|
Burgau
Burgau () is a Town#Germany, town in Günzburg (district), the district of Günzburg in Swabia (Bavaria), Swabia, Bavaria. Burgau lies on the river Mindel (river), Mindel and has a population of just under 10,000. History The territory around Burgau was originally part of the stem duchy of Duchy of Swabia, Swabia. The death of Conradin and the resulting extinction of the Hohenstaufen line in 1268 led to the collapse of the integrity of the duchy and its division into lands, after local nobles resisted the House of Habsburg, Habsburg Rudolph I, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Rudolph's attempts to annex the duchy. The Lords of Burgau are first found in documentary mention in 1147, as . Burgau was raised to a margraviate in 1212. With the death of Henry III, Margrave of Burgau, Margrave Henry III in 1301, the margravial line fell extinct and the Holy Roman Empire, Empire claimed the fief. Albert I of Germany transferred the feudalism, feudal rights to his two sons, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
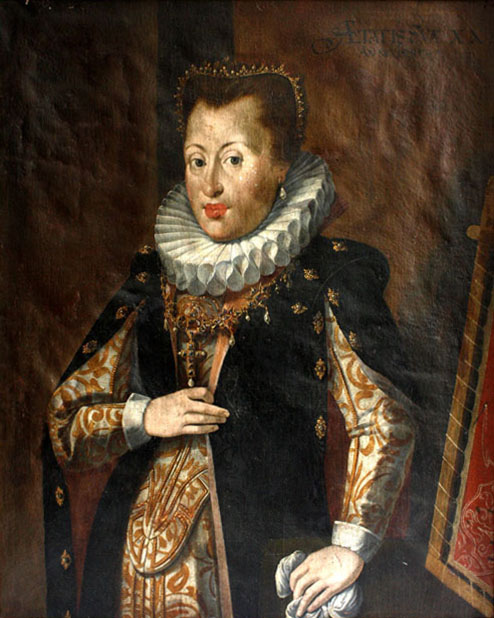
Ferdinand II, Archduke Of Austria
Ferdinand II, Archduke of Further Austria (Linz, 14 June 1529 – 24 January 1595, Innsbruck) was ruler of Further Austria and since 1564 Imperial count of County of Tyrol, Tyrol. The son of Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, he was married to Philippine Welser in his first marriage. In his second marriage to Anna Juliana Gonzaga, he was the father of Anna of Tyrol, future Holy Roman Empress. Biography Archduke Ferdinand of Austria was the second son of Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor and Anna of Bohemia and Hungary. He was a younger brother of Emperor Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian II. He grew up in Innsbruck, where his father governed the Austrian hereditary lands on behalf of Ferdinand's uncle Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V. Ferdinand was said to be the favorite son of his father. He was described by a visiting dignitary to court as "handsome and friendlier" than his brother Maximilian. Ferdinand and his siblings were raised very strictly and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Günzburg (district)
Günzburg is a ''Landkreis'' (district) in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. Its capital is the town Günzburg. It is bounded by (from the north and clockwise) the districts of Dillingen, Augsburg, Unterallgäu and Neu-Ulm, and by the state of Baden-Württemberg (districts Alb-Donau and Heidenheim). History In the early Middle Ages the tiny county of Burgau ruled the region. In 1213 the county was acquired by the lords of Berg; it was then known as Berg-Burgau, but the last ruler of this collateral line died in 1301, and Burgau (now raised to the level of a margraviate) became an exclave of Austria. In the early 17th century the administrative seat was moved from the town of Burgau to Günzburg, but the margraviate retained its name. When the Holy Roman Empire ceased to exist in 1806, the margraviate was dissolved and the region was annexed by Bavaria. The district was established in 1972 by merging the former districts of Günzburg and Krumbach. Günzburg lost its status as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindel (river)
The Mindel () is a river in Bavaria, southern Germany. The Mindel originates west of Kaufbeuren, in the Allgäu region, and flows generally north. It flows into the Danube (right tributary) in Gundremmingen, east of Günzburg. The towns Mindelheim, Burgau and Thannhausen lie along the Mindel. The Mindel gave its name to the Mindel glaciation The Mindel glaciation (, also ''Mindel-Glazial'', ''Mindel-Komplex'' or, colloquially, ''Mindel-Eiszeit'') is the third youngest glacial stage in the Alps. Its name was coined by Albrecht Penck and Eduard Brückner, who named it after the Swabi ... in the Alps. References Rivers of Bavaria Bodies of water of Günzburg (district) Rivers of Germany {{Bavaria-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Further Austria
Further Austria, Outer Austria or Anterior Austria (; , formerly ''die Vorlande'' (pl.)) was the collective name for the early (and later) possessions of the House of Habsburg in the former Swabian stem duchy of south-western Germany, including territories in the Alsace region west of the Rhine and in Vorarlberg. While the territories of Further Austria west of the Rhine and south of Lake Constance (except Konstanz itself) were gradually lost to France and the Swiss Confederacy, those in Swabia remained under Habsburg control until the Napoleonic Era, with Vorarlberg still forming a part of modern Austria. Geography Further Austria mainly comprised the Alsatian County of Ferrette in the Sundgau, including the town of Belfort, and the adjacent Breisgau region east of the Rhine, including Freiburg im Breisgau after 1368. Also ruled from the Habsburg residence in Ensisheim near Mühlhausen were numerous scattered territories stretching from Upper Swabia to the Allgäu region i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a former Bavarian dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including the Electorate of Bavaria, the Electoral Palatinate, the Electorate of Cologne, County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland under Swedish rule, Swedish-ruled Finland), Denmark, Norway, Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemia, and Kingdom of Greece, Greece. Their ancestral lands of Bavaria and the Electoral Palatinate, Palatinate were prince-electorates, and the family had three of its members elected emperors and kings of the Holy Roman Empire. They ruled over the Kingdom of Bavaria which was created in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. The House of Windsor, the reigning royal house of the British monarchy, are descendants of Sophia of Hanover (1630–1714), a Wittelsbach Princess of the Palatinate by birth and List of Hanoverian royal consorts, Electress of Hanover by marriage, who had inherited the success ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Title (property)
In property law, title is an intangible construct representing a bundle of rights in a piece of property in which a party may own either a legal interest or equitable interest. The rights in the bundle may be separated and held by different parties. It may also refer to a formal document, such as a deed, that serves as evidence of ownership. Conveyance of the document (transfer of title to the property) may be required in order to transfer ownership in the property to another person. Title is distinct from possession, a right that often accompanies ownership but is not necessarily sufficient to prove it (for example squatting). In many cases, possession and title may each be transferred independently of the other. For real property, land registration and recording provide public notice of ownership information. '' Possession'' is the actual holding of a thing, whether or not one has any right to do so. The '' right of possession'' is the legitimacy of possession (with or wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
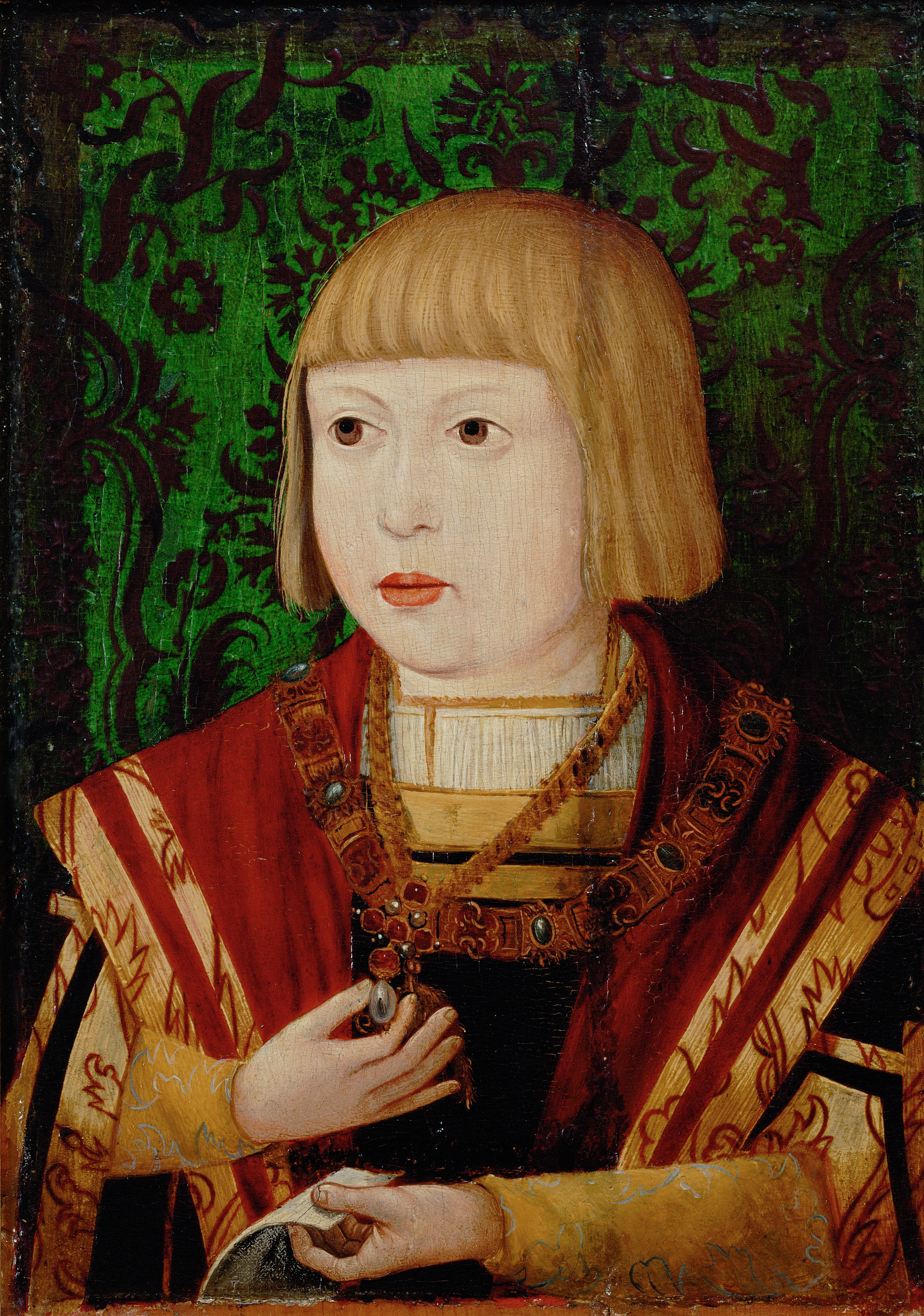
Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand I (10 March 1503 – 25 July 1564) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1556, King of Bohemia, King of Hungary, Hungary, and List of rulers of Croatia, Croatia from 1526, and Archduke of Austria from 1521 until his death in 1564.Milan Kruhek: Cetin, grad izbornog sabora Kraljevine Hrvatske 1527, Karlovačka Županija, 1997, Karslovac Before his accession as emperor, he ruled the Erblande, Austrian hereditary lands of the House of Habsburg in the name of his elder brother, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. Also, he often served as Charles' representative in the Holy Roman Empire and developed encouraging relationships with German princes. In addition, Ferdinand also developed valuable relationships with the German banking house of Jakob Fugger and the Catalan bank, Banca Palenzuela Levi Kahana. The key events during his reign were the conflict with the Ottoman Empire, which in the 1520s began a great advance into Central Europe, and the Protestant Reformation, which resulted in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swabian League
The Swabian League () was a military alliance of Imperial State, imperial estates – Free imperial city, imperial cities, prelates, principalities and knights – principally in the territory of the early Middle Ages, medieval stem duchy of Swabia established in 1488. New institutions created through imperial reform removed the need for the league, whilst the religious revolution of the Protestant Reformation divided its members, leading to the Swabian League being disbanded in 1534. History The Swabian League was established in 1488 at the behest of Emperor Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick III and supported as well by Berthold von Henneberg, Bertold, Elector of Mainz, whose conciliar rather than monarchic view of the ''Reich'' often put him at odds with Frederick's successor Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian. The Swabian League cooperated towards the keeping of the imperial peace and at least in the beginning curbing the expansionist History of Bavaria, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lech (river)
The Lech (; , ''Licca'') is a river in Austria and Germany. It is a right tributary of the Danube in length with a drainage basin of . Its average discharge (hydrology), discharge at the River mouth, mouth is . Its source is located in the Austrian States of Austria, state of Vorarlberg, where the river rises from lake Formarinsee in the Alps at an altitude of . It flows in a north-north-easterly direction and crosses the German border, forming the Lechfall, a waterfall; afterwards the river enters a narrow gorge (the Lechschlucht). Leaving the Alps, it enters the plains of the Allgäu at Füssen at an elevation of in the German state of Bavaria, where it used to be the location of the boundary with Swabia. The river runs through the city of Füssen and through the Forggensee, a man-made lake which is drained in winter. Here, it forms rapids and a waterfall. The river flows further northwards through a region called the Lechrain, and passes the cities of Schongau, Bavaria, Sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fugger
The House of Fugger () is a German family that was historically a prominent group of European bankers, members of the fifteenth- and sixteenth-century mercantile patriciate of Augsburg, international mercantile bankers, and venture capitalists. Alongside the Welser family, the Fugger family controlled much of the European economy in the sixteenth century and accumulated enormous wealth. The Fuggers held a near monopoly on the European copper market. This banking family replaced the Medici family who influenced all of Europe during the Renaissance. The Fuggers took over many of the Medicis' assets and their political power and influence. They were closely affiliated with the House of Habsburg whose rise to world power they financed. Unlike the citizenry of their hometown and most other trading patricians of German free imperial cities, such as the Tuchers, they never converted to Lutheranism, as presented in the Augsburg Confession, but rather remained with the Roman Catholi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-Bishopric Of Augsburg
The Prince-Bishopric of Augsburg () was one of the Prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire, and belonged to the Swabian Circle. It should not be confused with the larger diocese of Augsburg, over which the prince-bishop exercised only spiritual authority. The city of Augsburg proper, after it gained free imperial status, was a separate entity and constitutionally and politically independent of the prince-bishopric of the same name. The prince-bishopric covered some 2365 km2 and had approximately 100,000 inhabitants at the time it was annexed to Bavaria in the course of the German mediatization. History Medieval period Nothing is known with certainty about the history of the Augsburg Church during the centuries immediately following the collapse of Roman power in Germany and the turbulence of the great migrations, but it did survive. While two catalogues of the Bishops of Augsburg, dating from the eleventh and twelfth centuries, mention several bishops from this earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free City Of Augsburg
Augsburg ( , ; ; ) is a city in the Bavaria, Bavarian part of Swabia, Germany, around west of the Bavarian capital Munich. It is a College town, university town and the regional seat of the Swabia (administrative region), Swabia with a well preserved Altstadt (historical city centre). Augsburg is an Urban districts of Germany, urban district and home to the institutions of the Augsburg (district), Landkreis Augsburg. It is the List of cities in Bavaria by population, third-largest city in Bavaria (after Munich and Nuremberg), with a population of 304,000 and 885,000 in its metropolitan area. After Neuss, Trier, Worms, Germany, Worms, Cologne and Xanten, Augsburg is one of Germany's oldest cities, founded in 15 BC by the Romans as Augsburg#Early history, Augusta Vindelicorum and named after the Roman emperor Augustus. It was a Free Imperial City from 1276 to 1803 and the home of the patrician (post-Roman Europe), patrician Fugger and Welser families that dominated European ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |