|
Bismarck Sea
The Bismarck Sea (, ) lies in the southwestern Pacific Ocean within the nation of Papua New Guinea. It is located northeast of the island of New Guinea and south of the Bismarck Archipelago. It has coastlines in districts of the Islands Region, Momase Region, and Papua Region. Geography Like the Bismarck Archipelago, it is named in honour of the first German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck. The Bismarck Archipelago extends round to the east and north of the sea, enclosing the Bismarck Sea and separating it from the Southern Pacific Ocean. To the south it is linked to the Solomon Sea by the Vitiaz Strait. Official boundaries The International Hydrographic Organization defines the Bismarck Sea as "that area of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of New Guinea", with the following limits: ''On the North and East.'' By the Northern and Northeastern coasts of the islands of New Ireland (island), New Ireland, New Hanover Island, New Hanover, the Admiralty I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million as of 2021. When compared with (and sometimes described as being one of) the continents, the region of Oceania is the smallest in land area and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, second least populated after Antarctica. Its major population centres are Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Auckland, Adelaide, Honolulu, and Christchurch. Oceania has a diverse mix of economies from the developed country, highly developed and globally competitive market economy, financial markets of Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, Hawaii, New Caledonia, and New Zealand, which rank high in quality of life and Human Development Index, to the much least developed countries, less developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
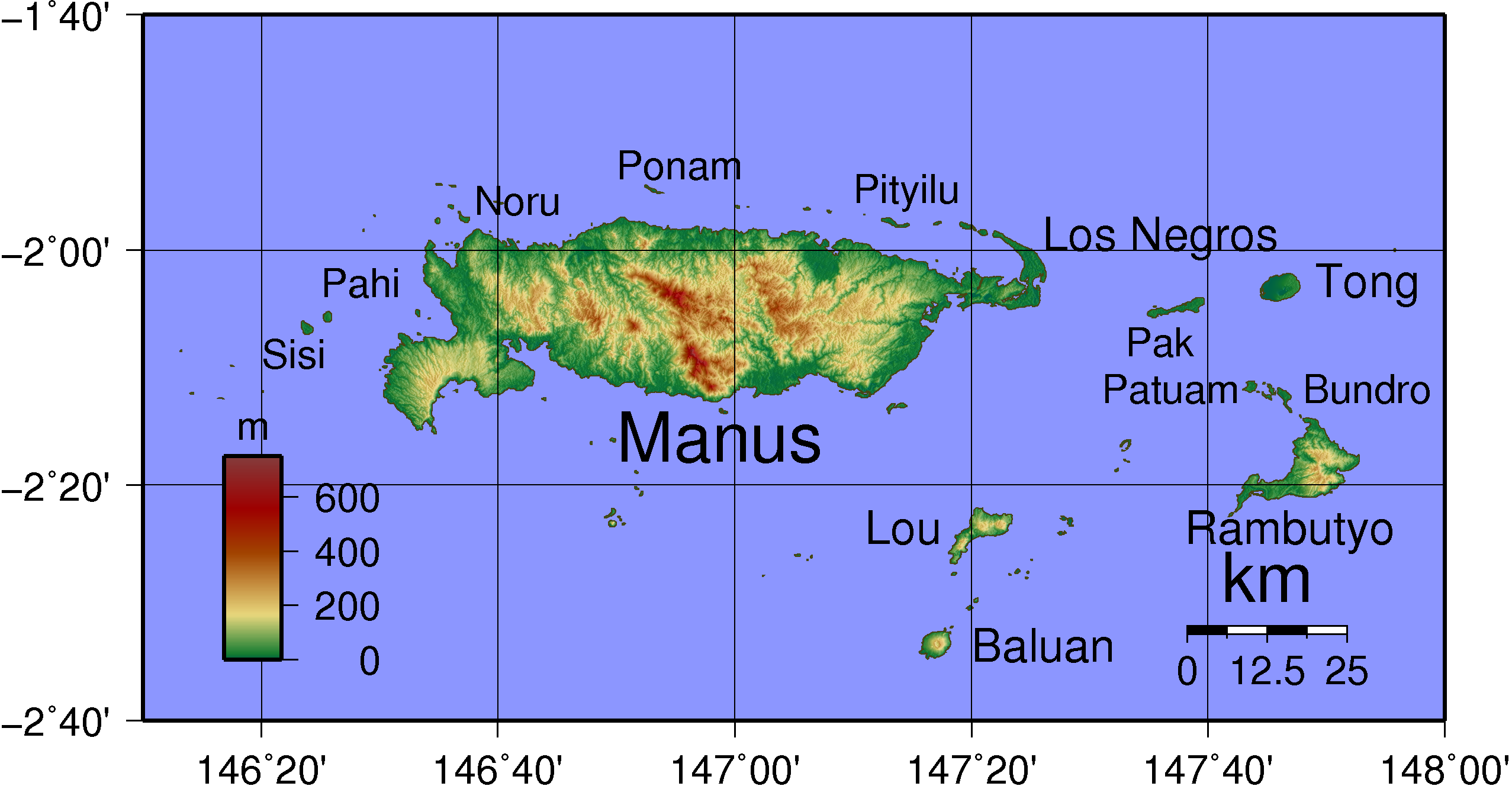
Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-covered islands form part of Manus Province, the smallest and least-populous province of Papua New Guinea, in its Islands Region. The total area is . Many of the Admiralty Islands are atolls and uninhabited. Islands The larger islands in the center of the group are Manus Island and Los Negros Island. The other larger islands are Tong Island, Pak Island, Rambutyo Island, Lou Island, and Baluan Island to the east, Mbuke Island to the south and Bipi Island to the west of Manus Island. Other islands that have been noted as significant places in the history of Manus include Ndrova Island, Pitylu Island and Ponam Island. Geography The temperature of the Admiralty Islands varies little throughout the year, reaching daily highs of and at night. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beck's Petrel
Beck's petrel (''Pseudobulweria becki'') is a small species of petrel. Its specific epithet commemorates American ornithologist Rollo Beck. It is believed to nest on small islands with tall mountains around Melanesia. Described in 1928, and long known from only two specimens, sightings and collections in the 2000s confirmed the birds still existed, but are considered critically endangered by the IUCN. Description It is dark brown above and on the head and throat. It is dark underneath the wings with a fairly distinct white wingbar. The belly and breast are white. It flies over open oceans with straight wings that are slightly bent back at the tips. History The petrel used to be known from only two specimens – a female east of New Ireland, PNG in 1928 and a male north-east of Rendova, Solomon Islands in 1929. In 2005, a bird possibly of this species was photographed in Australia's Coral Sea by birding tour guide Richard Baxter. He noted that it was definitely not the similar a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding important sites for birds, maintaining and restoring key bird habitats, and empowering conservationists worldwide. It has a membership of more than 2.5 million people across 116 country partner organizations, including the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, the Wild Bird Society of Japan, the National Audubon Society and American Bird Conservancy. BirdLife International has identified 13,000 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas and is the official International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List authority for birds. As of 2015, BirdLife International has established that 1,375 bird species (13% of the total) are threatened with extinction ( critically endangered, endangered or vulnerable). BirdLife International p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations. IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife International. There are over 13,000 IBAs worldwide. These sites are small enough to be entirely conserved and differ in their character, habitat or ornithological importance from the surrounding habitat. In the United States the Program is administered by the National Audubon Society. Often IBAs form part of a country's existing protected area network, and so are protected under national legislation. Legal recognition and protection of IBAs that are not within existing protected areas varies within different countries. Some countries have a National IBA Conservation Strategy, whereas in others protection is completely lacking. History In 1985, following a specific request from the European Economic Community, Birdlife International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for states across a broad range of domains, including war, diplomacy, economic relations, and human rights. Scholars distinguish between international legal institutions on the basis of their obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). The sources of international law include international custom (general state practice accepted as law), treaties, and general principles of law recognized by most national legal systems. Although international law may also be reflected in international comity—the practices adopted by states to maintain good relations and mutua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size.The elements are from different metal groups. See periodic table. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfides
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds large families of inorganic and organic compounds, e.g. lead sulfide and dimethyl sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and bisulfide (SH−) are the conjugate acids of sulfide. Chemical properties The sulfide ion, S2−, does not exist in aqueous alkaline solutions of Na2S. Instead sulfide converts to hydrosulfide: :S2− + H2O → SH− + OH− Upon treatment with an acid, sulfide salts convert to hydrogen sulfide: :S2− + H+ → SH− :SH− + H+ → H2S Oxidation of sulfide is a complicated process. Depending on the conditions, the oxidation can produce elemental sulfur, polysulfides, polythionates, sulfite, or sulfate. Metal sulfides react with halogens, forming sulfur and metal salts. :8 MgS + 8 I2 → S8 + 8&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
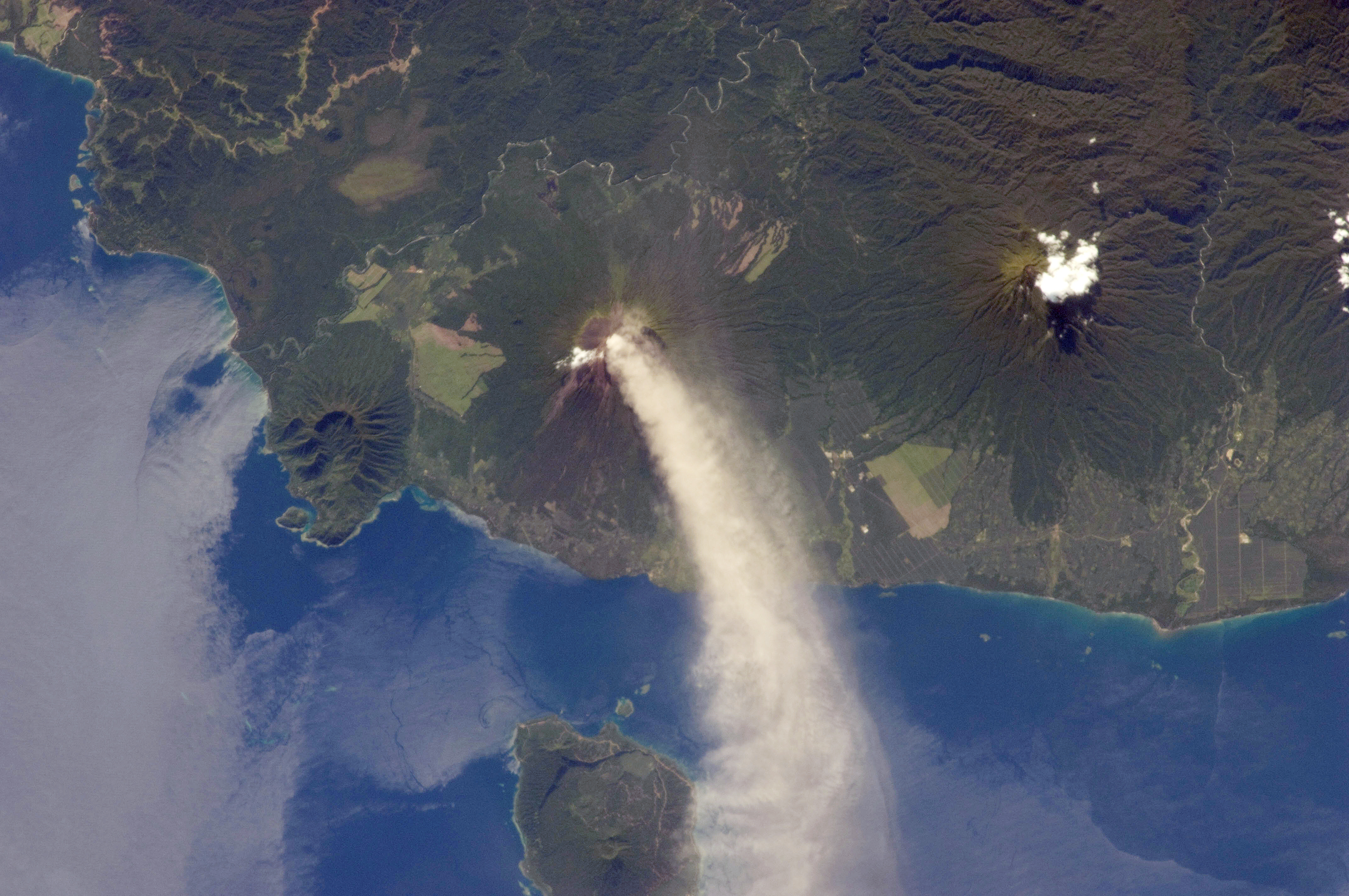
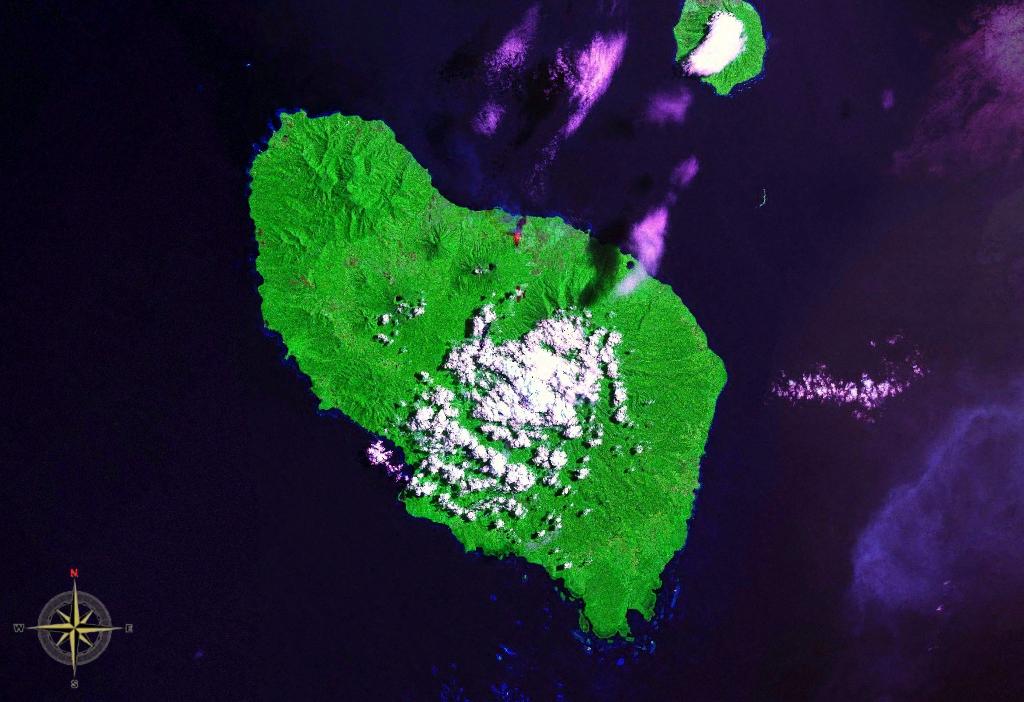
Umboi Island
Umboi (also named Rooke or Siassi) is a volcanic island between the mainland of Papua New Guinea and the island of New Britain. It is separated from New Britain by the Dampier Strait and Huon Peninsula, and New Guinea by the Vitiaz Strait. It has an elevation of . Languages are Papuan Kobai; and Austronesian: Mbula, Karanai, and Saveng languages. The Siassi Archipelago lies off the southeast coast of Umboi Island (a total of 18 islands, only seven are inhabited). During the mid-1920s, the population of the Siassi Islands was a little over 700 people. It had more than doubled (to almost 1700 people) by the early 1960s, and then decreased to a little more than 1600 people by the early 1980s. The Siassi support themselves through traditional trade based on a barter system; they are important middlemen who deliver pigs, pots and wooden bowls by sea in their canoes. See also * List of volcanoes in Papua New Guinea * Siassi Rural LLG Siassi Rural LLG is a local-level govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |