|
Basal Veins
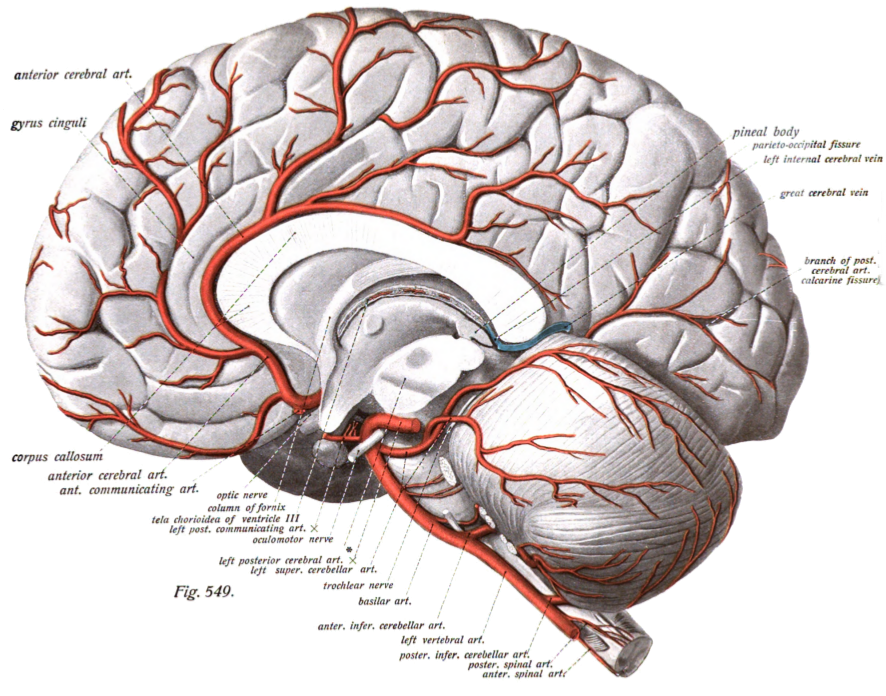
The basal vein is a vein in the brain. It is formed at the anterior perforated substance by the union of * (a) a ''small anterior cerebral vein'' which accompanies the anterior cerebral artery and supplies the medial surface of the frontal lobe by the fronto-basal vein. * (b) the ''deep middle cerebral vein'' (''deep Sylvian vein''), which receives tributaries from the insula and neighboring gyri, and runs in the lower part of the lateral cerebral fissure, and * (c) the ''inferior striate veins'', which leave the corpus striatum through the anterior perforated substance. The basal vein passes backward around the cerebral peduncle, and ends in the great cerebral vein; it receives tributaries from the interpeduncular fossa, the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle, the hippocampal gyrus, and the mid-brain The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choroid Plexus
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid. Structure Location There is a choroid plexus in each of the four ventricles. In the lateral ventricles it is found in the body, and continued in an enlarged amount in the atrium. There is no choroid plexus in the anterior horn. In the third ventricle there is a small amount in the roof that is continuous with that in the body, via the interventricular foramina, the channels that connect the lateral ventricles with the third ventricle. A choroid plexus is in part of the roof of the fourth ventricle. Microanatomy The chor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Cerebral Vein
The great cerebral vein is one of the large blood vessels in the skull draining the cerebrum of the brain. It is also known as the "vein of Galen", named for its discoverer, the Greek physician Galen. However, it is not the only vein with this eponym. Structure The great cerebral vein is considered one of the deep cerebral veins. Other deep cerebral veins are the internal cerebral veins, formed by the union of the superior thalamostriate vein and the superior choroid vein at the interventricular foramina. The internal cerebral veins can be seen on the superior surfaces of the caudate nuclei and thalami just under the corpus callosum. The veins at the anterior poles of the thalami merge posterior to the pineal gland to form the great cerebral vein. Most of the blood in the deep cerebral veins collects into the great cerebral vein. This comes from the inferior side of the posterior end of the corpus callosum and empties ie similarities, there are also differences between these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In contrast to veins, arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins are less muscular than arteries and are often closer to the skin. There are valves (called ''pocket valves'') in most veins to prevent backflow. Structure Veins are present throughout the body as tubes that carry blood back to the heart. Veins are classified in a number of ways, including superficial vs. deep, pulmonary vs. systemic, and large vs. small. * Superficial veins are those closer to the surface of the body, and have no corresponding arteries. *Deep veins are deeper in the body and have corresponding arteries. *Perforator veins drain from the superficial to the deep veins. These are usually referred to in the lower limbs and feet. *Communic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Perforated Substance
The anterior perforated substance is a part of the brain. It is bilateral. It is irregular and quadrilateral. It lies in front of the optic tract and behind the olfactory trigone. Structure The anterior perforated substance is bilateral. It lies in front of the optic tract. It lies behind the olfactory trigone, separated by the fissure prima. Medially and in front, it is continuous with the subcallosal gyrus. Laterally, it is bounded by the lateral stria of the olfactory tract, and is continued into the uncus. Its gray substance is confluent above with that of the corpus striatum, and is perforated anteriorly by numerous small blood vessels that supply such areas as the internal capsule. The anterior cerebral artery arises just below the anterior perforated substance. The middle cerebral artery passes through its lateral two thirds. Blood supply The anterior perforated substance is supplied by lenticulostriate arteries, which branch from the middle cerebral artery. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Cerebral Artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis. The left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery. Anterior cerebral artery syndrome refers to symptoms that follow a stroke occurring in the area normally supplied by one of the arteries. It is characterized by weakness and sensory loss in the lower leg and foot opposite to the lesion and behavioral changes. Structure The anterior cerebral artery is divided into 5 segments. Its smaller branches: the callosal (supracallosal) arteries are considered to be the A4 and A5 segments. *A1 originates from the internal carotid artery and extends to the ''anterior communicating artery'' (AComm). The ''anteromedial central'' (medial lent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes) within each hemisphere of the mammalian brain. The insulae are believed to be involved in consciousness and play a role in diverse functions usually linked to emotion or the regulation of the body's homeostasis. These functions include compassion, empathy, taste, perception, motor control, self-awareness, cognitive functioning, interpersonal experience, and awareness of homeostatic emotions such as hunger, pain and fatigue. In relation to these, it is involved in psychopathology. The insular cortex is divided into two parts: the anterior insula and the posterior insula in which more than a dozen field areas have been identified. The cortical area overlying the insula toward the lateral surface of the brain is the operculum (meaning ''lid''). The opercula are formed from parts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyri
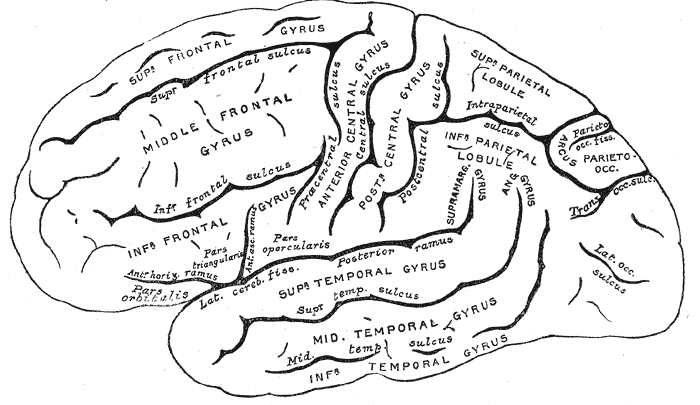
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. Structure The gyri are part of a system of folds and ridges that create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. Because the brain is confined to the skull, brain size is limited. Ridges and depressions create folds allowing a larger cortical surface area, and greater cognitive function, to exist in the confines of a smaller cranium. Development The human brain undergoes gyrification during fetal and neonatal development. In embryonic development, all mammalian brains begin as smooth structures derived from the neural tube. A cerebral cortex without surface convolutions is lissencephalic, meaning 'smooth-brained'. As development continues, gyri and sulci begin to take shape on the fetal brain, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Cerebral Fissure
In neuroanatomy, the lateral sulcus (also called Sylvian fissure, after Franciscus Sylvius, or lateral fissure) is one of the most prominent features of the human brain. The lateral sulcus is a deep fissure in each hemisphere that separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe. The insular cortex lies deep within the lateral sulcus. Anatomy The lateral sulcus divides both the frontal lobe and parietal lobe above from the temporal lobe below. It is in both hemispheres of the brain. The lateral sulcus is one of the earliest-developing sulci of the human brain. It first appears around the fourteenth gestational week. The insular cortex lies deep within the lateral sulcus. The lateral sulcus has a number of side branches. Two of the most prominent and most regularly found are the ascending (also called vertical) ramus and the horizontal ramus of the lateral fissure, which subdivide the inferior frontal gyrus. The lateral sulcus also contains the transverse tempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia. Functionally, the striatum coordinates multiple aspects of cognition, including both motor and action planning, decision-making, motivation, reinforcement, and reward perception. The striatum is made up of the caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus. The lentiform nucleus is made up of the larger putamen, and the smaller globus pallidus. Strictly speaking the globus pallidus is part of the striatum. It is common practice, however, to implicitly exclude the globus pallidus when referring to striatal structures. In primates, the striatum is divided into a ventral striatum, and a dorsal striatum, subdivisions that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Peduncle
The cerebral peduncles are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem. They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the ventral pons and contain the large ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) nerve tracts that run to and from the cerebrum from the pons. Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the cerebral cortex, the spinal cord and the cerebellum. The region includes the tegmentum, crus cerebri and pretectum. By this definition, the cerebral peduncles are also known as the basis pedunculi, while the large ventral bundle of efferent fibers is referred to as the cerebral crus or the pes pedunculi. The cerebral peduncles are located on either side of the midbrain and are the frontmost part of the midbrain, and act as the connectors between the rest of the midbrain and the thalamic nuclei and thus the cerebrum. As a whole, the cerebral peduncles assist in refining motor movements, learning new motor ski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Cerebral Vein
The great cerebral vein is one of the large blood vessels in the skull draining the cerebrum of the brain. It is also known as the "vein of Galen", named for its discoverer, the Greek physician Galen. However, it is not the only vein with this eponym. Structure The great cerebral vein is considered one of the deep cerebral veins. Other deep cerebral veins are the internal cerebral veins, formed by the union of the superior thalamostriate vein and the superior choroid vein at the interventricular foramina. The internal cerebral veins can be seen on the superior surfaces of the caudate nuclei and thalami just under the corpus callosum. The veins at the anterior poles of the thalami merge posterior to the pineal gland to form the great cerebral vein. Most of the blood in the deep cerebral veins collects into the great cerebral vein. This comes from the inferior side of the posterior end of the corpus callosum and empties ie similarities, there are also differences between these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |