|
Back (horse)
The back describes the area of horse anatomy where the saddle goes, and in popular usage extends to include the loin or lumbar region behind the thoracic vertebrae that also is crucial to a horse's weight-carrying ability. These two sections of the vertebral column beginning at the withers, the start of the thoracic vertebrae, and extend to the last lumbar vertebra. Because horses are ridden by humans, the strength and structure of the horse's back is critical to the animal's usefulness. The thoracic vertebrae are the true "back" vertebral structures of the skeleton, providing the underlying support of the saddle, and the lumbar vertebrae of the loin provide the ''coupling'' that joins the back to the hindquarters. Integral to the back structure is the rib cage, which also provides support to the horse and rider. A complex design of bone, muscle, tendons and ligaments all work together to allow a horse to support the weight of a rider. Anatomy of the back The structure of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
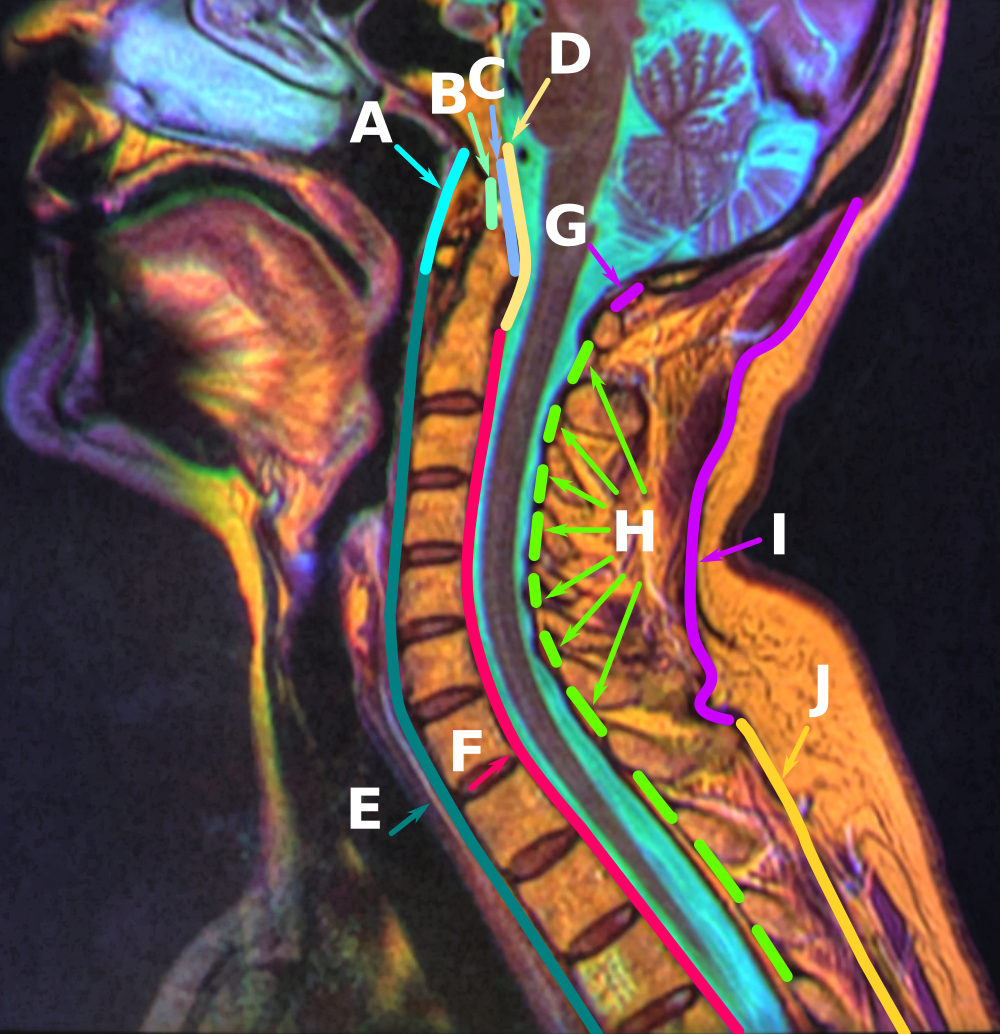
Nuchal Ligament
The nuchal ligament is a ligament at the back of the neck that is continuous with the supraspinous ligament. Structure The nuchal ligament extends from the external occipital protuberance on the skull and median nuchal line to the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra in the lower part of the neck. From the anterior border of the nuchal ligament, a fibrous lamina is given off. This is attached to the posterior tubercle of the atlas, and to the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae, and forms a septum between the muscles on either side of the neck. The trapezius and splenius capitis muscle attach to the nuchal ligament. Function It is a tendon-like structure that has developed independently in humans and other animals well adapted for running. In some four-legged animals, particularly ungulates, the nuchal ligament serves to sustain the weight of the head. Clinical significance In Chiari malformation treatment, decompression and duraplasty with a harvest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacral Vertebrae
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human body, human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the vertebral column, spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30. The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, between the two Ilium (bone), wings of the pelvis. It forms joints with four other bones. The two projections at the sides of the sacrum are called the alae (wings), and articulate with the Ilium (bone), ilium at the L-shaped sacroiliac joints. The upper part of the sacrum connects with the last lumbar vertebrae, lumbar vertebra (L5), and its lower part with the coccyx (tailbone) via the sacral and coccygeal cornua. The sacrum has three different surfaces which are shaped to accommodate surrounding pelvic structures. Overall it is wikt:concave, concave (curved upon itself). The base of the sacrum, the broadest and uppermost part, is tilted forward as the sacral promontory internally. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poll (livestock)
The poll is a name of the part of an animal's head, alternatively referencing a point immediately behind or right between the ears. This area of the anatomy is of particular significance for the horse. Specifically, the "poll" refers to the occipital protrusion at the back of the skull. However, in common usage, many horsemen refer to the poll joint, between the atlas (C1) and skull as the poll. The area at the joint has a slight depression, and is a sensitive location. Thus, because the crownpiece of a bridle passes over the poll joint, a rider can indirectly exert pressure on the horse's poll by means of the reins, bit, and bridle. Importance of the poll in riding The poll is especially important in riding, as ''correct'' flexion at the poll joint is a sign that the horse is properly on the bit. Over-flexion, with the poll lowered and the neck bent at a cervical vertebra farther down the neck, is usually a sign that the horse is either evading contact or that the rider is tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraspinous Ligament
The supraspinous ligament, also known as the supraspinal ligament, is a ligament found along the vertebral column. Structure The supraspinous ligament connects the tips of the spinous processes from the seventh cervical vertebra to the sacrum. Above the seventh cervical vertebra, the supraspinous ligament is continuous with the nuchal ligament. Between the spinous processes it is continuous with the interspinous ligaments. It is thicker and broader in the lumbar than in the thoracic region, and intimately blended, in both situations, with the neighboring fascia. The most superficial fibers of this ligament extend over three or four vertebrae; those more deeply seated pass between two or three vertebrae while the deepest connect the spinous processes of neighboring vertebrae. Development Function The supraspinous ligament, along with the posterior longitudinal ligament, interspinous ligaments and ligamentum flavum, help to limit hyperflexion of the vertebral column. Clinical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal External Oblique Muscle
The abdominal external oblique muscle (also external oblique muscle, or exterior oblique) is the largest and outermost of the three flat abdominal muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen. Structure The external oblique is situated on the lateral and anterior parts of the abdomen. It is broad, thin, and irregularly quadrilateral, its muscular portion occupying the side, its aponeurosis the anterior wall of the abdomen. In most humans (especially females), the oblique is not visible, due to subcutaneous fat deposits and the small size of the muscle. It arises from eight fleshy digitations, each from the external surfaces and inferior borders of the fifth to twelfth ribs (lower eight ribs). These digitations are arranged in an oblique line which runs inferiorly and anteriorly, with the upper digitations being attached close to the cartilages of the corresponding ribs, the lowest to the apex of the cartilage of the last rib, the intermediate ones to the ribs at some distance from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercostal Muscle
Intercostal muscles are many different groups of muscles that run between the ribs, and help form and move the chest wall. The intercostal muscles are mainly involved in the mechanical aspect of breathing by helping expand and shrink the size of the chest cavity. Structure There are three principal layers; #External intercostal muscles also known as intercostalis externus aid in quiet and forced inhalation. They originate on ribs 1–11 and have their insertion on ribs 2–12. The external intercostals are responsible for the elevation of the ribs and bending them more open, thus expanding the transverse dimensions of the thoracic cavity. The muscle fibers are directed downwards, forwards and medially in the anterior part. #Internal intercostal muscles also known as intercostalis internus aid in forced expiration (quiet expiration is a passive process). They originate on ribs 2–12 and have their insertions on ribs 1–11.Their fibers pass anterior and superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longissimus Dorsi
The longissimus ( la, the longest one) is the muscle lateral to the semispinalis muscles. It is the longest subdivision of the erector spinae muscles that extends forward into the transverse processes of the posterior cervical vertebrae. Structure Longissimus thoracis et lumborum The longissimus thoracis et lumborum is the intermediate and largest of the continuations of the erector spinae. In the lumbar region (longissimus lumborum), where it is as yet blended with the iliocostalis, some of its fibers are attached to the whole length of the posterior surfaces of the transverse processes and the accessory processes of the lumbar vertebrae, and to the anterior layer of the lumbodorsal fascia. In the thoracic region (longissimus thoracis), it is inserted, by rounded tendons, into the tips of the transverse processes of all the thoracic vertebrae, and by fleshy processes into the lower nine or ten ribs between their tubercles and angles. Longissimus cervicis The longissimus cerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
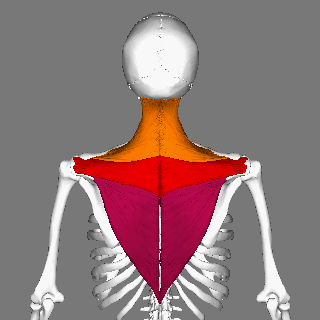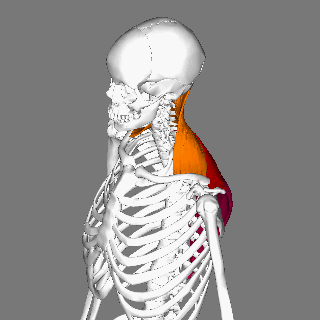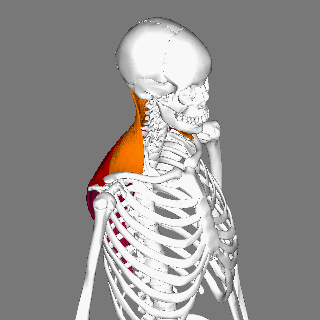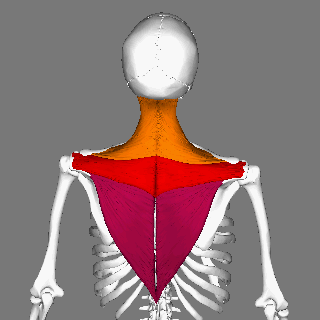
Trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Similarly, the term "tri-axle back plate" was historically used to describe the trapezius muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |