|
Bentheim-Lingen
Bentheim-Lingen was a county seated in Lingen in Germany. Bentheim-Lingen emerged as a partition of Bentheim-Tecklenburg in 1450, and was absorbed by Spain in 1555. Over the next century, ownership of Bentheim-Lingen passed between Spain and Nassau-Orange, before being annexed by Prussia Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ... 1702. Counts of Bentheim-Lingen (1450–1555) *Otto (1450–1508) ''with...'' *Nicholas III ''(Count of Bentheim-Tecklenburg)'' (1493–1508) *Nicholas IV (1508–1541) *Conrad ''(Count of Bentheim-Tecklenburg)'' (1541–1547) *Maximilian (1547–1548) *Anna (1548–1555) {{coord missing, Lower Saxony Counties of the Holy Roman Empire States and territories established in 1450 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bentheim-Tecklenburg
Bentheim-Tecklenburg was a German county based in the region around Tecklenburg in northern North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. History Bentheim-Tecklenburg emerged as a partition of the County of Bentheim in 1277, and was partitioned between itself and Bentheim-Lingen in 1450. Count Conrad converted his county to Lutheranism in 1541. In 1557, it was inherited by Bentheim-Steinfurt. Arnold III, Count of Bentheim-Steinfurt-Tecklenburg-Limburg (1554-1606) held the counties of Bentheim, Tecklenburg, Steinfurt, Limburg (with Hohenlimburg Castle), the Lordship of Rheda, possessions on the Lower Rhine and bailiff rights in the Archbishopric of Cologne. After his death his possessions were divided between his three eldest sons while the younger sons received lands from their mother. Adolf (1577-1623) received Tecklenburg and Rheda, Wilhelm Heinrich (1584-1632) Steinfurt (with Burgsteinfurt Castle), but left no offspring, Konrad Gumprecht (1585-1618) received Limburg, but his only s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nassau-Orange
The House of Orange-Nassau (Dutch: ''Huis van Oranje-Nassau'', ) is the current reigning house of the Netherlands. A branch of the European House of Nassau, the house has played a central role in the politics and government of the Netherlands and Europe especially since William the Silent organised the Dutch Revolt against Spanish rule, which after the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) led to an independent Dutch state. Several members of the house served during this war and after as stadtholder ("governor"; Dutch: ''stadhouder'') during the Dutch Republic. However, in 1815, after a long period as a republic, the Netherlands became a monarchy under the House of Orange-Nassau. The dynasty was established as a result of the marriage of Henry III of Nassau-Breda from Germany and Claudia of Châlon-Orange from French Burgundy in 1515. Their son René of Chalon inherited in 1530 the independent and sovereign Principality of Orange from his mother's brother, Philibert of Châlon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingen
Lingen (), officially Lingen (Ems), is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany. In 2008, its population was 52,353, and in addition there were about 5,000 people who registered the city as their secondary residence. Lingen, specifically "Lingen (Ems)" is located on the river Ems in the southern part of the Emsland District, which borders North Rhine-Westphalia in the south and the Netherlands in the west. History Lingen was first mentioned in the Middle Ages (975 AD). Economy and education Lingen is known for its offshore- and nuclear industry (Emsland Nuclear Power Plant). The University of Applied Sciences Osnabrueck has set up a branch campus, located in the centre of Lingen, with the three Institutes for Management and Engineering, Communications Management and Teaching of Theatre. In 2000 the institutes in Lingen merged into the Faculty of Society and Technology. In 2010 there are expected to be about 2,000 students attending. Climate On 25 July 2019, Lingen set the record for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a "Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
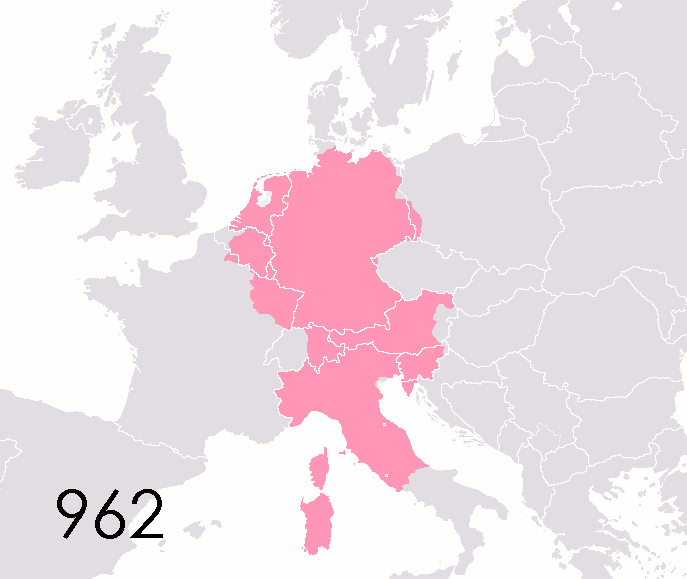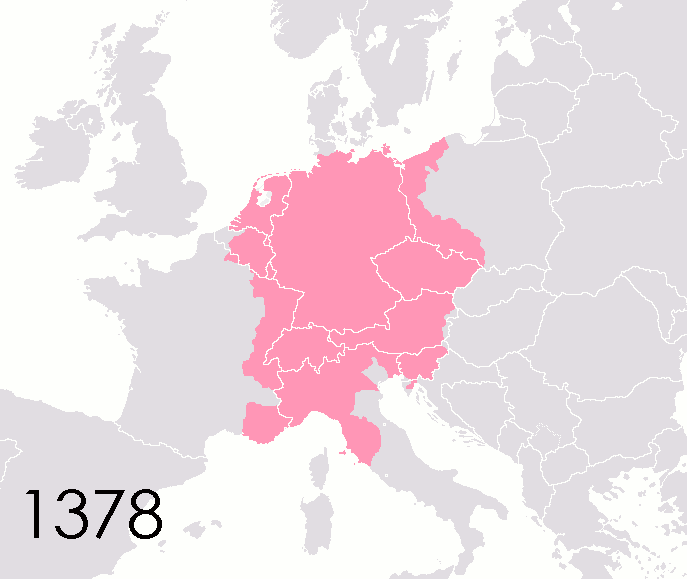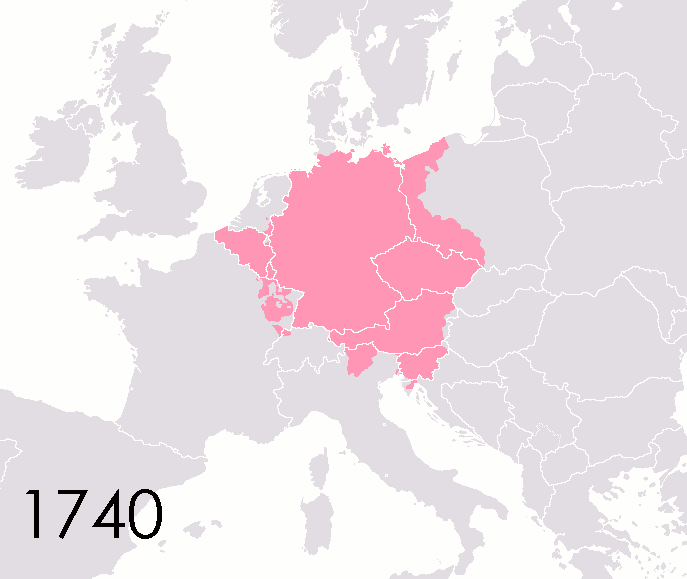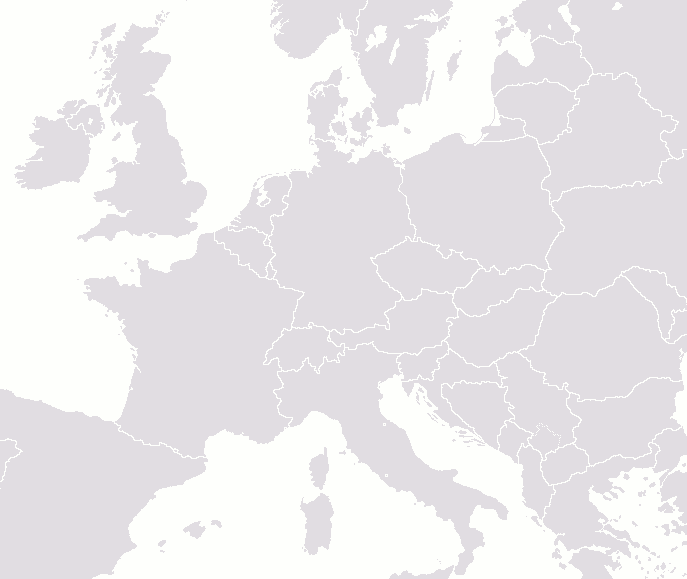
Counties Of The Holy Roman Empire
This list of states in the Holy Roman Empire includes any territory ruled by an authority that had been granted imperial immediacy, as well as many other feudal entities such as lordships, sous-fiefs and allodial fiefs. The Holy Roman Empire was a complex political entity that existed in central Europe for most of the medieval and early modern periods and was generally ruled by a German-speaking Emperor. The states that composed the Empire, while enjoying a unique form of territorial authority (called '' Landeshoheit'') that granted them many attributes of sovereignty, were never fully sovereign states in the sense that term is understood today. In the 18th century, the Holy Roman Empire consisted of approximately 1,800 such territories, the majority being tiny estates owned by the families of Imperial Knights. This page does not directly contain the list but discusses the format of the various lists and offers some background to understand the complex organisation of the Holy R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |