|
Bäumer Sausewind
The Bäumer B II Sausewind ("Whizzing Wind" or "Restless Person") was a light sports tandem two-seat, open cockpit, wooden Cantilever#Aircraft, cantilever monoplane. It was built by Germany, German aviation company Bäumer Aero GmbH, based at Hamburg Airport. It was the first aircraft made in Germany to be designed for aerodynamic performance. Design and development The Sausewind's development was triggered when the newspaper ''B.Z. (newspaper), BZ am Mittag'' announced the ''B.Z. Preis der Lüfte'' ("''B.Z.'' Prize of the Skies") as part of the 1925 ''Deutschland-Rundflug'' ("Round-Germany Flight"), which offered prize money of 100,000 Reichsmarks for the winner. The twin brothers Siegfried and Walter Günter designed the B II at Bäumer Aero GmbH. The Sausewind was the first aircraft to make use of elliptical wing and Empennage, tail units, which offered aerodynamic advantages over the rectangular wings that were common at the time. To reduce air resistance all control cab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of , making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The Capital of Germany, nation's capital and List of cities in Germany by population, most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in the territory of modern Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces both Lift (force), lift and drag while moving through air. Wings are defined by two shape characteristics, an airfoil section and a planform (aeronautics), planform. Wing efficiency is expressed as lift-to-drag ratio, which compares the benefit of lift with the air resistance of a given wing shape, as it flies. Aerodynamics is the study of wing performance in air. Equivalent Foil (fluid mechanics), foils that move through water are found on Hydrofoil, hydrofoil power vessels and Sailing hydrofoil, foiling sailboats that lift out of the water at speed and on submarines that use diving planes to point the boat upwards or downwards, while running submerged. Hydrodynamics is the study of foil performance in water. Etymology and usage The word "wing" from the Old Norse ''vængr'' for many centuries referred mainly to the foremost limb (anatomy), limbs of birds (in addition to the architectural aisle). But in recent centuries the word's meaning ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-wing Aircraft
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplane (aeronautics), multiplanes, which have multiple wings. A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing configuration and is the simplest to build. However, during the early years of flight, these advantages were offset by its greater weight and lower manoeuvrability, making it relatively rare until the 1930s. Since then, the monoplane has been the most common form for a fixed-wing aircraft. Characteristics Support and weight The inherent efficiency of the monoplane is best achieved in the cantilever wing, which carries all structural forces internally. However, to fly at practical speeds the wing must be made thin, which requires a heavy structure to make it strong and stiff enough. External Bracing (aeronautics), bracing can be used to improve structural efficiency, reducing weight and cost. For a wing of a given size, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1920s German Sport Aircraft
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number) * One of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (1987 film), a 1987 science fiction film * '' 19-Nineteen'', a 2009 South Korean film * '' Diciannove'', a 2024 Italian drama film informally referred to as "Nineteen" in some sources Science * Potassium, an alkali metal * 19 Fortuna, an asteroid Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle * "Stone in Focus", officially "#19", a composition by Aphex Twin * "Nineteen", a song from the 1992 album ''Refugee'' by Bad4Good * "Nineteen", a song from the 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight International
''Flight International'', formerly ''Flight'', is a monthly magazine focused on aerospace. Published in the United Kingdom and founded in 1909 as "A Journal devoted to the Interests, Practice, and Progress of Aerial Locomotion and Transport", it is the world's oldest continuously published aviation news magazine. ''Flight International'' is published by DVV Media Group. Competitors include Jane's Information Group and '' Aviation Week''. Former editors of, and contributors include H. F. King, Bill Gunston, John W. R. Taylor and David Learmount. History The founder and first editor of ''Flight'' was Stanley Spooner. He was also the creator and editor of ''The Automotor Journal'', originally titled ''The Automotor Journal and Horseless Vehicle''.Guide To British Industrial His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston Engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more Reciprocating motion, reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a Circular motion, rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition engine, spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition engine, compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, Adiabatic process, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected diesel engine, then or hot-bulb engine, earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bäumer Sausewind 3-view L'Aerophile Salon 1932
Bäumer is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Gertrud Bäumer (1873–1954), German lawyer and politician * Jens Bäumer (born 1978), German footballer * Ludwig Bäumer (1888–1928), German writer and Communist activist * Marie Bäumer (born 1969), German actress * Paul Bäumer (1896–1927), German pilot See also * Baumer Baumer is a surname. People with the surname include the following: * Bettina Baumer (born 1940), Austrian-born Indian scholar of religion *Christoph Baumer (born 1952), Swiss scholar and explorer * Daniela Baumer (born 1971), Swiss sprint canoer *J ... * Bäumler {{DEFAULTSORT:Baumer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin-Tempelhof
Tempelhof () is a locality of Berlin within the borough of Tempelhof-Schöneberg. It is the location of the former Tempelhof Airport, one of the earliest commercial airports in the world. The former airport and surroundings are now a park called Tempelhofer Feld, making it the largest inner city open space in the world. The Tempelhof locality is located in the south-central part of the city. Before Berlin's 2001 administrative reform, the area of Tempelhof, together with the localities of Mariendorf, Marienfelde, and Lichtenrade, constituted a borough of its own, also called ''Tempelhof''. These localities grew from historic villages on the Teltow plateau founded in the early 13th century in the course of the German Ostsiedlung. History ''Tempelhove'' was first mentioned in a 1247 deed issued at the Walkenried Abbey as a ''Komturhof'' (''commander's court'', the smallest holding entity of a military order) of the Knights Templar, whose leadership and many fellow knights had be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamic Drag
In fluid dynamics, drag, sometimes referred to as fluid resistance, is a force acting opposite to the direction of motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers, two solid surfaces, or between a fluid and a solid surface. Drag forces tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path. Unlike other resistive forces, drag force depends on velocity. Drag force is proportional to the relative velocity for low-speed flow and is proportional to the velocity squared for high-speed flow. This distinction between low and high-speed flow is measured by the Reynolds number. Drag is instantaneously related to vorticity dynamics through the Josephson-Anderson relation. Examples Examples of drag include: * Net force, Net Aerodynamic force, aerodynamic or Fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic force: Drag acting opposite to the direction of movement of a solid object such as cars, aircraft, and boat hulls. * Viscou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
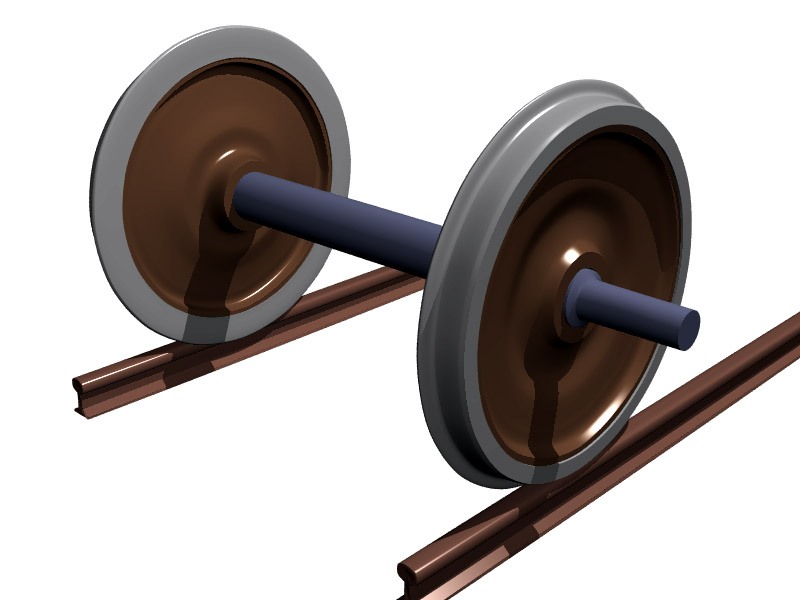
Axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotation, rotating wheel and axle, wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearing (mechanical), bearings or Bushing (bearing), bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type of axle is referred to as a ''spindle (tool), spindle''. Terminology On cars and trucks, several senses of the word ''axle'' occur in casual usage, referring to the shaft itself, its housing, or simply any transverse pair of wheels. Strictly speaking, a shaft that rotates with the wheel, being either Bolt (fastener), bolted or rotating spline, splined in fixed relation to it, is called an ''axle'' or ''axle shaft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landing Gear
Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for taxiing, takeoff or landing. For aircraft, it is generally needed for all three of these. It was also formerly called ''alighting gear'' by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Martin Company. For aircraft, Stinton makes the terminology distinction ''undercarriage (British) = landing gear (US)''. For aircraft, the landing gear supports the craft when it is not flying, allowing it to take off, land, and taxi without damage. Wheeled landing gear is the most common, with skis or Seaplane, floats needed to operate from snow/ice/water and skids for vertical operation on land. Retractable undercarriages fold away during flight, which reduces drag (physics), drag, allowing for faster airspeeds. Landing gear must be strong enough to support the aircraft and its design affects the weight, balance and performance. It often comprises three wheels, or wheel-sets, giving a tripod effect. Some unusual land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empennage
The empennage ( or ), also known as the tail or tail assembly, is a structure at the rear of an aircraft that provides stability during flight, in a way similar to the feathers on an arrow.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 194. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Aviation Publishers Co. Limited, ''From the Ground Up'', p. 10 (27th revised edition) The term derives from the French language verb which means " to feather an arrow". Most aircraft feature an empennage incorporating vertical and horizontal stabilising surfaces which stabilise the flight dynamics of yaw and pitch, as well as housing control surfaces. In spite of effective control surfaces, many early aircraft that lacked a stabilising empennage were virtually unflyable. Even so-called "tailless aircraft" usually have a tail fin (usually a vertical stabiliser). Heavier-than-air aircraft without any kind of empennage (such as the Northrop B-2) are rare, and generally use specially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |