|
Ballistic Table
A ballistic table or ballistic chart is a tool which predicts the trajectory of a projectile, and is used to compensate for physical effects in order to increase the probability of the projectile reaching the intended target. Ballistic tables are used in hunting, sport shooting, military and scientific applications. Corrections in ballistic tables are given relative to a zero range. Ballistic charts are often given in angular measurements, with units in either milliradians (mil) or minutes of arc (moa). The tables are usually generated using specifically designed computer programs built on mathematical functions, known as ballistic calculators. The number of inputs to the ballistic calculator can sometimes vary depended on the specific generator, or the user may choose to only input certain variables. For example, a very simple drop table can be made using inputs for the sight adjustment value (in mil or moa), the zero range, intended target ranges, muzzle velocity, caliber, bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Table For 7
Ballistics may refer to: Science * Ballistics, the science that deals with the motion, behavior, and effects of projectiles ** Forensic ballistics, the science of analyzing firearm usage in crimes ** Internal ballistics, the study of the processes accelerating a projectile ** Transition ballistics, the study of the projectile's behavior when it leaves the barrel ** External ballistics, the study of the passage of the projectile through space or the air ** Terminal ballistics, the study of the interaction of a projectile with its target * Ballistic conduction, conduction of electricity with negligible charge scattering * Ballistic movement of muscles in an animal Combat * Ballistic missile, a missile that follows a sub-orbital flightpath * Ballistic knife, a specialized combat knife with a detachable, self-propelled blade * Ballistic shield, a shield meant to protect the user from bullets Arts and media Comics * Ballistic (Image Comics), a comic character of Top Cow Produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Function
In mathematics, a function from a set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words map, mapping, transformation, correspondence, and operator are often used synonymously. The set is called the domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function.Codomain ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'Codomain. ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics''/ref> The earliest known approach to the notion of function can be traced back to works of Persian mathematicians Al-Biruni and Sharaf al-Din al-Tusi. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectiles
A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found in warfare and sports (for example, a thrown baseball, kicked football, fired bullet, shot arrow, stone released from catapult). In ballistics mathematical equations of motion are used to analyze projectile trajectories through launch, flight, and impact. Motive force Blowguns and pneumatic rifles use compressed gases, while most other guns and cannons utilize expanding gases liberated by sudden chemical reactions by propellants like smokeless powder. Light-gas guns use a combination of these mechanisms. Railguns utilize electromagnetic fields to provide a constant acceleration along the entire length of the device, greatly increasing the muzzle velocity. Some projectiles provide propulsion during flight by means of a rocket engine or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Ballistics
External ballistics or exterior ballistics is the part of ballistics that deals with the behavior of a projectile in flight. The projectile may be powered or un-powered, guided or unguided, spin or fin stabilized, flying through an atmosphere or in the vacuum of space, but most certainly flying under the influence of a gravitational field. Gun-launched projectiles may be unpowered, deriving all their velocity from the propellant's ignition until the projectile exits the gun barrel. However, exterior ballistics analysis also deals with the trajectories of rocket-assisted gun-launched projectiles and gun-launched rockets; and rockets that acquire all their trajectory velocity from the interior ballistics of their on-board propulsion system, either a rocket motor or air-breathing engine, both during their boost phase and after motor burnout. External ballistics is also concerned with the free-flight of other projectiles, such as balls, arrows etc. Forces acting on the projectile W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Range Shooting
Long range shooting is a collective term for shooting disciplines where the distance to target is significant enough that shooter has to put effort into calculating various ballistic factors, especially in regards to the deviating effects of gravity and wind. While shooting at shorter ranges, a shooter only has to slightly adjust the sights to compensate for limited bullet drop at most, but when the range is extended, wind drift will be the first factor affecting precision to the extent that it must be taken into serious account. Some would argue that long range shooting starts where assessment of wind, distance and various atmospheric conditions are equally important for the results as pure shooting skills - meaning that even if one conducts a technically perfect shot, the shooter will miss the target because of incorrect calculations, neglecting to take some elements into consideration, or merely due to unpredictable downrange conditions. It is widely accepted within in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Coefficient
In ballistics, the ballistic coefficient (BC, ''C'') of a body is a measure of its ability to overcome air resistance in flight. It is inversely proportional to the negative acceleration: a high number indicates a low negative acceleration—the drag on the body is small in proportion to its mass. BC can be expressed with the units kilograms per square meter (kg/m2) or pounds per square inch (lb/in2) (where 1 lb/in2 corresponds to ). Formulas General :C_\text = \frac = \frac where: *''C''b,Physics, ballistic coefficient as used in physics and engineering *''m'', mass *''A'', cross-sectional area *''C''d, drag coefficient *\rho, density *\ell, characteristic body length Ballistics The formula for calculating the ballistic coefficient for small and large arms projectiles ''only'' is as follows: :C_\text = \frac where: *''C''b,Projectile, ballistic coefficient as used in point mass trajectory from the Siacci method (less than 20 degrees). *''m'', mass of bullet *''d'', mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
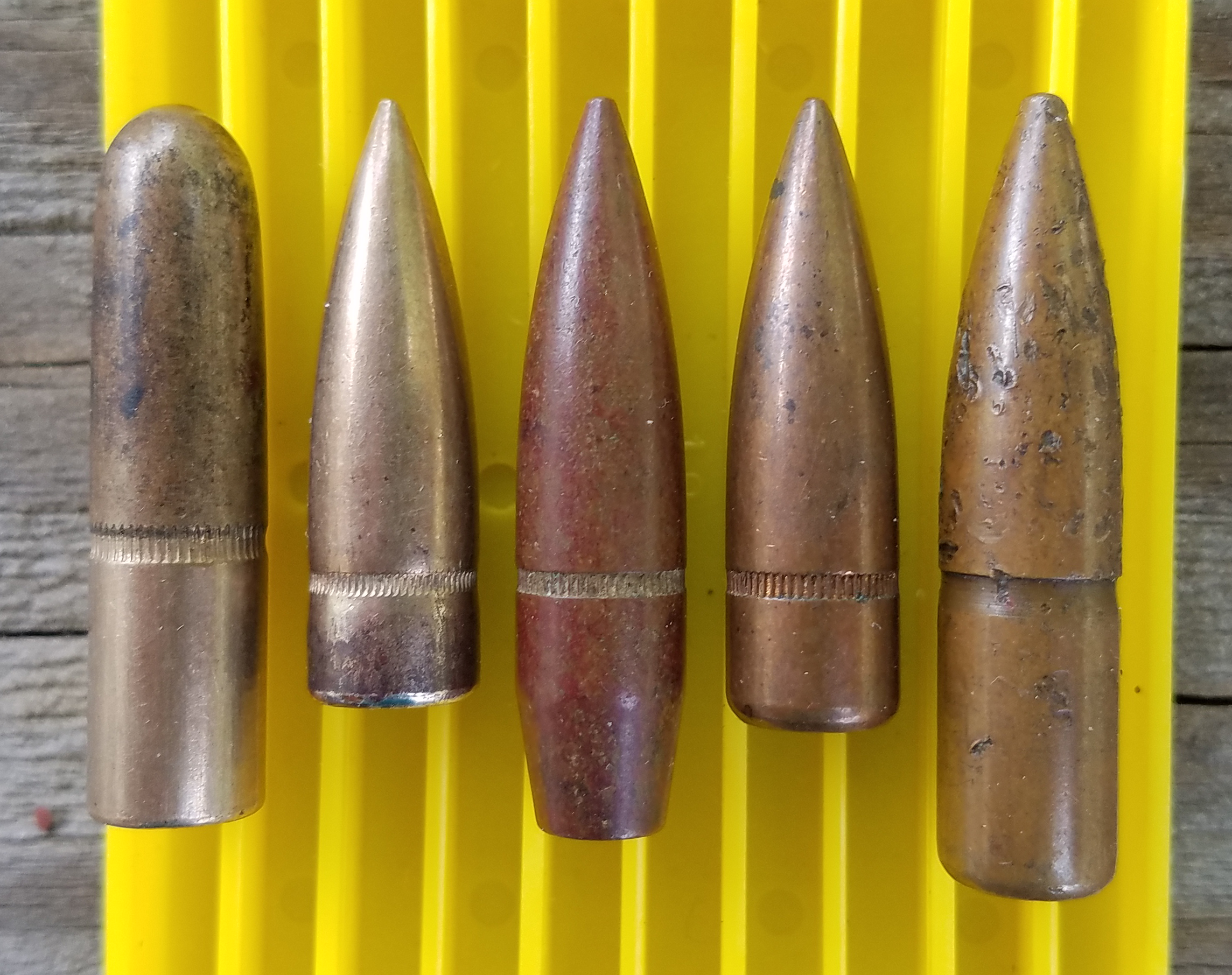
Caliber
In guns, particularly firearms, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel Gauge (firearms) , bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the finished bore matches that specification. It is measured in inches or in millimetres, millimeters. In the United States it is expressed in hundredths of an inch; in the United Kingdom in thousandths; and elsewhere in millimeters. For example, a "45 caliber" firearm has a barrel diameter of roughly . Barrel diameters can also be expressed using metric dimensions. For example, a "9 mm pistol" has a barrel diameter of about 9 millimeters. Since metric and US customary units do not convert evenly at this scale, metric conversions of caliber measured in decimal inches are typically approximations of the precise specifications in non-metric units, and vice versa. In a rifling , rifled barrel, the distance is measured between opposing Rifling#C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzzle Velocity
Muzzle velocity is the speed of a projectile (bullet, pellet, slug, ball/shots or shell) with respect to the muzzle at the moment it leaves the end of a gun's barrel (i.e. the muzzle). Firearm muzzle velocities range from approximately to in black powder muskets, to more than in modern rifles with high-velocity cartridges such as the .220 Swift and .204 Ruger, all the way to for tank guns firing kinetic energy penetrator ammunition. To simulate orbital debris impacts on spacecraft, NASA launches projectiles through light-gas guns at speeds up to . Projectile velocity For projectiles in unpowered flight, its velocity is highest at leaving the muzzle and drops off steadily because of air resistance. Projectiles traveling less than the speed of sound (about in dry air at sea level) are ''subsonic'', while those traveling faster are ''supersonic'' and thus can travel a substantial distance and even hit a target before a nearby observer hears the "bang" of the shot. Projec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components. A computer program in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be translated to machine instructions using the language's compiler. ( Assembly language programs are translated using an assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within the language's interpreter. If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system loads it into memory and starts a process. The central processing unit will soon switch to this process so it can fetch, decode, and then execute each machine instruction. If the source code is requested for execution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trajectory
A trajectory or flight path is the path that an object with mass in motion follows through space as a function of time. In classical mechanics, a trajectory is defined by Hamiltonian mechanics via canonical coordinates; hence, a complete trajectory is defined by position and momentum, simultaneously. The mass might be a projectile or a satellite. For example, it can be an orbit — the path of a planet, asteroid, or comet as it travels around a central mass. In control theory, a trajectory is a time-ordered set of states of a dynamical system (see e.g. Poincaré map). In discrete mathematics, a trajectory is a sequence (f^k(x))_ of values calculated by the iterated application of a mapping f to an element x of its source. Physics of trajectories A familiar example of a trajectory is the path of a projectile, such as a thrown ball or rock. In a significantly simplified model, the object moves only under the influence of a uniform gravitational force field. This can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minutes Of Arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milliradian
A milliradian ( SI-symbol mrad, sometimes also abbreviated mil) is an SI derived unit for angular measurement which is defined as a thousandth of a radian (0.001 radian). Milliradians are used in adjustment of firearm sights by adjusting the angle of the sight compared to the barrel (up, down, left, or right). Milliradians are also used for comparing shot groupings, or to compare the difficulty of hitting different sized shooting targets at different distances. When using a scope with both mrad adjustment and a reticle with mrad markings (called an "mrad/mrad scope"), the shooter can use the reticle as a ruler to count the number of mrads a shot was off-target, which directly translates to the sight adjustment needed to hit the target with a follow up shot. Optics with mrad markings in the reticle can also be used to make a range estimation of a known size target, or vice versa, to determine a target size if the distance is known, a practice called "milling". Milliradian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)