|
Birmingham And Liverpool Junction Canal
The Birmingham and Liverpool Junction Canal was a canal in England which ran from Nantwich, where it joined the Chester Canal, to Autherley, where it joined the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal. Forming part of a major link between Liverpool and the industrial heartlands of the Midlands, the canal was opened in 1835, and merged with the Ellesmere and Chester Canal Company in 1845, which became the Shropshire Union Railways and Canal Company in the following year. History In 1824, the Birmingham Canal was experiencing unprecedented levels of traffic, and asked the civil engineer Thomas Telford to recommend how the canal could be improved. He reported his suggestions in September, and probably also recommended that an additional link northwards from the western end to the River Mersey would be beneficial, since the Birmingham Canal Company described him as the 'originator and proposer' of the route in January 1825. Faced with competition from a proposed railway line from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shropshire Union Canal
The Shropshire Union Canal, nicknamed the "Shroppie", is a navigable canal in England. The Llangollen and Montgomery canals are the modern names of branches of the Shropshire Union (SU) system and lie partially in Wales. The canal lies in the counties of Staffordshire, Shropshire and Cheshire in the north-west English Midlands. It links the canal system of the West Midlands, at Wolverhampton, with the River Mersey and Manchester Ship Canal at Ellesmere Port, Cheshire, distant. The "SU main line" runs southeast from Ellesmere Port on the River Mersey to the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal at Autherley Junction in Wolverhampton. Other links are to the Llangollen Canal (at Hurleston Junction), the Middlewich Branch (at Barbridge Junction), which itself connects via the Wardle Canal with the Trent and Mersey Canal, and the River Dee (in Chester). With two connections to the Trent and Mersey (via the Middlewich Branch and the Staffordshire and Worcestershire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Union Canal
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another ends in Birmingham, with the latter stretching for with 166 locks from London. The Birmingham line has a number of short branches to places including Slough, Aylesbury, Wendover, and Northampton. The Leicester line has two short arms of its own, to Market Harborough and Welford. It has links with other canals and navigable waterways, including the River Thames, the Regent's Canal, the River Nene and River Soar, the Oxford Canal, the Stratford-upon-Avon Canal, the Digbeth Branch Canal and the Birmingham and Fazeley Canal. The canal south of Braunston to the River Thames at Brentford in London is the original Grand Junction Canal. At Braunston the latter met the Oxford Canal linking back to the Thames to the south and to Coventry to the north via the Covent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shilling (British Coin)
The British shilling, abbreviated "1/-", was a unit of currency and a denomination of sterling coinage worth of one pound, or twelve pence. It was first minted in the reign of Henry VII as the testoon, and became known as the shilling, from the Old English , sometime in the mid-16th century. It circulated until 1990. The word ''bob'' was sometimes used for a monetary value of several shillings, e.g. "ten-bob note". Following decimalisation on 15 February 1971 the coin had a value of five new pence, and a new coin of the same value but labelled as "five new pence" or "five pence" was minted with the same size as the shilling until 1990, after which the shilling no longer remained legal tender. It was made from silver from its introduction in or around 1503 until 1946, and thereafter in cupronickel. Before Decimal Day in 1971, sterling used the Carolingian monetary system ("£sd"), under which the largest unit was a pound (£) divided into 20 shillings (s), each of 12 pence (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macclesfield Canal
The Macclesfield Canal is a canal in east Cheshire, England. There were various proposals for a canal to connect the town of Macclesfield to the national network from 1765 onwards, but it was not until 1824 that a scheme came to fruition. There were already suggestions by that date that a railway would be better, but the committee that had been formed elected for a canal, and the engineer Thomas Telford endorsed the decision. The canal as built was a typical Telford canal, constructed using cut and fill, with numerous cuttings and embankments to enable it to follow as straight a course as possible, although Telford had little to do with its construction, which was managed by William Crosley. The canal opened in 1831, and is long. All of its twelve locks are concentrated in a single flight at Bosley, which alters the level by . The canal runs from a junction with the Peak Forest Canal at Marple in the north, in a generally southerly direction, through the towns of Macclesfield ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the L&NWR was the largest joint stock company in the United Kingdom. In 1923, it became a constituent of the London, Midland and Scottish (LMS) railway, and, in 1948, the London Midland Region of British Railways: the LNWR is effectively an ancestor of today's West Coast Main Line. History The company was formed on 16 July 1846 by the amalgamation of the Grand Junction Railway, London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway. This move was prompted, in part, by the Great Western Railway's plans for a railway north from Oxford to Birmingham. The company initially had a network of approximately , connecting London with Birmingham, Crewe, Chester, Liverpool and Manchester. The headquarters were at Euston railway station. As traffic increased, it was greatly expanded with the opening in 1849 of the Great Hall, designe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audlem
Audlem is a village and civil parish located in the unitary authority of Cheshire East and the ceremonial county of Cheshire in North West England, approximately south of Nantwich. Close to the border with the neighbouring county of Shropshire, the village is eight miles (13 km) east of Whitchurch and seven miles (11 km) north of Market Drayton. According to the 2001 census, the population of the entire civil parish was 1,790, increasing to 1,991 at the 2011 Census. History Audlem was mentioned in the Domesday Book as ''Aldelime'', and Edward I granted it a market charter in 1295.Scholes, R. (2000). pages 24–25. Geography Audlem is on the Shropshire Union Canal, which has a flight of 15 locks, designed by Thomas Telford, to raise the canal from the Cheshire Plain to the Shropshire Plain. The River Weaver passes west of the village. Audlem railway station closed along with the local railway line in the 1960s. Landmarks Moss Hall is an Elizabethan timber-framed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belvide Reservoir
Belvide Reservoir is a reservoir in South Staffordshire, England. It was built in 1833 to supply the Birmingham and Liverpool Junction Canal, and has been managed as a nature reserve since 1977. It has been used to study the effect of water level changes on bird populations. Details Owned by the Canal & River Trust, the reservoir was constructed around 1833 to feed the Birmingham and Liverpool Junction Canal, which became part of the Shropshire Union Canal in 1846. Work began on it in 1832, and the canal opened in early 1835. Traffic levels were high, and the company had to buy 2,000 lockfulls of water in the first year, for which they paid £800 to the Wyrley and Essington Canal. In 1836, there was still pressure on the water supply, and the engineer William Cubitt was instructed to enlarge the reservoir in May. In order to finance the improvements, the Commissioners agreed that they would not be paid until £20,000 had been spent on the improvements. The enlarged reservoir was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Cubitt
Sir William Cubitt FRS (bapt. 9 October 1785 – 13 October 1861) was an eminent English civil engineer and millwright. Born in Norfolk, England, he was employed in many of the great engineering undertakings of his time. He invented a type of windmill sail and the prison treadwheel, and was employed as chief engineer, at Ransomes of Ipswich, before moving to London. He worked on canals, docks, and railways, including the South Eastern Railway and the Great Northern Railway. He was the chief engineer of Crystal Palace erected at Hyde Park in 1851. He was president of the Institution of Civil Engineers between 1850 and 1851. Early life Cubitt was born in Dilham, Norfolk, the son of Joseph Cubitt of Bacton Wood, a miller, and Hannah Lubbock. He attended the village school. His father moved to Southrepps, and William at an early age was employed in the mill, but in 1800 was apprenticed to James Lyon, a cabinet-maker at Stalham, from whom he parted after four years. At Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Avon, Warwickshire
The River Avon () in central England flows generally southwestwards and is a major left-bank tributary of the River Severn, of which it is the easternmost. It is also known as the Warwickshire Avon or Shakespeare's Avon, to distinguish it from several other rivers of the same name in the United Kingdom. Beginning in Northamptonshire, the river flows through or adjoining the counties of Leicestershire, Northamptonshire, Warwickshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire, near the Cotswold Hills area. Notable towns it flows through include Rugby, Warwick, Stratford-upon-Avon, Evesham, Pershore and Tewkesbury, where it joins the Severn. It has traditionally been divided since 1719 into the Lower Avon, below Evesham, and the Upper Avon, from Evesham to above Stratford-upon-Avon. Improvements to aid navigation began in 1635, and a series of locks and weirs made it possible to reach Stratford, and to within of Warwick. The Upper Avon was tortuous and prone to flooding, and was ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrewsbury Canal
The Shrewsbury Canal (or Shrewsbury and Newport Canal) was a canal in Shropshire, England. Authorised in 1793, the main line from Trench to Shrewsbury was fully open by 1797, but it remained isolated from the rest of the canal network until 1835, when the Birmingham and Liverpool Junction Canal built the Newport Branch from Norbury Junction to a new junction with the Shrewsbury Canal at Wappenshall. After ownership passed to a series of railway companies, the canal was officially abandoned in 1944; many sections have disappeared, though some bridges and other structures can still be found. There is an active campaign to preserve the remnants of the canal and to restore the Norbury to Shrewsbury line to navigation. History From 1768 several small canals were built in the area of what is now Telford. These canals carried tub boats. The first of these was the Donnington Wood Canal which opened in 1768, to be followed by the Wombridge Canal and the Ketley Canal, both opened in 178 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stourbridge Canal
The Stourbridge Canal is a canal in the West Midlands of England. It links the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal (at Stourton Junction, affording access to traffic from the River Severn) with the Dudley Canal, and hence, via the Birmingham Canal Navigations, to Birmingham and the Black Country. History The Stourbridge and Dudley canals were originally proposed as a single canal in 1775, with a primary purpose of carrying coal from Dudley to Stourbridge. Robert Whitworth had carried out a survey, which was approved at a meeting held in Stourbridge in February, at which the estimated cost was promised by subscribers. The chief promoter was Lord Dudley, but the bill was withdrawn from Parliament following fierce opposition from the Birmingham Canals. Two bills were presented in the autumn, one for each of the canals, with the details largely unchanged, and both became Acts of Parliament on 2 April 1776, despite continued opposition from Birmingham. The Act allowed the promo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
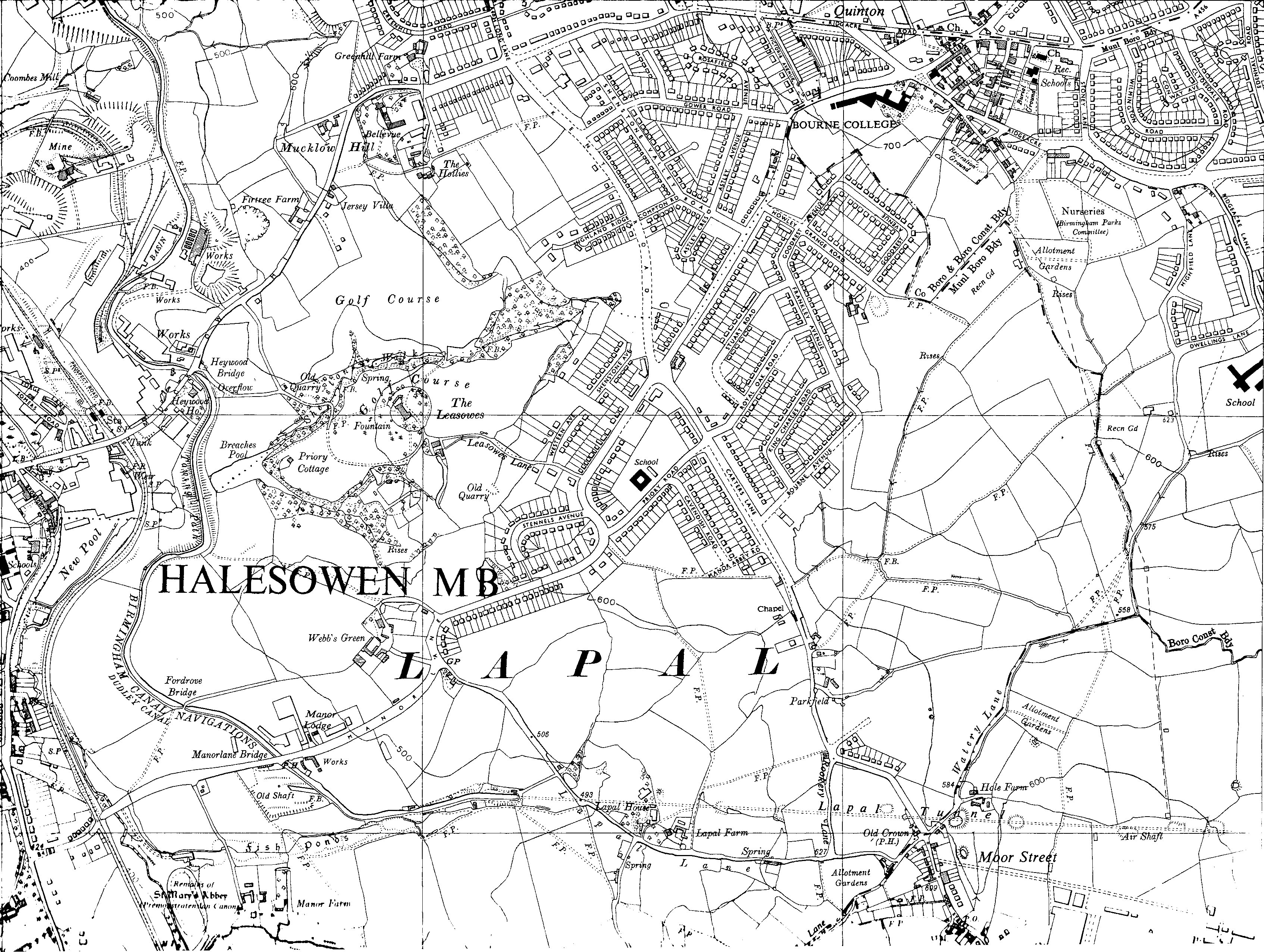
Dudley Canal
The Dudley Canal is a canal passing through Dudley in the West Midlands of England. The canal is part of the English and Welsh connected network of navigable inland waterways, and in particular forms part of the popular Stourport Ring narrowboat cruising route. The first short section, which connected to the Stourbridge Canal, opened in 1779, and this was connected through the Dudley Tunnel to the Birmingham Canal system in 1792. Almost immediately, work started on an extension, called Line No. 2, which ran through another long tunnel at Lapal, to reach the Worcester and Birmingham Canal. This was completed in 1798, but significant trade had to wait until the Worcester and Birmingham was completed in 1802. In 1846, the company amalgamated with the Birmingham Canal Navigations, and various improvements followed, including the Netherton Tunnel, of a similar length to the Dudley Tunnel, but much bigger, with towpaths on both sides and gas lighting. It was the last canal tunnel buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |