|
Biogeochemical
Biogeochemistry is the scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natural environment (including the biosphere, the cryosphere, the hydrosphere, the pedosphere, the atmosphere, and the lithosphere). In particular, biogeochemistry is the study of biogeochemical cycles, the cycles of chemical elements such as carbon and nitrogen, and their interactions with and incorporation into living things transported through earth scale biological systems in space and time. The field focuses on chemical cycles which are either driven by or influence biological activity. Particular emphasis is placed on the study of carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, iron, and phosphorus cycles. Biogeochemistry is a systems science closely related to systems ecology. History Early History Early Greeks established some of the core ideas of biogeochemistry, such as nature consisting of cycles. 17th - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeochemical Cycle
A biogeochemical cycle (or more generally a cycle of matter) is the pathway by which a chemical substance cycles (is turned over or moves through) the biotic and the abiotic compartments of Earth. The biotic compartment is the biosphere and the abiotic compartments are the atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere. There are biogeochemical cycles for chemical elements, such as for calcium, carbon, hydrogen, mercury, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, selenium, iron and sulfur, as well as molecular cycles, such as for water and silica. There are also macroscopic cycles, such as the rock cycle, and human-induced cycles for synthetic compounds such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). In some cycles there are reservoirs where a substance can remain or be sequestered for a long period of time. Overview Energy flows directionally through ecosystems, entering as sunlight (or inorganic molecules for chemoautotrophs) and leaving as heat during the many transfers between trophic levels. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Cycle
The iron cycle (Fe) is the biogeochemical cycle of iron through the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere and lithosphere. While Fe is highly abundant in the Earth's crust, it is less common in oxygenated surface waters. Iron is a key micronutrient in primary productivity, and a limiting nutrient in the Southern ocean, eastern equatorial Pacific, and the subarctic Pacific referred to as High-Nutrient, Low-Chlorophyll (HNLC) regions of the ocean. Iron exists in a range of oxidation states from -2 to +7; however, on Earth it is predominantly in its +2 or +3 redox state and is a primary redox-active metal on Earth. The cycling of iron between its +2 and +3 oxidation states is referred to as the iron cycle. This process can be entirely abiotic or facilitated by microorganisms, especially iron-oxidizing bacteria. The abiotic processes include the rusting of iron-bearing metals, where Fe2+ is abiotically oxidized to Fe3+ in the presence of oxygen, and the reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+ by iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
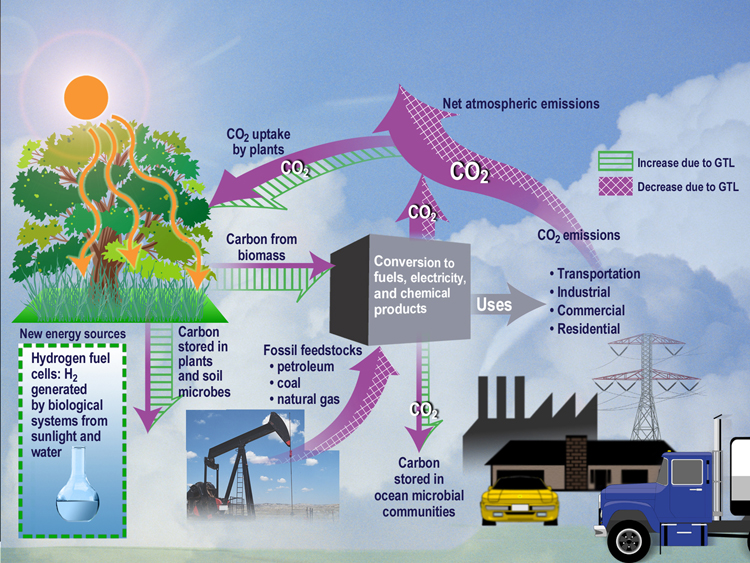
Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many minerals such as limestone. Along with the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle, the carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to make Earth capable of sustaining life. It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere, as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration to and release from carbon sinks. Carbon sinks in the land and the ocean each currently take up about one-quarter of anthropogenic carbon emissions each year. Humans have disturbed the biological carbon cycle for many centuries by modifying land use, and moreover with the recent industrial-scale mining of fossil carbon (coal, petroleum and natural gas, gas extraction, and cement manufacture) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is atmospheric nitrogen, making it the largest source of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems. The nitrogen cycle is of particular interest to ecologists because nitrogen availability can affect the rate of key ecosystem processes, including primary production and decomposition. Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, use of artificial nitrogen fertilizers, and release of nitrogen in wastewater have dramatically altered the global nitr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Cycle
The sulfur cycle is a biogeochemical cycle in which the sulfur moves between rocks, waterways and living systems. It is important in geology as it affects many minerals and in life because sulfur is an essential element ( CHNOPS), being a constituent of many proteins and cofactors, and sulfur compounds can be used as oxidants or reductants in microbial respiration. The global sulfur cycle involves the transformations of sulfur species through different oxidation states, which play an important role in both geological and biological processes. Steps of the sulfur cycle are: * Mineralization of organic sulfur into inorganic forms, such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S), elemental sulfur, as well as sulfide minerals. * Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide, sulfide, and elemental sulfur (S) to sulfate (). * Reduction of sulfate to sulfide. * Incorporation of sulfide into organic compounds (including metal-containing derivatives). These are often termed as follows: :''Assimilative sulfate reducti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
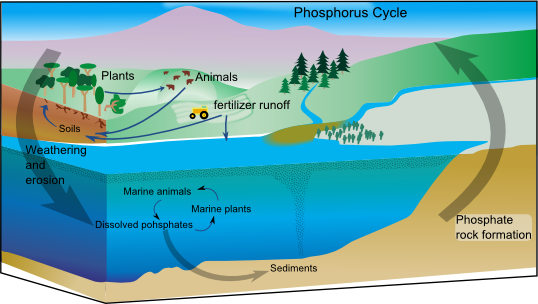
Phosphorus Cycle
The phosphorus cycle is the biogeochemical cycle that describes the movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. Unlike many other biogeochemical cycles, the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere does not play a significant role in the movement of phosphorus, because phosphorus and phosphorus-based compounds are usually solids at the typical ranges of temperature and pressure found on Earth. The production of phosphine gas occurs in only specialized, local conditions. Therefore, the phosphorus cycle should be viewed from whole Earth system and then specifically focused on the cycle in terrestrial and aquatic systems. Living organisms require phosphorus, a vital component of DNA, RNA, Adenosine triphosphate, ATP, etc, for their proper functioning. Plants assimilate phosphorus as phosphate and incorporate it into organic compounds and in animals, phosphorus is a key component of bones, teeth, etc. On the land, phosphorus gradually becomes less available to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments. Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations.Based on definition from: Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Ecology
Systems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, a subset of Earth system science, that takes a holism, holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem is a complex system exhibiting emergent properties. Systems ecology focuses on interactions and transactions within and between biological and ecological systems, and is especially concerned with the way the functioning of ecosystems can be influenced by human interventions. It uses and extends concepts from thermodynamics and develops other macroscopic descriptions of complex systems. Overview Systems ecology seeks a Holism, holistic view of the interactions and transactions within and between biological and ecological systems. Systems ecologists realise that the function of any ecosystem can be influenced by human economics in fundamental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Thinking
Systems thinking is a way of making sense of the complexity of the world by looking at it in terms of wholes and relationships rather than by splitting it down into its parts. It has been used as a way of exploring and developing effective action in complex contexts, enablinsystems change Systems thinking draws on and contributes to systems theory and the system sciences. History Frameworks and methodologies Frameworks and methodologies for systems thinking include: * Critical systems thinking * Soft systems methodology * Systemic design * System dynamics * Viable system model Multi-method approach See also * Management cybernetics * Operational research Operations research ( en-GB, operational research) (U.S. Air Force Specialty Code: Operations Analysis), often shortened to the initialism OR, is a discipline that deals with the development and application of analytical methods to improve deci ... References Systems science Cybernetics Systems theory Systems th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Dumas
Jean Baptiste André Dumas (14 July 180010 April 1884) was a French chemist, best known for his works on organic analysis and synthesis, as well as the determination of atomic weights (relative atomic masses) and molecular weights by measuring vapor densities. He also developed a method for the analysis of nitrogen in compounds. Biography Dumas was born in Alès (Gard), and became an apprentice to an apothecary in his native town. In 1816, he moved to Geneva, where he attended lectures by M. A. Pictet in physics, C. G. de la Rive in chemistry, and A. P. de Candolle in botany, and before he had reached his majority, he was engaged with Pierre Prévost in original work on problems of physiological chemistry and embryology. In 1822, he moved to Paris, acting on the advice of Alexander von Humboldt, where he became professor of chemistry, initially at the Lyceum, later (1835) at the École polytechnique. He was one of the founders of the École centrale des arts et manufactures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biological evolution occurred and proceeded in accordance with Naturalism (philosophy), natural laws. Lamarck fought in the Seven Years' War against Prussia, and was awarded a commission for bravery on the battlefield. Posted to Monaco, Lamarck became interested in natural history and resolved to study medicine.#Packard, Packard (1901), p. 15. He retired from the army after being injured in 1766, and returned to his medical studies. Lamarck developed a particular interest in botany, and later, after he published the three-volume work ''Flore françoise'' (1778), he gained membership of the French Academy of Sciences in 1779. Lamarck became involved in the Jardin des Plantes and was appointed to the Chair of Botany in 1788. When the French Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |