|
Bayons
Bayons ( oc, Baion) is a commune in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of south-eastern France. The inhabitants of the commune are known as ''Bayonnais'' or ''Bayonnaises''. Geography Bayons is located in the Massif des Monges some 20 km south by south-east of Gap and 15 km north-east of Sisteron. Access to the commune is by the D1 road from Clamensane in the west which passes through the commune and the village before continuing north to Turriers. Bayons is situated in a vast Cirque surrounded by high mountains, through which the ''Sasse'' flows - exiting through a narrow clue. The commune was formed from the merger of four communes in 1973: Astoin, Bayons, Esparron-la-Bâtie and Reynier. Except for Astoin, the communes joined to Bayons in 1973 are located in parallel valleys perpendicular to the Sasse and downstream from Bayons. The commune is located in a region of mountainous relief and has a Mediterranean climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barles
Barles () is a Communes of France, commune in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of south-eastern France. The inhabitants of the commune are known as ''Barlatans'' or ''Barlatanes'' in French. Geography The village is located at an altitude of 987 m in the Bès valley some 30 km north by north-east of Digne-les-Bains and 30 km south by south-east of Gap, Hautes-Alpes, Gap. Access to the commune is by the D900A road from Verdaches in the east which passes through the village and continues south to Esclangon. The D7 road also comes from Auzet in the north-east and joins the D900A on the eastern border of the commune. Relief Barles is very compartmentalized, divided into valleys separated by high mountains and steep ridges. The Bès Valley links these valleys but, cut by Water gaps, it was not a means of travel for many decades and most travel was on foot and mule along mule tracks via the heights. Bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turriers
Turriers () is a commune in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department in southeastern France. Since 2016, it has been designated a key village in the UNESCO Geopark of Haute Provence because of its outstanding geological features, its rich biodiversity, and its historical interest. Population Turriers and the UNESCO Geopark of Haute Provence In 2001 UNESCO began its Geopark program, with the purpose of identifying areas of international geological significance in order to provide management that includes protection, education, and sustainable development. The first group of UNESCO Geoparks to be designated was in 2004 and Haute Provence was one of 17 European areas selected. Because of its geological, natural and cultural heritage, in 2016 Turriers was nominated as a key or heartland village of the Haute Provence Geopark. Residents and the press are in the process of collecting and publishing information and organizing events to bring attention to Turriers' role in the Geopa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authon, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence
Authon (; oc, Auton) is a commune in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of south-eastern France. The inhabitants of the commune are known as ''Authoniers'' or ''Authonières''. Geography Authon is located in the northern part of the Digne foothills, some 15 km north-east of Sisteron and 22 km north by north-west of Digne-les-Bains. Geology The commune is located on the eastern boundary of the ''Baronnies Orientales'' on Provençal limestone formations of the Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous periods (sedimentary rocks from a former Alpine Ocean) between three main geological formations of the Alps: *the Digne Nappe at the level of the Valavoire lobe: there is a thrust sheet or Nappe - i.e. a slab about 5000 m thick which was moved to the south-west during the Oligocene and at the end of the formation of the Alps. The lobes (or scales) correspond to the exposed edges to the west of the Nappe; *the Durance fault to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auzet
Auzet is a commune in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of south-eastern France. The inhabitants of the commune are known as ''Auzetans'' or ''Auzetanes''. Geography Auzet is located some 45 km north-east of Sisteron and 35 km west by south-west of Barcelonnette. Access to the commune is by the D7 road from Seyne in the north which passes through the length of the commune and the village and joins the D900A on the southern border of the commune. Apart from the village there are the hamlets of L'Infernet, L'Infernet Haut, and L'Infernet Bas north of the village. The commune is very rugged with snow-capped mountains and forested slopes with 1,168 hectares of forest. Numerous streams rise mostly in the north of the commune and flow south: the ''Grave'' river rises in the north of the commune and gathers countless tributaries as it flows south to join the ''Bés'' on the southern border; on the western side the ''Ravin de Gau' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus (organic matter). The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies ( marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detritus (geology)
Detritus (; adj. ''detrital'' ) is particles of rock derived from pre-existing rock through weathering and erosion.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p G-7 A fragment of detritus is called a clast.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p G-5 Detrital particles can consist of lithic fragments (particles of recognisable rock), or of monomineralic fragments (mineral grains). These particles are often transported through sedimentary processes into depositional systems such as riverbeds, lakes or the ocean, forming sedimentary successions. Diagenetic processes can transform these sediments into rock through cementation and lithification Lithification (from the Ancient Greek word ''lithos'' meaning 'rock' and the Latin-derived suffix ''-ific'') is the process in which sediments compact under pressure, expel connate fluids, and gradually become solid rock. Essentially, lithificatio ..., forming sedimentary rocks such as sandstone. These rocks can then in turn ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''olígos'', "few") and (''kainós'', "new"), and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major changes during the Oligocene included a global expansi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
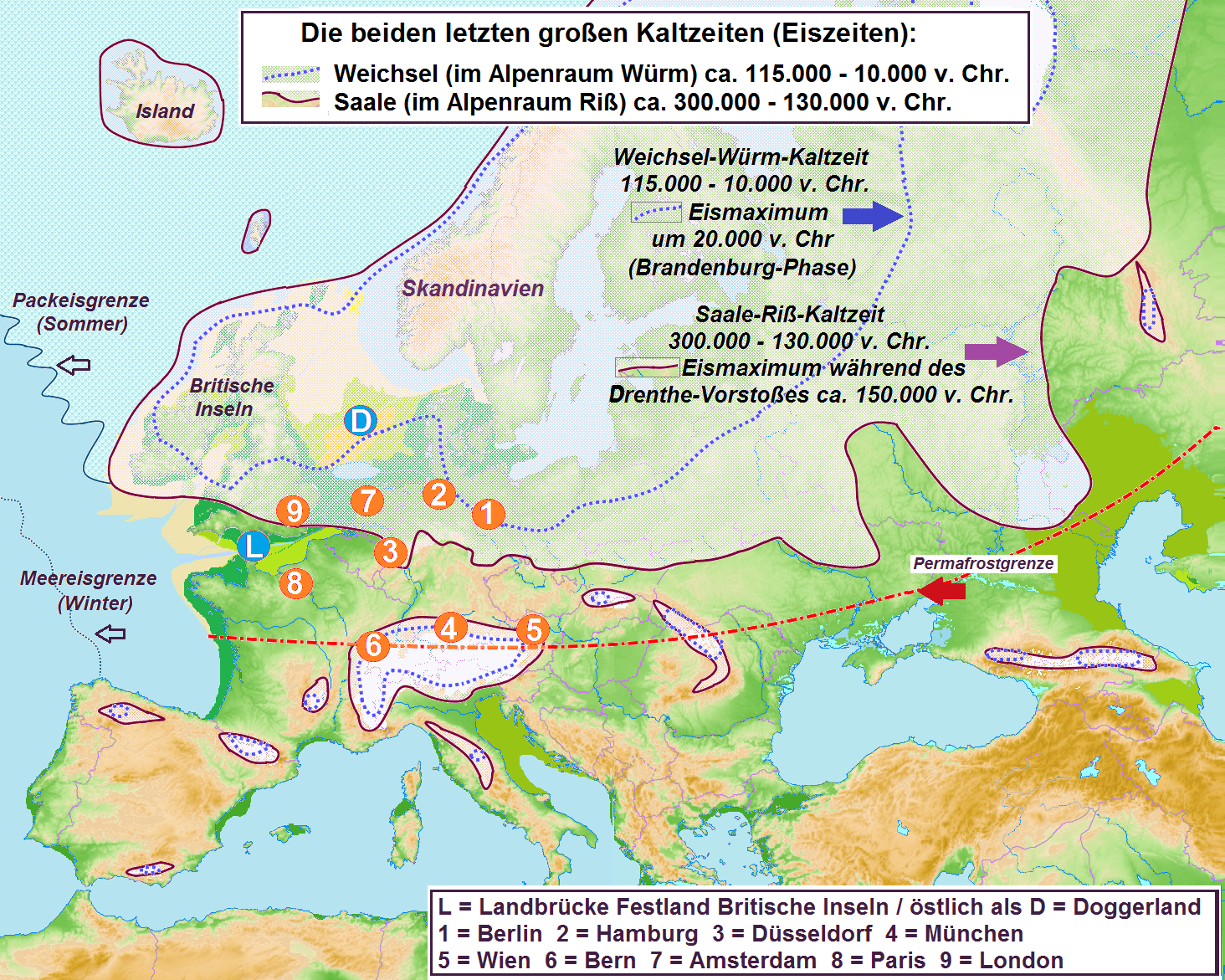
Riss Glaciation
The Riss glaciation, Riss Glaciation, Riss ice age, Riss Ice Age, Riss glacial or Riss Glacial (german: Riß-Kaltzeit, ', ' or (obsolete) ') is the second youngest glaciation of the Pleistocene epoch in the traditional, quadripartite glacial classification of the Alps. The literature variously dates it to between about 300,000 to 130,000 years ago and 347,000 to 128,000 years ago. It coincides with the glaciation of North Germany. The name goes back to and who named this cold period after the river in Upper Swabia in their three-volume work ' ("The Alps in the Ice Age") published between 1901 and 1909. Boundaries and division The Riss glaciation was defined by Penck and Brückner as the Lower (''Niedere'') or Younger Old Moraines and Old Terminal Moraines High Terraces (''Jüngere Altmoränen und Alt-Endmoränen-Hochterrassen''). The type locality lies near Biberach an der Riß where the end of the northeastern Rhine Glacier stood. Results gained from over a century of resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Würm Glaciation
The Würm glaciation or Würm stage (german: Würm-Kaltzeit or ''Würm-Glazial'', colloquially often also ''Würmeiszeit'' or ''Würmzeit''; cf. ice age), usually referred to in the literature as the Würm (often spelled "Wurm"), was the last glacial period in the Alpine region. It is the youngest of the major glaciations of the region that extended beyond the Alps themselves. Like most of the other ice ages of the Pleistocene epoch, it is named after a river, in this case the Würm in Bavaria, a tributary of the Amper. The Würm ice age can be dated to about 115,000 to 11,700 years ago, but sources differ about the dates, depending on whether the long transition phases between the glacials and interglacials (warmer periods) are allocated to one or other of those periods. The average annual temperatures during the Würm ice age in the Alpine Foreland were below −3 °C (today +7 °C). That has been determined from changes in the vegetation ( pollen analysis), as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |