|
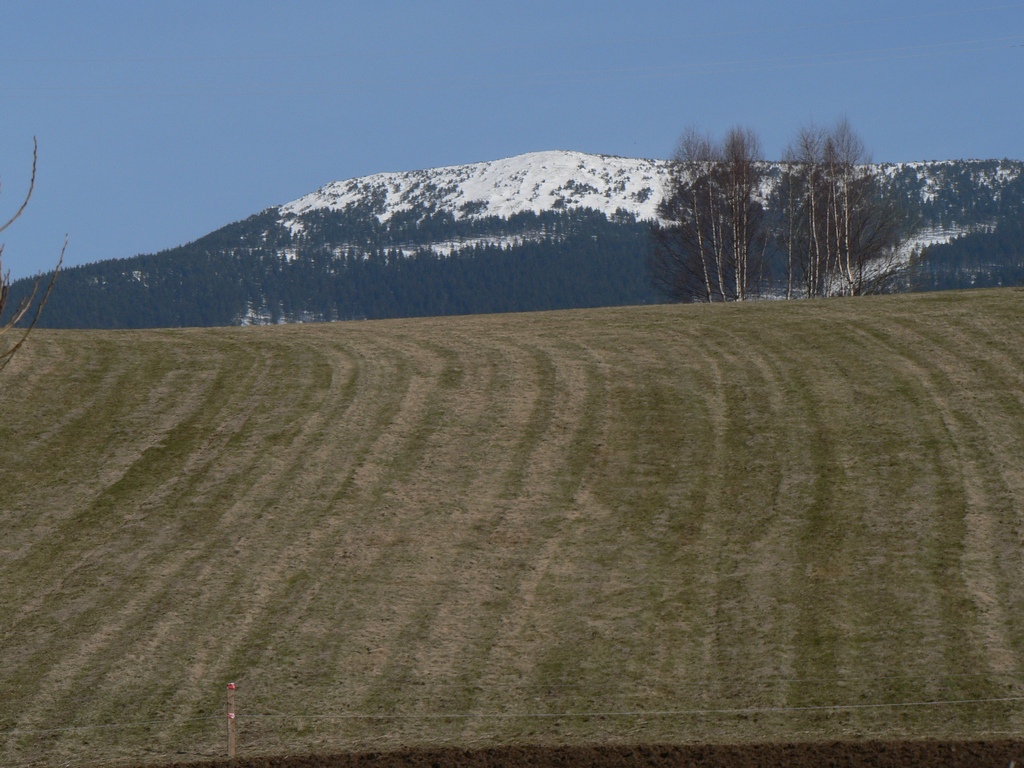
Břidličná Hora
Břidličná hora () is a mountain in the Hrubý Jeseník mountain range in the Czech Republic. It has an elevation of Height above mean sea level, above sea level. It is located in the municipality of Vernířovice. The peak is approximately 6 km southwest of the summit of Praděd mountain, situated on its main ridge between the summits of Jelení hřbet and Pecný. History Airplane crash A German military bomber, the Heinkel He 111, of the ''Luftwaffe,'' with a crew of likely three members, crashed into the mountain (below the main ridge) on its western slope at an elevation of approximately 1,300 m above sea level during poor weather conditions, probably in 1942 or 1943. The plane completely burned up upon impact. After receiving information about the crash, the German gendarmerie removed the larger pieces of the wreckage, but numerous smaller fragments remained and were later discovered at the site. Despite extensive archival search efforts, it was not possible to identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernířovice
Vernířovice () is a municipality and village in Šumperk District in the Olomouc Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 200 inhabitants. Vernířovice lies approximately north-east of Šumperk, north of Olomouc, and east of Prague Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P .... Demographics References External links * Villages in Šumperk District {{Olomouc-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Couloir
A couloir (, "passage" or "corridor") is a narrow gully with a steep gradient in a mountainous terrain.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, p. 121. . Geology A couloir may be a seam, scar, or fissure, or vertical crevasse in an otherwise solid mountain mass. Though often hemmed in by sheer cliff walls, couloirs may also be less well-defined, and may often simply be a line of broken talus or scree ascending the mountainside and bordered by trees, rocks or other natural features. Couloirs are especially significant in winter months when they may be filled in with snow or ice, and become much more noticeable than in warmer months when most of the snow and ice may recede. These physical features make the use of couloirs popular for both mountaineering and extreme skiing. References {{reflist Landforms Mountains Montane ecology Geographical terminology in mountaineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 30 to 60 known taxa of which 11 are on the IUCN 2011 Red List of Threatened Species. They are typically short-lived pioneer species and are widespread in the Northern Hemisphere, particularly in northern areas of temperate climates and in boreal climates. Birch wood is used for a wide range of purposes. Description Birch species are generally small to medium-sized trees or shrubs, mostly of northern temperate and boreal climates. The simple leaves are alternate, singly or doubly serrate, feather-veined, petiolate and stipulate. They often appear in pairs, but these pairs are really borne on spur-like, two-leaved, lateral branchlets. The fruit is a small samara, although the wings may be obscure in some species. They differ from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
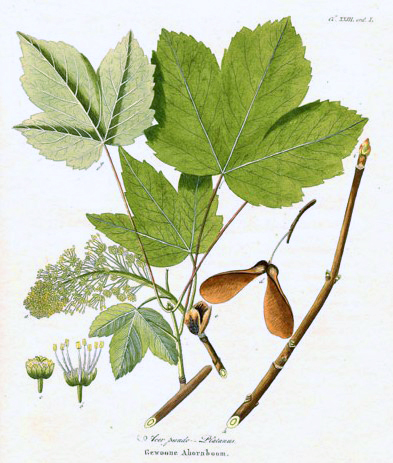
Acer Pseudoplatanus
''Acer pseudoplatanus'', known as the sycamore in the British Isles and as the sycamore maple in the United States, is a species of maple native to Central Europe and Western Asia. It is a large deciduous, broad-leaved tree, tolerant of wind and coastal exposure. Although native to an area ranging from France eastward to Ukraine, northern Turkey and the Caucasus, and southward to the mountains of Italy and northern Iberia, the sycamore establishes itself easily from seed and was introduced to the British Isles by 1500. It is now Naturalisation (biology), naturalised there and in other parts of Europe, North America, Australia and New Zealand, where it may become an invasive species. The sycamore can grow to a height of about and the branches form a broad, rounded Crown (botany), crown. The Bark (botany), bark is grey, smooth when young and later flaking in irregular patches. The leaves grow on long Petiole (botany), leafstalks and are large and List of botanical terms#palmate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larix Decidua
''Larix decidua'', the European larch, is a species of larch native to the mountains of central Europe, in the Alps and Carpathian Mountains, with small disjunct lowland populations in northern Poland. Its life span has been confirmed to be close to 1000 years, with ages of around 2000 years likely. Description ''Larix decidua'' is a medium-size to large deciduous Pinophyta, coniferous tree reaching 25–45 m tall, with a trunk up to 1.5 m diameter (exceptionally, to 53.8 m tall and 11.20 m girth [3.56 m diameter]). The crown is conic when young, becoming broad and often irregular with age; the main branches are level to upswept, with the side branches often pendulous. The shoots are dimorphic, with growth divided into long shoots (typically 10–50 cm long) and bearing several buds, and short shoots only 1–2 mm long with only a single bud. The leaf, leaves are needle-like, light green, 2–4 cm long which turn bright yellow before they fall in the autumn, leavin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fagus Sylvatica
''Fagus sylvatica'', the European beech or common beech, is a large, graceful deciduous tree in the Fagaceae, beech family with smooth silvery-gray bark, large leaf area, and a short trunk with low branches. Description ''Fagus sylvatica'' is a large tree, capable of reaching heights of up to tall and trunk diameter, though more typically tall and up to trunk diameter. A 10-year-old sapling will stand about tall. Undisturbed, the European beech has a lifespan of 300 years; one tree at the Valle Cervara site was more than 500 years old—the oldest known in the northern hemisphere. In cultivated forest stands trees are normally harvested at 80–120 years of age. 30 years are needed to attain full maturity (as compared to 40 for Fagus grandifolia, American beech). Like most trees, its form depends on the location: in forest areas, ''F. sylvatica'' grows to over , with branches being high up on the trunk. In open locations, it will become much shorter (typically ) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picea Abies
''Picea abies'', the Norway spruce or European spruce, is a species of spruce native to Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It has branchlets that typically hang downwards, and the largest cones of any spruce, 9–17 cm long. It is very closely related to the Siberian spruce (''Picea obovata''), which replaces it east of the Ural Mountains, and with which it hybridizes freely. The Norway spruce has a wide distribution for it being planted for its wood, and is the species used as the main Christmas tree in several countries around the world. It was the first gymnosperm to have its genome sequenced. The Latin binomial nomenclature, specific epithet ''abies'' means "like ''Abies'', Fir tree". Description Norway spruce is a large, fast-growing evergreen coniferous tree growing tall and with a trunk diameter of 1 to 1.5 m. It can grow fast when young, up to 1 m per year for the first 25 years under good conditions, but becomes slower once over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Coniferous Forest
Mixed conifer forest is a vegetation type dominated by a mixture of broadleaf trees and conifers.Sierra Nevada Wildflowers, Karen Wiese, 2nd ed, 2013, p 13–14 It is generally located in mountains, below the upper montane vegetation type. Sierra Nevada range In the Sierra Nevada mountain range of the western United States, the mixed conifer forest is found at elevations of in the north, in central areas, and in the south. Characteristic conifers include Ponderosa Pine (''Pinus ponderosa''), Sugar Pine (''Pinus lambertiana''), Incense Cedar ('' Calocedrus decurrens''), White Fir (''Abies concolor''), Douglas Fir (''Pseudotsuga menziesii''), and Giant Sequoias (''Sequoiadendron giganteum'') in pockets. Characteristic broadleaved trees include Black Oak ('' Quercus kelloggii''), and understory trees and shrubs, including Canyon Live Oak (''Quercus chrysolepis''), Dogwood ( ''Cornus'' spp.), Mountain Misery ('' Chamaebatia foliolosa''), and Manzanitas ( ''Arctostaphylos'' spp.). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Mugo
''Pinus mugo'', known as dwarf mountain pine, mountain pine, scrub mountain pine, Swiss mountain pine, bog pine, creeping pine, or mugo pine, is a species of conifer, native to high elevation habitats from southwestern to Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Description The tree has dark green leaves ("needles") in pairs, long. The cones are nut-brown, long. Custura Bucurei.jpg, ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''mugo'', Romania Pinus mugo uncinata trees.jpg, ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''uncinata'' Swiss National Park 007.JPG, ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''rotundata'', Swiss National Park Бор кривул 01.JPG, On Jakupica mountain, Republic of North Macedonia Taxonomy There are three subspecies: * ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''mugo'' — in the east and south of the range (southern & eastern Alps, Balkan Peninsula), a low, shrubby, often multi-stemmed plant to tall with matt-textured symmetrical cones, which are thin-scaled. * ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''uncinata'' — in the west and north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Tundra
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alpine tundra gets lower until it reaches sea level and merges with polar tundra. The high elevation causes an adverse climate, which is too cold and windy to support tree growth. Alpine tundra transitions to sub-alpine forests below the tree line; stunted forests occurring at the forest-tundra ecotone are known as '' krummholz''. With increasing elevation it ends at the snow line where snow and ice persist through summer. Alpine tundra occurs in mountains worldwide. The flora of the alpine tundra is characterized by dwarf shrubs close to the ground. The cold climate of the alpine tundra is caused by adiabatic cooling of air, and is similar to polar climate. Geography Alpine tundra occurs at high enough altitude at any latitude. Portions of montane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitudinal Zonation
Altitudinal zonation (or elevational zonation) in mountainous regions describes the natural layering of ecosystems that occurs at distinct elevations due to varying environmental conditions. Temperature, humidity, soil composition, and solar radiation are important factors in determining altitudinal zones, which consequently support different vegetation and animal species. Altitudinal zonation was first hypothesized by geographer Alexander von Humboldt who noticed that temperature drops with increasing elevation. Zonation also occurs in intertidal and marine environments, as well as on shorelines and in wetlands. Scientist C. Hart Merriam observed that changes in vegetation and animals in altitudinal zones map onto changes expected with increased latitude in his concept of life zones. Today, altitudinal zonation represents a core concept in mountain research. Factors A variety of environmental factors determines the boundaries of altitudinal zones found on mountains, rangin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' ( ), a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal (taiga) regions of the Northern hemisphere. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Piceoideae. Spruces are large trees, from about 20 to 60 m (about 60–200 ft) tall when mature, and have Whorl (botany), whorled branches and cone (geometry), conical form. Spruces can be distinguished from other Genus, genera of the family Pinaceae by their pine needle, needles (leaves), which are four-sided and attached singly to small persistent peg-like structures (pulvini or sterigmata) on the branches, and by their seed cone, cones (without any protruding bracts), which hang downwards after they are pollinated. The needles are shed when 4–10 years old, leaving the branches rough with the retained pegs. In other similar genera, the branches are fairly smooth. Spruce are used as food pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |