|
Bufanolides
Bufadienolide is a chemical compound with steroid structure. Its derivatives are collectively known as bufadienolides, including many in the form of bufadienolide glycosides (bufadienolides that contain structural groups derived from sugars). These are a type of cardiac glycoside, the other being the cardenolide glycosides. Both bufadienolides and their glycosides are toxic; specifically, they can cause an atrioventricular block, bradycardia (slow heartbeat), ventricular tachycardia (a type of rapid heartbeat), and possibly lethal cardiac arrest. Etymology The term derives from the toad genus '' Bufo'' that contains bufadienolide glycosides, the suffix ''-adien-'' that refers to the two double bonds in the lactone ring, and the ending ''-olide'' that denotes the lactone structure. Consequently, related structures with only one double bond are called ''bufenolides'', and the saturated equivalent is ''bufanolide''. Classification According to MeSH, bufadienolides and bufanol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daigremontianin
Daigremontianin is a bufadienolide. Bufadienolides are steroids and cardiac glycoside aglycones (meaning that they bind with carbohydrates to form cardiac glycosides) that are similar to cardenolides, differing only in the structure of the C-17 substituent on the D ring. This chemical has been found to be toxic in experiments on mice. It is one of five bufadienolides that have been isolated from '' Kalanchoe daigremontiana''. Toxicity Crassulaceans are one of the prime sources of bufadienolide cardiac glycosides (including daigremontianin) responsible for an estimated 33% of cattle mortalities related to plant poisoning in South Africa. Crassulacean bufadienolides cause cardiac poisoning, but repeated small doses cause a condition called cotyledonosis, an intoxication affecting nervous and muscular systems of small animals, particularly, sheep in the Karoo The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe Khoemana (also known as !Orakobab or Korana) word is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proscillaridin
Proscillaridin is a cardiac glycoside, a kind of drug that can be used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat). It is of the bufanolide type and can be obtained from plants of the genus ''Scilla'' and in ''Drimia maritima'' (''Scilla maritima''). The aglycone An aglycone (aglycon or genin) is the chemical compound remaining after the glycosyl group on a glycoside is replaced by a hydrogen atom. For example, the aglycone of a cardiac glycoside would be a steroid A steroid is an organic compoun ... of proscillaridin is scillarenin. References Rhamnosides Bufanolides {{cardiovascular-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
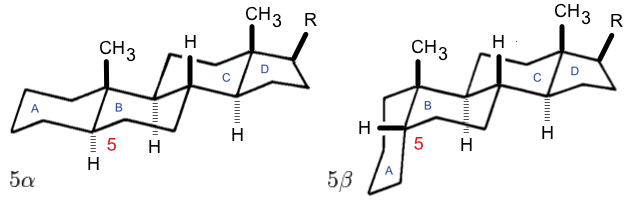
Bufanolide Structure
Bufanolide is a C24 steroid and, indirectly, a parent structure of bufadienolide. Its derivatives was found in ''Bufo'' and ''Scilla'', as an aglycone of cardiac glycosides and is usually toxic Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst .... References {{Cardiac glycosides Bufanolides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. IUPAC's executive director heads this administrative office, currently Greta Heydenrych. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national List of chemistry societies, chemistry societies, national Academy of Sciences, academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Glycoside
Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the cellular sodium-potassium ATPase pump. Their beneficial medical uses include treatments for congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias; however, their relative toxicity prevents them from being widely used. Most commonly found as defensive poisons in several plant genera such as ''Digitalis'' (the foxgloves) and '' Asclepias'' (the milkweeds), these compounds nevertheless have a diverse range of biochemical effects regarding cardiac cell function and have also been suggested for use in cancer treatment. Classification General structure The general structure of a cardiac glycoside consists of a steroid molecule attached to a sugar (glycoside) and an R group. The steroid nucleus consists of four fused rings to which other functional groups such as methyl, hydroxyl, and aldehyde groups can be attached to influence th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardanolide
Cardanolide is a steroid with a molecular weight of 344.54 g/mol. See also * Cardiac glycoside Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the cellular sodium-potassium ATPase pump. Their beneficial medical uses include treatments for ... External links * Steroids {{Steroid classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Compound
In the field of organic chemistry, a polycyclic compound is an organic compound featuring several closed ring (chemistry), rings of atoms, primarily carbon. These ring substructures include cycloalkanes, aromaticity, aromatics, and other ring types. They come in sizes of three atoms and upward, and in combinations of linkages that include tethering (such as in biaryls), fusing (edge-to-edge, such as in anthracene and steroids), links via a single atom (such as in spiro compounds), bridged compounds, and longifolene. Though poly- literally means "many", there is some latitude in determining how many rings are required to be considered polycyclic; many smaller rings are described by specific prefixes (e.g., bicyclic molecule, bicyclic, tricyclic, tetracyclic, etc.), and so while it can refer to these, the title term is used with most specificity when these alternative names and prefixes are unavailable. In general, the term polycyclic includes polycyclic aromatic compounds, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing Academic journal, journal articles and books in the Life science, life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus of index terms that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), it is used by the MEDLINE/PubMed article database and by NLM's catalog of book holdings. MeSH is also used by ClinicalTrials.gov registry to classify which diseases are studied by trials registered in ClinicalTrials. MeSH was introduced in the 1960s, with the NLM's own index catalogue and the subject headings of the Quarterly Cumulative Index Medicus (1940 edition) as precursors. The yearly printed version of MeSH was discontinued in 2007; MeSH is now available only online. It can be browsed and downloaded free of charge through PubMed. Originally in English, MeSH has been translated into numerous other languages and allows retrieval of documents from differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturated And Unsaturated Compounds
A saturated compound is a chemical compound (or ion) that resists addition reactions, such as hydrogenation, oxidative addition, and the binding of a Lewis acids and bases, Lewis base. The term is used in many contexts and classes of chemical compounds. Overall, saturated compounds are less reactive than unsaturated compounds. Saturation is derived from the Latin word ''saturare'', meaning 'to fill'.An unsaturated compound is also a chemical compound (or ion) that attracts reduction reactions, such as dehydrogenation,oxidative reduction Organic chemistry Generally distinct types of unsaturated organic compounds are recognized. For hydrocarbons: *alkene (unsaturated) vs alkane (saturated) *alkyne (unsaturated) vs alkane (saturated) *arene (unsaturated) vs cycloalkane (saturated) For organic compounds containing heteroatoms (other than C and H), the list of unsaturated groups is long but some common types are: *carbonyl, e.g. ketones, aldehydes, esters, carboxylic acids (unsatura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosides
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. These can be activated by enzymatic, enzyme hydrolysis, which causes the sugar part to be broken off, making the chemical available for use. Many such plant glycosides are used as medications. Several species of ''Heliconius'' butterfly are capable of incorporating these plant compounds as a form of chemical defense against predators. In animals and humans, poisons are often bound to sugar molecules as part of their elimination from the body. In formal terms, a glycoside is any molecule in which a sugar group is bonded through its anomeric carbon to another group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides can be linked by an O- (an ''O-glycoside''), N- (a ''glycosylamine''), S-(a ''thioglycoside''), or C- (a ''C-glycoside'') glycosidic bond. Accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |