and demography" In Nikolakopoulos, Ilias, Kouloubis Theodoros A. & Thanos M. Veremis (eds). ''Ο Ελληνισμός της Αλβανίας [The Greeks of Albania]''. University of Athens. p. 51. " AM Αλβανοί Μουσουλμάνοι”; p.53. “BORSH ΜΠΟΡΣΙ 1243 AM" many of whom have traditionally been Bektashi Order, Bektashi. In Borsh, the Lab dialect of Albanian is spoken. Borsh borders with Fterra, Qeparo, Piqeras, Kuç, Çorraj, Kalasa, Zhulat, Tatzat, and has a populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demetrios Chomatenos
Demetrios Chomatenos or Chomatianos ( el, Δημήτριος Χωματηνός/Χωματιανός, 13th century), Eastern Orthodox Archbishop of Ohrid from 1216 to 1236, was a Byzantine priest and judge. His comprehensive legal education allowed him to exert substantial influence as judge, arbiter, confessor and advisor to the Byzantine imperial house. This makes him a characteristic representative of a time where judicial power was devolving from the weakened secular authorities to the Church, and also one of the last legal practitioners in full command of Justinian's laws as recovered by the Macedonian legal renaissance. According to the eminent Byzantinist Donald Nicol, Chomatenos' court at Ohrid was a rare centre of stability and law in an uncertain and tumultuous era; "From Kerkyra in the west to Drama in the east, from Dyrrachion in the north to Ioannina and Arta in the south, plaintiffs and defendants brought their problems to the humane and learned Archbishop". Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos III Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos_III_Palaiologos.jpg , caption = 14th-century miniature. Stuttgart, Württembergische Landesbibliothek. , succession = Byzantine emperor , reign = 24 May 1328 – 15 June 1341 , coronation = 2 February 1325 , cor-type1 = Coronation , predecessor = Andronikos II Palaiologos , successor = John V Palaiologos , spouse = Irene of BrunswickAnna of Savoy , issue = Irene, Empress of Trebizond Maria (renamed Irene)John V Palaiologos Michael Palaiologos , issue-link=#Family , issue-pipe = more... , house = Palaiologos , father = Michael IX Palaiologos , mother = Rita of Armenia , birth_date = 25 March 1297 , birth_place = Constantinople, Byzantine Empire(now Istanbul, Turkey) , death_date = 15 June 1341 (aged 44) , death_place = Constantinople, Byzantine Empire , burial_place= Andronikos III Palaiologos ( grc-x-medieval, Ἀνδρόνικος Δούκ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaiologan Period
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by the Palaiologos dynasty in the period between 1261 and 1453, from the restoration of Byzantine rule to Constantinople by the usurper Michael VIII Palaiologos following its recapture from the Latin Empire, founded after the Fourth Crusade (1204), up to the Fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire. Together with the preceding Nicaean Empire and the contemporary ''Frankokratia'', this period is known as the late Byzantine Empire. From the start, the regime faced numerous problems.Mango, p. 255 The Turks of Asia Minor had begun conducting raids and expanding into Byzantine territory in Asia Minor by 1263, just two years after the enthronment of the first Palaiologos emperor Michael VIII. Anatolia, which had formed the very heart of the shrinking empire, was systematically lost to numerous Turkic ''ghazis'', whose raids evolved into conquering expeditions inspired by Islamic zeal, the prospect of economic gain, and the desire to seek refuge from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles I Of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the Capetian House of Anjou, second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–85) and County of Forcalquier, Forcalquier (1246–48, 1256–85) in the Holy Roman Empire, Count of Anjou and Count of Maine, Maine (1246–85) in France; he was also King of Sicily (1266–85) and Prince of Achaea (1278–85). In 1272, he was proclaimed Kingdom of Albania (medieval), King of Albania, and in 1277 he purchased a claim to the Kingdom of Jerusalem. The youngest son of Louis VIII of France and Blanche of Castile, Charles was destined for a Church career until the early 1240s. He acquired Provence and Forcalquier through his marriage to their heiress, Beatrice of Provence, Beatrice. His attempts to restore central authority brought him into conflict with his mother-in-law, Beatrice of Savoy, and the nobility. Charles received Anjou and Maine from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
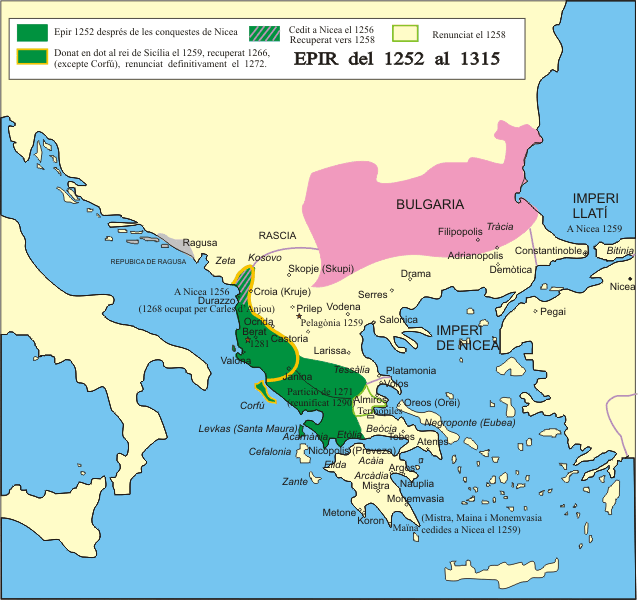
Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas
Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Nicephorus I Comnenus Ducas ( el, Νικηφόρος Κομνηνός Δούκας, Nikēphoros Komnēnos Doukas; – ) was ruler of Epirus from 1267/8 to his death in 1296/98. Life Born around 1240, Nikephoros was the eldest son of the Despot of Epirus, Michael II Komnenos Doukas, and Theodora Petraliphaina. In , at Pegai, Nikephoros was betrothed to Maria, the granddaughter of the Nicaean emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes, who conferred on him the dignity of . The marriage took place at Thessalonica in October 1256, but Maria died in 1258. In the following years Nikephoros was engaged in his father's struggle against Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos and together with his father retreated before the Battle of Pelagonia. After the Nicaeans overran most of Epirus in 1259, Nikephoros left for the Italian Peninsula, where he received reinforcements from his brother-in-law King Manfred of Sicily. With this support Nikephoros helped hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manfred, King Of Sicily
Manfred ( scn, Manfredi di Sicilia; 123226 February 1266) was the last King of Sicily from the Hohenstaufen dynasty, reigning from 1258 until his death. The natural son of the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, Manfred became regent over the kingdom of Sicily on behalf of his nephew Conradin in 1254. As regent he subdued rebellions in the kingdom, until in 1258 he usurped Conradin's rule. After an initial attempt to appease Pope Innocent IV he took up the ongoing conflict between the Hohenstaufens and the papacy through combat and political alliances. He defeated the papal army at Foggia on 2 December 1254. Excommunicated by three successive popes, Manfred was the target of a Crusade (1255–66) called first by Pope Alexander IV and then by Urban IV. Nothing came of Alexander's call, but Urban enlisted the aid of Charles of Anjou in overthrowing Manfred. Manfred was killed during his defeat by Charles at the Battle of Benevento, and Charles assumed kingship of Sicily. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helena Angelina Doukaina
Helena Angelina Doukaina ( 1242 – 1271) was Queen of Sicily as the second wife of King Manfred. Queen Helena was the daughter of Michael II Komnenos Doukas, Despot of Epirus, and Theodora Petraliphaina. Her marriage was an expression of the alliance of her father and the ruler of Sicily against the growing power of the Empire of Nicaea.Donald M. Nicol, ''The last centuries of Byzantium, 1261-1453'', second edition (Cambridge: University Press, 1993), p. 28 Marriage She was married to Manfred of Sicily 2 June 1259, after the death of his first wife Beatrice of Savoy in 1257 and his own rise to the throne on 10 August 1258. D. J. Geanakoplos notes that this marriage was surprising, considering Manfred's father Frederick II had been in an alliance with John III Vatatzes, the late ruler of the Empire of Nicaea, but "one must consider that conquest of the Byzantine Empire had been a traditional Norman aim for almost a century, and that Manfred was now in a strong enough position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corfu
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered by three municipalities with the islands of Othonoi, Ereikoussa, and Mathraki.https://corfutvnews.gr/diaspasi-deite-tin-tropologia/ The principal city of the island (pop. 32,095) is also named Corfu. Corfu is home to the Ionian University. The island is bound up with the history of Greece from the beginnings of Greek mythology, and is marked by numerous battles and conquests. Ancient Korkyra took part in the Battle of Sybota which was a catalyst for the Peloponnesian War, and, according to Thucydides, the largest naval battle between Greek city states until that time. Thucydides also reports that Korkyra was one of the three great naval powers of fifth century BC Greece, alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buthrotum
Butrint ( el, Βουθρωτόν and Βουθρωτός, ''Bouthrōtón'', la, Buthrōtum) was an ancient Greek and later Roman city and bishopric in Epirus. "Speakers of these various Greek dialects settled different parts of Greece at different times during the Middle Bronze Age, with one group, the 'northwest' Greeks, developing their own dialect and peopling central Epirus. This was the origin of the Molossian or Epirotic tribes." " ..a proper dialect of Greek, like the dialects spoken by Dorians and Molossians." "The western mountains were peopled by the Molossians (the western Greeks of Epirus)." "That the Molossians... spoke Illyrian or another barbaric tongue was nowhere suggested, although Aeschylus and Pindar wrote of Molossian lands. That they in fact spoke greek was implied by Herodotus' inclusion of Molossi among the Greek colonists of Asia Minor, but became demonstrable only when D. Evangelides published two long inscriptions of the Molossian State, set up p. 369 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael II Komnenos Doukas
Michael II Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Comnenus Ducas ( el, Μιχαήλ Β΄ Κομνηνός Δούκας, ''Mikhaēl II Komnēnos Doukas''), often called Michael Angelos in narrative sources, was from 1230 until his death in 1266/68 the ruler of the Despotate of Epirus, which included Epirus in northwestern Greece, the western part of Greek Macedonia and Thessaly, and western Greece as far south as Nafpaktos. Life Michael was an illegitimate son of Michael I Komnenos Doukas, the founder of the state of Epirus. The historian Demetrios Polemis estimates that he was born in the early years of his father's reign (1205–15), probably in ca. 1206. Like most members of his family, originally descended from the Angelos family, he preferred the surname "Doukas", or the variant "Komnenos Doukas" (Κομνηνός ὁ Δούκας), but is also referred to by contemporary Byzantine historians as "Angelos". After his father's murder in 1215 and the succession of his uncle Theodore Ko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |