|
Buno People
Buno is an ethnic minority people of Bangladesh mostly found in Rajshahi, Rangpur, Khulna and Dhaka division. They are nomadic tribal people like Romani and Bede people. They do not live in a single place permanently. They often move one village to another village. They keep pigs, sheep and goats with them. They move into the grasslands for their animals. They are animist. They believe in animistic faith. Recently, some of them have converted to Hinduism and Christianity. They have their own distinct language related to Munda, Dravid, Oraon Sadri and Romani or Domari languages. But they can speak Bengali fluently. The exact figure of the population of Buno people is unavailable. Perhaps, 100000 to 200000 Buno exist throughout Bangladesh. This ethnic group is less studied and less known to scholars. Sometimes, Buno people can be considered as Oraon, Santal or Dom Dom or DOM may refer to: People and fictional characters * Dom (given name), including fictional characters * Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated countries in the world, and shares land borders with India to the west, north, and east, and Myanmar to the southeast; to the south it has a coastline along the Bay of Bengal. It is narrowly separated from Bhutan and Nepal by the Siliguri Corridor; and from China by the Indian state of Sikkim in the north. Dhaka, the capital and list of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city, is the nation's political, financial and cultural centre. Chittagong, the second-largest city, is the busiest port on the Bay of Bengal. The official language is Bengali language, Bengali, one of the easternmost branches of the Indo-Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oraon Language
Kurukh (; Devanagari: कुंड़ुख़), also Kurux, Oraon or Uranw, is a Dravidian language spoken by the Kurukh (Oraon) and Kisan people of East India. It is spoken by about two million people in the Indian states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal, Assam, Bihar and Tripura, as well as by 65,000 in northern Bangladesh, 28,600 of a dialect called Uranw in Nepal and about 5,000 in Bhutan. Some Kurukh speakers are in Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is most closely related to the Malto language. It is marked as being in a "vulnerable" state in UNESCO's list of endangered languages. The Kisan dialect has 206,100 speakers as of 2011. Classification Kurukh belongs to the Northern Dravidian group of the Dravidian family languages, and is closely related to Sauria Paharia and Kumarbhag Paharia, which are often together referred to as Malto. Writing systems Kurukh is written in Devanagari, a script also used to write Sanskrit, Hindi, Marathi, Nepali and other I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doms
The Dom (Sanskrit ''ḍoma'', dialectally also Domra, Domba, Domaka, Dombari and variants) are castes, or groups, scattered across India. Dom were a caste of drummer. According to Tantra scriptures, the Dom were engaged in the occupations of singing and playing music. Historically, they were considered an untouchable caste and their traditional occupation was the disposal and cremation of dead bodies. They are in the list of Scheduled caste for Reservation in India in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Odisha and West Bengal. Etymology According to Tantra scriptures, individuals who live by singing and music were mention as Dom. According to historian M.P Joshi, the word Duma is connected to the sound of a drum. Its presumed root, ''ḍom'', which is connected with drumming, is linked to ''damara'' and ''damaru'', Sanskrit terms for "drum" and the Sanskrit verbal root डम् ''ḍam-'' 'to sound (as a drum)', perhaps a loan from Dravidian, e.g. Kannada ''ḍamāra' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santal
The Santal or Santhal are an Austroasiatic speaking Munda ethnic group in South Asia. Santals are the largest tribe in the Jharkhand and West Bengal state of India in terms of population and are also found in the states of Odisha, Bihar and Assam. They are the largest ethnic minority in northern Bangladesh's Rajshahi Division and Rangpur Division. They have a sizeable population in Nepal. The Santals speak Santali, the most widely spoken Munda languages of Austro-asiatic language family. Etymology Santal is most likely derived from an exonym. The term refers to inhabitants of in erstwhile Silda in Medinapore region in West Bengal. The sanskrit word ''Samant'' or Bengali ''Saont'' means plain land. Their ethnonym is ("sons of mankind"). History Origins According to linguist Paul Sidwell, Austro-Asiatic language speakers probably arrived on coast of Odisha from Indochina about 4,000–3,500 years ago. The Austroasiatic speakers spread from Southeast Asia and mixed exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oraon People
The Kurukh or Oraon, also spelt Uraon, or Dhangar (Kurukh language, Kurukh: ''Karḵẖ'' and ''Oṛāōn'') are a Dravidian languages, Dravidian speaking ethnolinguistic group inhabiting Chota Nagpur Plateau, Chhotanagpur Plateau and adjoining areas - mainly the Indian states of Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Chhattisgarh. They predominantly speak Kurukh language, Kurukh as their native language, which belongs to the Dravidian languages, Dravidian language family. In Maharashtra, Oraon people are also known as Dhangad or Dhangar. Traditionally, Oraons depended on the forest and farms for their ritual practices and livelihoods, but in recent times, they have become mainly settled agriculturalists. Many Oraon migrated to tea gardens of Assam, West Bengal and Bangladesh as well as to countries like Fiji, Guyana, Trinidad and Tobago and Mauritius during British Raj, British rule, where they were known as ''Hill Coolies''. They are listed as a Scheduled Tribe for the purpose of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Language
Bengali ( ), generally known by its endonym Bangla (, ), is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Bengal region of South Asia. It is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second most widely spoken of the 22 scheduled languages of India. With approximately 300 million native speakers and another 37 million as second language speakers, Bengali is the fifth most-spoken native language and the seventh most spoken language by total number of speakers in the world. Bengali is the fifth most spoken Indo-European language. Bengali is the official and national language of Bangladesh, with 98% of Bangladeshis using Bengali as their first language. Within India, Bengali is the official language of the states of West Bengal, Tripura and the Barak Valley region of the state of Assam. It is also a second official language of the Indian state of Jharkhand since September 2011. It is the most widely spoken language in the Andaman and Nic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domari
Domari is an endangered Indo-Aryan language, spoken by Dom people scattered across the Middle East and North Africa. The language is reported to be spoken as far north as Azerbaijan and as far south as central Sudan, in Turkey, Iran, Iraq, Palestine, Israel, Jordan, Egypt, Sudan, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Syria and Lebanon. Based on the systematicity of sound changes, it is known with a fair degree of certainty that the names ''Domari'' and ''Romani'' derive from the Indo-Aryan word ''ḍom''. However, the Domari and Romani languages do not derive from the same ancestor idiom. Domari derives from an Indo-Aryan language. The Arabs referred to them as '' Nawar'' as they were a nomadic people that originally immigrated to the Middle East from the Indian subcontinent. Domari is also known as "Middle Eastern Romani", "Tsigene", "Luti", or "Mehtar". There is no standard written form. In the Arab world, it is occasionally written using the Arabic script and has many Arabic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romani Language
Romani (; also Romany, Romanes , Roma; rom, rromani ćhib, links=no) is an Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani communities. According to '' Ethnologue'', seven varieties of Romani are divergent enough to be considered languages of their own. The largest of these are Vlax Romani (about 500,000 speakers), Balkan Romani (600,000), and Sinte Romani (300,000). Some Romani communities speak mixed languages based on the surrounding language with retained Romani-derived vocabulary – these are known by linguists as Para-Romani varieties, rather than dialects of the Romani language itself. The differences between the various varieties can be as large as, for example, the differences between the Slavic languages. Name Speakers of the Romani language usually refer to the language as ' "the Romani language" or '' (adverb)'' "in a Rom way". This derives from the Romani word ', meaning either "a member of the (Romani) group" or "husband". This is also the origin of the term "Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadri
Sadri is a municipality in the Pali district of Rajasthan, India. It is considered the gateway to Marwar from Mewar. Sadri is one of the main places of worship for the Jain community. Ranakpur Temple and Shri Parshuram Mahadev Mandir are located in Sadri, which became a municipality (Nagar Palika) in 1961. Bhadras is located 3 km from Sadri along the Suhai river. Sadri was previously populated by Nandwana brahman community. The Jagir used to belong to Sindhal Rathore Community. Geography Sadri is located at . It has an average elevation of 502 meters. Demographics According to the 2011 Census of India, Sadri had a population of 27,393. Males account for 50.2% (13,762) of the population and females 49.8% (13,631). Sadri has an average literacy rate of 65.54%, which is lower than the national average of 74.04%. The male literacy rate is 83.76%, while the female literacy rate is 46.55%. 14% of the population is under 6 years of age. Transport The nearest railway stati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
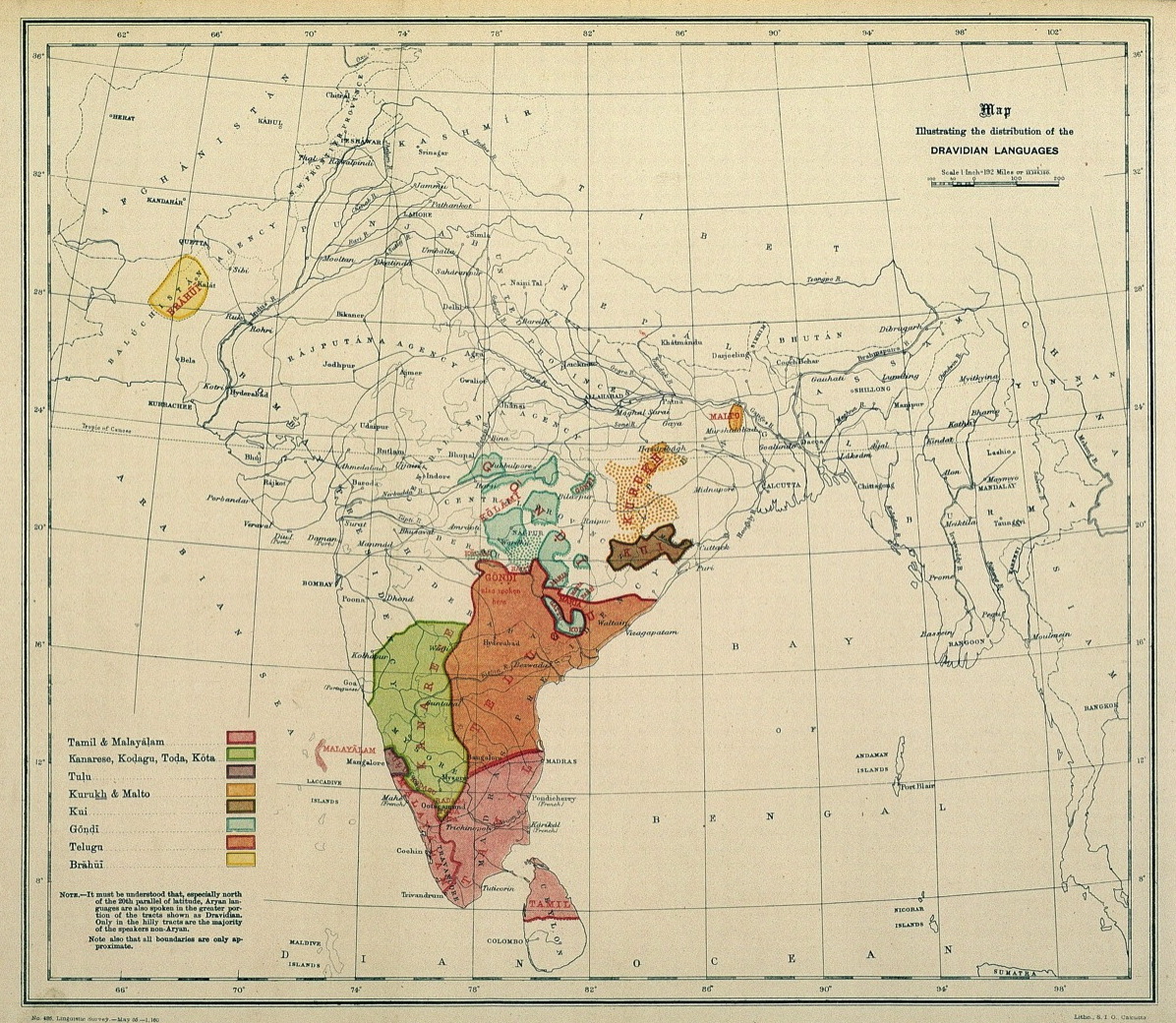
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages (or sometimes Dravidic) are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, mainly in southern India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan. Since the colonial era, there have been small but significant immigrant communities in Mauritius, Myanmar, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, United Kingdom, Australia, France, Canada, Germany, South Africa, and the United States. The Dravidian languages are first attested in the 2nd century BCE, as Tamil-Brahmi script, inscribed on the cave walls in the Madurai and Tirunelveli districts of Tamil Nadu. The Dravidian languages with the most speakers are (in descending order of number of speakers) Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam, all of which have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu and Kodava. There are also a number of Dravidian-speaking scheduled tribes, such as the Kurukh in Eastern India and Gondi in Central India. Outside of India, Brahui is mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajshahi
Rajshahi ( bn, রাজশাহী, ) is a metropolis, metropolitan city and a major urban, commercial and educational centre of Bangladesh. It is also the administrative seat of the eponymous Rajshahi Division, division and Rajshahi District, district. Located on the north bank of the Padma River, near the Bangladesh-India border, the city has a population of over 763,580 residents. The town is surrounded by the satellite towns of Nowhata and Katakhali, which together build an urban agglomeration of about 1 million population. Modern Rajshahi Division, Rajshahi lies in the ancient region of Pundravardhana. The foundation of the city dates to 1634, according to epigraphic records at the mausoleum of Sufi saint Shah Makhdum. The area hosted a Dutch settlement in Rajshahi, Dutch settlement in the 18th century. The Rajshahi municipality was constituted during the British Raj in 1876. It was a divisional capital of the Bengal Presidency. Rajshahi is a significant administrative, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munda Languages
The Munda languages are a group of closely related languages spoken by about nine million people in India and Bangladesh. Historically, they have been called the Kolarian languages. They constitute a branch of the Austroasiatic language family, which means they are more distantly related to languages such as the Mon and Khmer languages, to Vietnamese, as well as to minority languages in Thailand and Laos and the minority Mangic languages of South China. Bhumij, Ho, Mundari, and Santali are notable Munda languages. The family is generally divided into two branches: North Munda, spoken in the Chota Nagpur Plateau of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, and Odisha, and South Munda, spoken in central Odisha and along the border between Andhra Pradesh and Odisha. North Munda, of which Santali is the most widely spoken, has twice as many speakers as South Munda. After Santali, the Mundari and Ho languages rank next in number of speakers, followed by Korku and Sora. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |