|
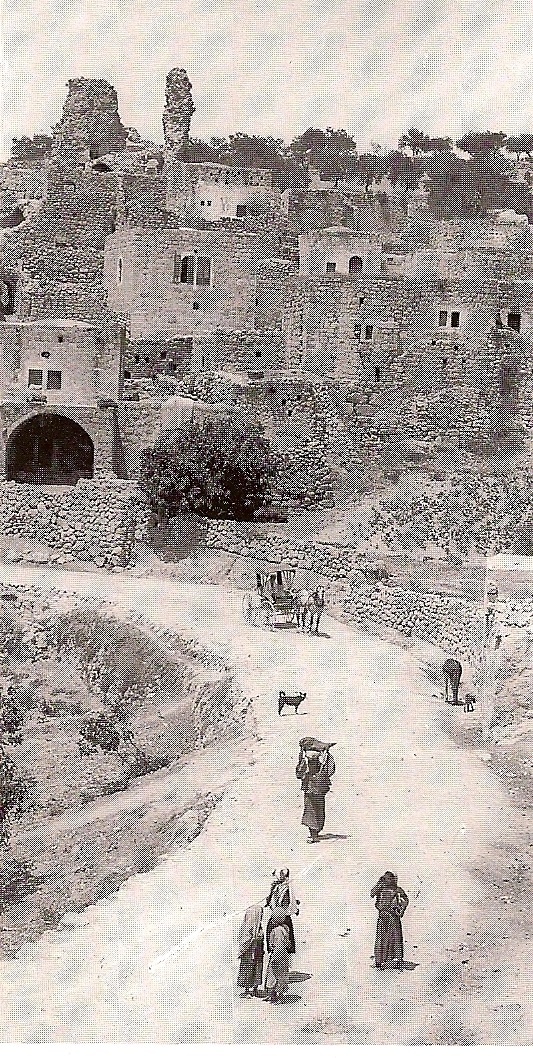
Bethany (biblical Village)
Bethany ( grc-gre, Βηθανία,Murphy-O'Connor, 2008, p152/ref> Syriac: ܒܝܬ ܥܢܝܐ ''Bēṯ ʿAnyā'') or what is locally known as Al-Eizariya or al-Azariya ( ar, العيزرية, " laceof Lazarus"), is a Palestinian town in the West Bank. The name al-Eizariya refers to the New Testament figure Lazarus of Bethany, who according to the Gospel of John, was raised from the dead by Jesus. The traditional site of the miracle, the Tomb of Lazarus, in the city is a place of pilgrimage. The town is located on the southeastern slope of the Mount of Olives, less than from Jerusalem. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, it is the second largest Palestinian city in the Jerusalem Governorate (not including East Jerusalem, which is under Israeli control), with a population of 17,606 inhabitants. Being mostly in Area C, it is controlled by the Israeli military rather than the Palestinian Authority. Name Al-Eizariya The name Al-Eizariya ( ar, العيزري ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the third-most by number of users (after the Latin and Chinese scripts). The script was first used to write texts in Arabic, most notably the Quran, the holy book of Islam. With the religion's spread, it came to be used as the primary script for many language families, leading to the addition of new letters and other symbols. Such languages still using it are: Persian (Farsi/Dari), Malay ( Jawi), Uyghur, Kurdish, Punjabi (Shahmukhi), Sindhi, Balti, Balochi, Pashto, Lurish, Urdu, Kashmiri, Rohingya, Somali and Mandinka, Mooré among others. Until the 16th century, it was also used for some Spanish texts, and—prior to the language reform in 1928—it was the writing system of Turkish. The script is written from right to left in a cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Of Olives
The Mount of Olives or Mount Olivet ( he, הַר הַזֵּיתִים, Har ha-Zeitim; ar, جبل الزيتون, Jabal az-Zaytūn; both lit. 'Mount of Olives'; in Arabic also , , 'the Mountain') is a mountain ridge east of and adjacent to Jerusalem's Old City. It is named for the olive groves that once covered its slopes. The southern part of the mount was the Silwan necropolis, attributed to the elite of the ancient Kingdom of Judah. The mount has been used as a Jewish cemetery for over 3,000 years and holds approximately 150,000 graves, making it central in the tradition of Jewish cemeteries. Several key events in the life of Jesus, as related in the Gospels, took place on the Mount of Olives, and in the Acts of the Apostles it is described as the place from which Jesus ascended to heaven. Because of its association with both Jesus and Mary, the mount has been a site of Christian worship since ancient times and is today a major site of pilgrimage for Catholics, the Easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustaf Dalman
Gustaf Hermann Dalman (9 June 1855 – 19 August 1941) was a German Lutheran theologian and orientalist. He did extensive field work in Palestine before the First World War, collecting inscriptions, poetry, and proverbs. He also collected physical articles illustrative of the life of the indigenous farmers and herders of the country, including rock and plant samples, house and farm tools, small archaeological finds, and ceramics. He pioneered the study of biblical and early post-biblical Aramaic, publishing an authoritative grammar (1894) and dictionary (1901), as well as other works. His collection of 15,000 historic photographs and 5,000 books, including rare 16th century prints, and maps formed the basis of the Gustaf Dalman Institute at the Ernst Moritz Arndt University, Greifswald, which commemorates and continues his work. Dalman was appointed by Kaiser Wilhelm II as director of the ''Deutsches Evangelisches Institut für Altertumswissenschaft des heiligen Landes zu Jerusa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The term ''Talmud'' normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (). It may also traditionally be called (), a Hebrew abbreviation of , or the "six orders" of the Mishnah. The Talmud has two components: the Mishnah (, 200 CE), a written compendium of the Oral Torah; and the Gemara (, 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may refer to eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.Among the national museums in London, sculpture and decorative and applied art are in the Victoria and Albert Museum; the British Museum houses earlier art, non-Western art, prints and drawings. The National Gallery holds the national collection of Western European art to about 1900, while art of the 20th century on is at Tate Modern. Tate Britain holds British Art from 1500 onwards. Books, manuscripts and many works on paper are in the British Library. There are significant overlaps between the coverage of the various collections. The British Museum was the first public national museum to cover all fields of knowledge. The museum was established in 1753, largely b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emanuel Deutsch
Emanuel Oscar Menahem Deutsch (1829 – 28 October 1873) was a German Jewish scholar of Semitic studies, the Talmud and Middle Eastern studies. Biography He was born in Neisse, Prussian Silesia (now Nysa, Poland). His education was begun by an uncle, to whose inspiration he owed his interest in oriental languages and literature. On reaching his sixteenth year, he began his studies at the University of Berlin, paying special attention to theology and the Talmud. He also mastered the English language and studied English literature. In 1855 Deutsch was appointed assistant in the library of the British Museum. He worked intensely on the Talmud and contributed no less than 190 papers to Chambers' ''Encyclopaedia'', as well as essays on the Targum and the Samaritan Pentateuch for Smith's ''Dictionary of the Bible'', essays for John Kitto's Biblical dictionary, and articles in periodicals. The monument of his official work in the British Museum is to be found in the ''Phoenician Inscript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Barber Lightfoot
Joseph Barber Lightfoot (13 April 1828 – 21 December 1889), known as J. B. Lightfoot, was an English theologian and Bishop of Durham. Life Lightfoot was born in Liverpool, where his father John Jackson Lightfoot was an accountant. His mother, Ann Matilda Barber, was from a family of Birmingham artists. He was educated at King Edward's School, Birmingham, under James Prince Lee. His contemporaries included Brooke Foss Westcott and Edward White Benson. In 1847, Lightfoot went to Trinity College, Cambridge, and read for his degree along with Westcott. He graduated senior classic and 30th wrangler, and was elected a fellow of his college. From 1854 to 1859 he edited the ''Journal of Classical and Sacred Philology''. In 1857, he became tutor and his fame as a scholar grew. He was made Hulsean professor in 1861, and shortly afterwards chaplain to the Prince Consort and honorary chaplain in ordinary to Queen Victoria. In 1866, he was Whitehall preacher, and in 1871 he becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hepworth Dixon
William Hepworth Dixon (30 June 1821 – 26 December 1879) was an English historian and traveller from Manchester. He was active in organizing London's Great Exhibition of 1851. Early life Dixon was born on 30 June 1821, at Great Ancoats in Manchester to Abner Dixon of Holmfirth and Kirkburton in the West Riding of Yorkshire and Mary Cryer. His uncle, Elijah Dixon, was the reform campaigner and manufacturer. He spent his boyhood in the hill country of Over Darwen, being schooled by a great-uncle, Michael Beswick. As a lad he became clerk to a Manchester merchant named Thompson. Man of letters Early in 1846 Dixon decided on a literary career. He was for two months editor of the ''Cheltenham Journal''. While there he won two main essay prizes in Madden's ''Prize Essay Magazine''. In the summer of 1846, he was advised by Douglas Jerrold to move to London. He entered the Inner Temple, but was not called to the bar until 1 May 1854 and never practised. About 1850 Dixon became a depu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Robinson (scholar)
Edward Robinson (April 10, 1794 – January 27, 1863) was an American biblical scholar known for his magnum opus, ''Biblical Researches in Palestine'', the first major work in Biblical Geography and Biblical Archaeology, which earned him the epithets "Father of Biblical Geography" and "Founder of Modern Palestinology." He studied in the United States and Germany, a center of biblical scholarship and exploration of the Bible as history. He translated scriptural works from classical languages, as well as German translations. His ''Greek and English Lexicon of the New Testament'' (1836; last revision, 1850) became a standard authority in the United States, and was reprinted several times in Great Britain. Biography Robinson was born in Southington, Connecticut, and raised on a farm. His father was a minister in the Congregational Church of the town for four decades. The younger Robinson taught at schools in East Haven and Farmington in 1810–11 to earn money for college. He atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Researches In Palestine
''Biblical researches in Palestine, Mount Sinai and Arabia Petraea'' (1841 edition), also ''Biblical Researches in Palestine and the Adjacent Regions'' (1856 edition), was a Travelogues of Ottoman Palestine, travelogue of 19th-century Palestine and the magnum opus of the "Father of Biblical Geography", Edward Robinson (scholar), Edward Robinson. The work was published simultaneously in England, the United States (dedicated to Moses Stuart) and Germany (dedicated to Carl Ritter). The work identified numerous Biblical localities for the first time, as well as significant Jerusalem archaeological sites such as Robinson's Arch (subsequently named for the author), and undertook the first scientific surveys of other sites such as the Siloam tunnel. Robinson received a Royal Geographical Society Patron's Medal as a result of his work. The work was accompanied by the Kiepert maps of Palestine and Jerusalem. Field work Robinson made two journeys to Palestine. The first began on 12 March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area C (West Bank)
Area C ( he, שטח C; ar, منطقة ج) is an West Bank Areas in the Oslo II Accord, Oslo II administrative division of the West Bank, defined as "areas of the West Bank outside West_Bank_Areas_in_the_Oslo_II_Accord#Area_B, Areas A and B". Area C constitutes about 61 percent of the West Bank territory; the area was committed in 1995 under West_Bank_Areas_in_the_Oslo_II_Accord, the Oslo II Accord to be "gradually transferred to Palestinian jurisdiction" (with an option for land swaps under a final agreement), but such transfer did not happen. Area C (excluding East Jerusalem), which along with Area B is under Israeli military control since June 1967, is home to roughly 400,000 Israeli settlers, and approximately 300,000 Palestinians; who live in more than 500 residential areas located partially or fully in Area C. The Jewish population in Area C is administered by the Israeli Judea and Samaria Area administration, whereas the Palestinian population is directly administered by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
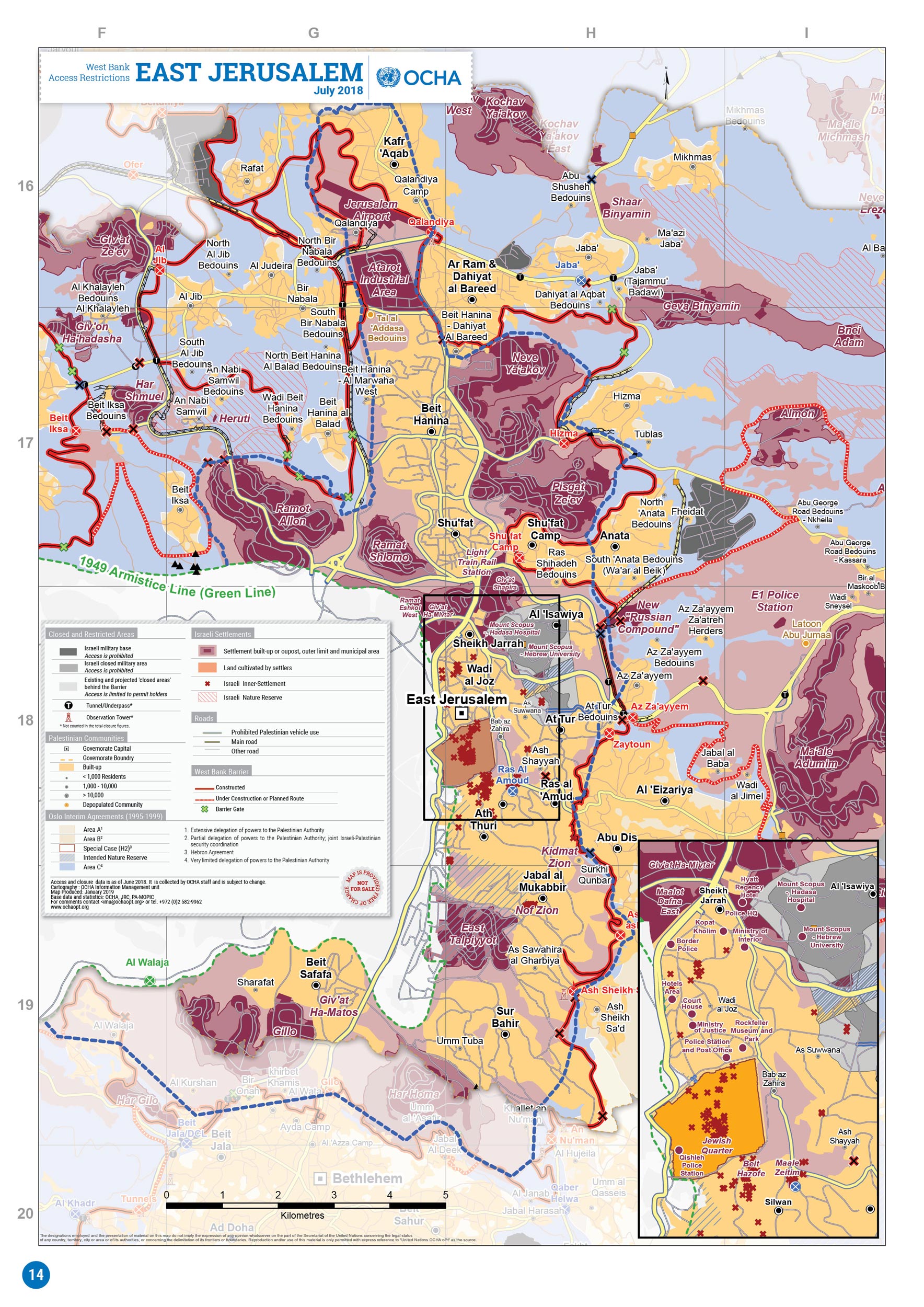
East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the sector of Jerusalem that was held by Jordan during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to the western sector of the city, West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel. Jerusalem was envisaged as a separate, international city under the 1947 United Nations partition plan. It was, however, divided by the 1948 war that followed Israel's declaration of independence. As a result of the 1949 Armistice Agreements, the city's western half came under Israeli control, while its eastern half, containing the famed Old City, fell under Jordanian control. Israel occupied East Jerusalem during the 1967 Six-Day War; since then, the entire city has been under Israeli control. The 1980 Jerusalem Law declared unified Jerusalem the capital of Israel, formalizing the effective annexation of East Jerusalem. Palestinians and many in the international community consider East Jerusalem to be the future capital of the State of Palestine. This includes (out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)