|
Banking In Germany
Banking in Germany is a highly leveraged industry, as its average leverage ratio (assets divided by net worth) as of 11 October 2008 is 52 to 1 (while, in comparison, that of France is 28 to 1 and United Kingdom is 24 to 1); its short-term liabilities are equal to 60% of the German GDP or 167% of its national debt. History From the 15th century, banking families such as Fugger, Welser and Hochstetter were international mercantile bankers and venture capitalists. The oldest bank still in existence in Germany, Berenberg Bank, was founded by Dutch brothers Hans and Paul Berenberg in 1590, is still owned by the Berenberg family, and is the world's oldest or second oldest bank, depending on the exact definition. Market overview Germany has universal banking. The private customer mostly has to choose between three kinds of banks (German "three pillar system"): (A) private banks (including direct banks): *the largest ones are Deutsche Bank, Postbank (acquired by Deutsche Bank), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankfurter Altstadt Mit Skyline 2019
Frankfurter may refer to: * Various varieties of sausage ** Frankfurter Würstchen ** Frankfurter Rindswurst ** Vienna sausage, or also called a ''Frankfurter Würstel'' in Austria ** Hot dog, a fully cooked sausage, traditionally grilled or steamed * Frankfurter (surname) * Frankfurter, a resident of Frankfurt am Main, Germany ** Any of the major newspapers from the city: ''Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung'', ''Frankfurter Rundschau'', ''Frankfurter Neue Presse'' * Frankfurter, a resident of Frankfurt (Oder), Frankfurt an der Oder, Germany * Dr. Frank-N-Furter, the main antagonist in ''The Rocky Horror Show'' and its film counterpart ''The Rocky Horror Picture Show'' * Frankfurter, a display typeface designed in 1970 for Letraset See also * Frankfurt (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HypoVereinsbank
UniCredit Bank AG, better known under its brand name HypoVereinsbank (HVB), is the fifth-largest of the German financial institutions, ranked according to its total assets, and the fourth-largest bank in Germany according to the number of its employees. Its registered office is in Munich, and it is a member of the Cash Group. Since 2005, UniCredit Bank AG has been a subsidiary of UniCredit S.p.A., an Italian financial service provider headquartered in Milan. When the transfer resolution was entered in the commercial register in 2008, the equities of the minority shareholders were transferred to the principal shareholder, UniCredit S.p.A., as part of a squeeze-out. HVB thus became a wholly owned subsidiary and has not been listed on a stock exchange since that time. Operating in Germany, HVB mainly focuses on private clients business and corporate banking, customer-related capital market activities and private banking (also known as wealth management). As a mixed mortgage bank, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe
The ''Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe'' ("Savings Banks Financial Group") is a network of public banks that together form the largest financial services group in Germany and in all of Europe. Its name refers to local government-controlled savings banks that are known in German as , plural . Its activity is overwhelmingly located in Germany. History The first savings banks in Germany were founded in the 18th century in its major trading cities. One of the first institutions with the business model of modern savings banks was the ''Ersparungscasse der Hamburgischen Allgemeinen Versorgungsanstalt'' in Hamburg in 1778. Founders were rich merchants, clerks and academics. They intended to develop solutions for people with low income to save small sums of money and to support business start-ups. In 1801 the first savings bank with a municipal guarantor was founded in Göttingen to fight poverty. In 1838, Prussia adopted the first savings banks legislation (), which subsequently served as a mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landesbank
In German-speaking jurisdictions, ''Landesbank'' (plural ), , generally refers to a bank operating within a territorial subdivision () that has autonomy but not full sovereignty. It is occasionally translated as "provincial bank". Austria-Hungary In the Austro-Hungarian Empire under the rule of the Habsburg monarchy, were government-sponsored banks established in some of the kingdoms and lands of the crown: * '' Landesbank des Königreichs Galizien und Lodomerien mit dem Grossherzogtum Krakau'', est. 1883 in Lemberg (now Lviv) for the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria and the Grand Duchy of Kraków * '' Landesbank des Königreiches Böhmen'', est. 1890 in Prague for the Kingdom of Bohemia * '' Landesbank für Bosnien und Herzegowina'', est. 1895 in Sarajevo for Bosnia and Herzegovina under Austro-Hungarian rule * ''Bukowinaer Landesbank'', est. 1905 in Czernowitz (now Chernivtsi) for the Duchy of Bukovina * ''Kroatische Landesbank'', est. 1909 in Osijek for the Kingdom of Croati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparkasse (Germany)
The ''Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe'' ("Savings Banks Financial Group") is a network of public banks that together form the largest financial services group in Germany and in all of Europe. Its name refers to local government-controlled savings banks that are known in German as , plural . Its activity is overwhelmingly located in Germany. History The first savings banks in Germany were founded in the 18th century in its major trading cities. One of the first institutions with the business model of modern savings banks was the ''Ersparungscasse der Hamburgischen Allgemeinen Versorgungsanstalt'' in Hamburg in 1778. Founders were rich merchants, clerks and academics. They intended to develop solutions for people with low income to save small sums of money and to support business start-ups. In 1801 the first savings bank with a municipal guarantor was founded in Göttingen to fight poverty. In 1838, Prussia adopted the first savings banks legislation (), which subsequently served as a mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savings Bank
A savings bank is a financial institution whose primary purpose is accepting savings account, savings deposits and paying interest on those deposits. History of banking, They originated in Europe during the 18th century with the aim of providing access to Wealth, savings products to all levels in the population. Often associated with social good, these early banks were often designed to encourage low-income people to Saving, save money and have access to banking services. They were set up by governments or by socially committed groups or organisations such as with credit unions. The structure and legislation took many different forms in different countries over the 20th century. Savings banks and Savings and loan association, savings-and-loans are often confused. The original function of savings banks to service consumers was limited to savings. Savings banks invested in Government debt, government and Corporate bond, corporate debt. Savings and loan associations had a dual p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Bank
A public bank is a bank, a financial institution, in which a state, municipality, or public actors are the owners. It is an enterprise under government control.Banque publique : une entreprise bancaire qui dépend de l’État - ComprendreChoisir.com Prominent among current public banking models are the Bank of North Dakota, the in Germany, and many nations’ postal bank systems. Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Cooperative Financial Group
The German Cooperative Financial Group, german: Genossenschaftliche FinanzGruppe Volksbanken Raiffeisenbanken, sometimes referred to in English as "Volksbanken Raiffeisenbanken Cooperative Financial Network", is a major cooperative banking network in Germany that includes local banks named Volksbanken ("people's banks") and Raiffeisenbanken ("Raiffeisen banks"), the latter in tribute to 19th-century cooperative movement pioneer Friedrich Wilhelm Raiffeisen. The Cooperative Group represents one of the three "pillars" of Germany's banking sector, the other two being, respectively, the of public banks, and the commercial banking sector represented by the Association of German Banks. The Bundesverband der Deutschen Volksbanken und Raiffeisenbanken (BVR) is the nationwide representative body of the Cooperative Financial Group. It operates under the Deutscher Genossenschafts- und Raiffeisenverband, the umbrella organization of the German cooperative movement. History Founders' era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DZ Bank
DZ Bank AG () is the second largest bank in Germany by asset size and the central institution for around 800 cooperative banks and their around 8,500 branch offices. Within the German Cooperative Financial Group, which is one of Germany's largest private sector financial service organizations, DZ Bank functions both as a central institution and as a corporate and investment bank. DZ Bank is an acronym for Deutsche Zentral-Genossenschaftsbank (literally "German Central Cooperative Bank"). As a holding, the DZ Bank Group defines itself primarily as a service provider for local cooperative banks and their 30 million or so clients. The DZ Bank Group includes: DVB Bank, a transportation finance bank; Bausparkasse Schwäbisch Hall, a building society; DZ HYP (), a provider of commercial real estate finance; DZ Privatbank Gruppe; R+V Versicherung, an insurance company; TeamBank, a provider of consumer finance; Union Investment Group, an asset management company; VR Leasing; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparda-Bank
The Sparda-Banks in Germany are eleven cooperative banks which are consolidated in the Verband der Sparda-Banken e. V. (Union of Sparda-Banks). Traditionally they are specialized in the retail banking business. The eleven, legally independent banks operate according to the regional principle, which means that each bank is responsible for a set business area and only accepts customers from that area. Development The oldest Sparda-Bank was founded on 6 May 1896 as Spar- und Vorschuss-Verein der badischen Eisenbahn beamten (Savings and Imprest Association of the Baden Railroad Officials) in Karlsruhe. Based on this model equal cooperatives were founded in other places, which, in the spring of 1906, consolidated in the Revisionsverband der Eisenbahn-Spar- und Darlehnskassen (Revision Federation of the Railroad Savings and Loan Associations) in Kassel. In 1969 the railroad savings banks were opened for staff of other public services and in 1974 for all employees (steady income in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volksbanken Und Raiffeisenbanken
The German Cooperative Financial Group, german: Genossenschaftliche FinanzGruppe Volksbanken Raiffeisenbanken, sometimes referred to in English as "Volksbanken Raiffeisenbanken Cooperative Financial Network", is a major cooperative banking network in Germany that includes local banks named Volksbanken ("people's banks") and Raiffeisenbanken ("Raiffeisen banks"), the latter in tribute to 19th-century cooperative movement pioneer Friedrich Wilhelm Raiffeisen. The Cooperative Group represents one of the three "pillars" of Germany's banking sector, the other two being, respectively, the of public banks, and the commercial banking sector represented by the Association of German Banks. The Bundesverband der Deutschen Volksbanken und Raiffeisenbanken (BVR) is the nationwide representative body of the Cooperative Financial Group. It operates under the Deutscher Genossenschafts- und Raiffeisenverband, the umbrella organization of the German cooperative movement. History Founders' era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
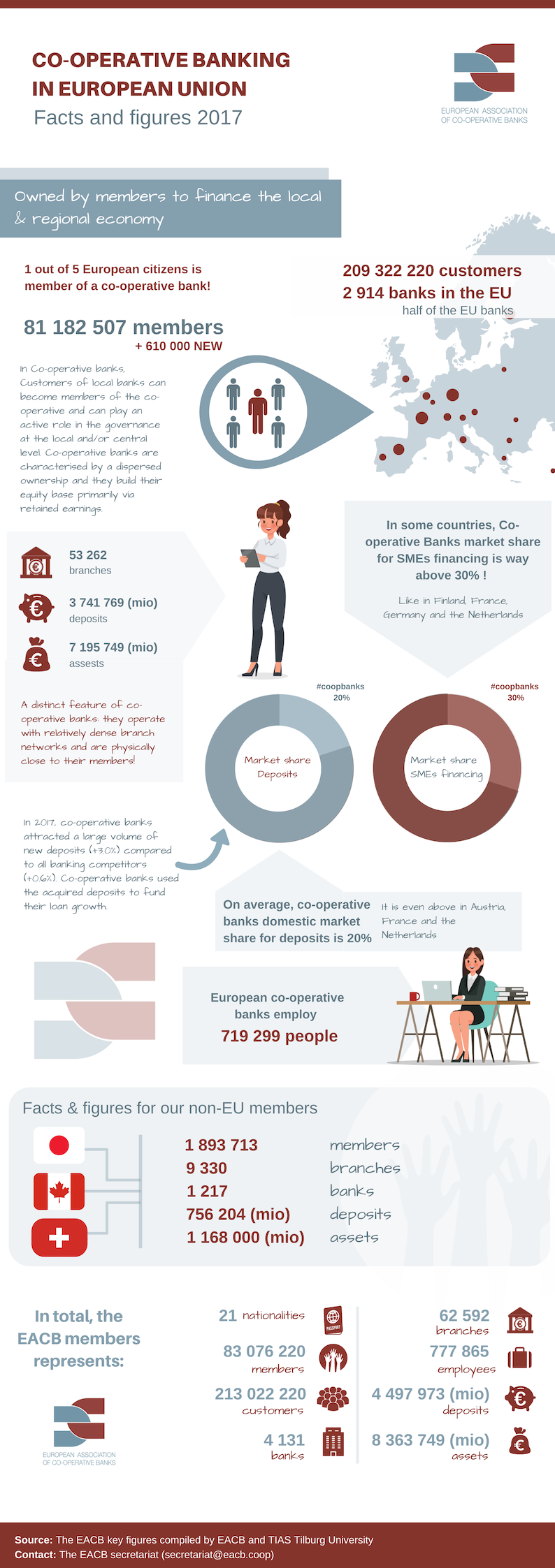
Cooperative Banking
Cooperative banking is retail and commercial banking organized on a cooperative basis. Cooperative banking institutions take deposits and lend money in most parts of the world. Cooperative banking, as discussed here, includes retail banking carried out by credit unions, mutual savings banks, building societies and cooperatives, as well as commercial banking services provided by mutual organizations (such as cooperative federations) to cooperative businesses. A 2013 report by ILO concluded that cooperative banks outperformed their competitors during the financial crisis of 2007–2008. The cooperative banking sector had 20% market share of the European banking sector, but accounted for only 7% of all the write-downs and losses between the third quarter of 2007 and first quarter of 2011. Cooperative banks were also over-represented in lending to small and medium-sized businesses in all of the 10 countries included in the report. Credit unions in the US had five times lower failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |