|
Budini
The Budini (Ancient Greek: Βουδίνοι; ''Boudínoi'') was a group of people (a tribe) described by Herodotus and several later classical authors. Described as nomads living near settled Gelonians, Herodotus located them east of the Tanais river (which is usually assumed to correspond with modern Don River) beyond the Sarmatians. Pliny the Elder mentions the Budini together with the Geloni and other peoples living around the rivers which drain into the Black Sea from the north. During the European Scythian campaign of Darius I, in which the Persian king invaded the Scythian lands of Eastern Europe, the Budini were allies of the Scythians. During the campaign, he captured and burnt down one of the Budini's large fortified cities. The Budini are also mentioned by Classical authors in connection with reindeer. Both Aristotle and Theophrastus have short accounts – probably based on the same source – of an ox-sized deer species, named ''tarandos'' (τάρανδος), living i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelonians
The Gelonians (or Geloni) ( grc, Γελωνοί), also known as Helonians (or Heloni), are mentioned as a nation in northwestern Scythia by Herodotus. Herodotus states that they were originally Hellenes who settled among the Budinoi, and that they are bilingual in Greek and the Scythian language. Their capital was called Gelonos or Helonos, originally a Greek market town. In his account of Scythia, Herodotus writes that the Gelonii were formerly Greeks, having settled away from the coastal emporia among the Budini, where they "use a tongue partly Scythian and partly Greek": :The Budini for their part, being a large and numerous nation, is all mightily blue-eyed and ruddy. And a city among them has been built, a wooden city, and the name of the city is Gelonus. Of its wall then in size each side is of thirty stades and high and all wooden. And their homes are wooden and their shrines. For indeed there is in the very place Greek gods’ shrines adorned in the Greek way with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
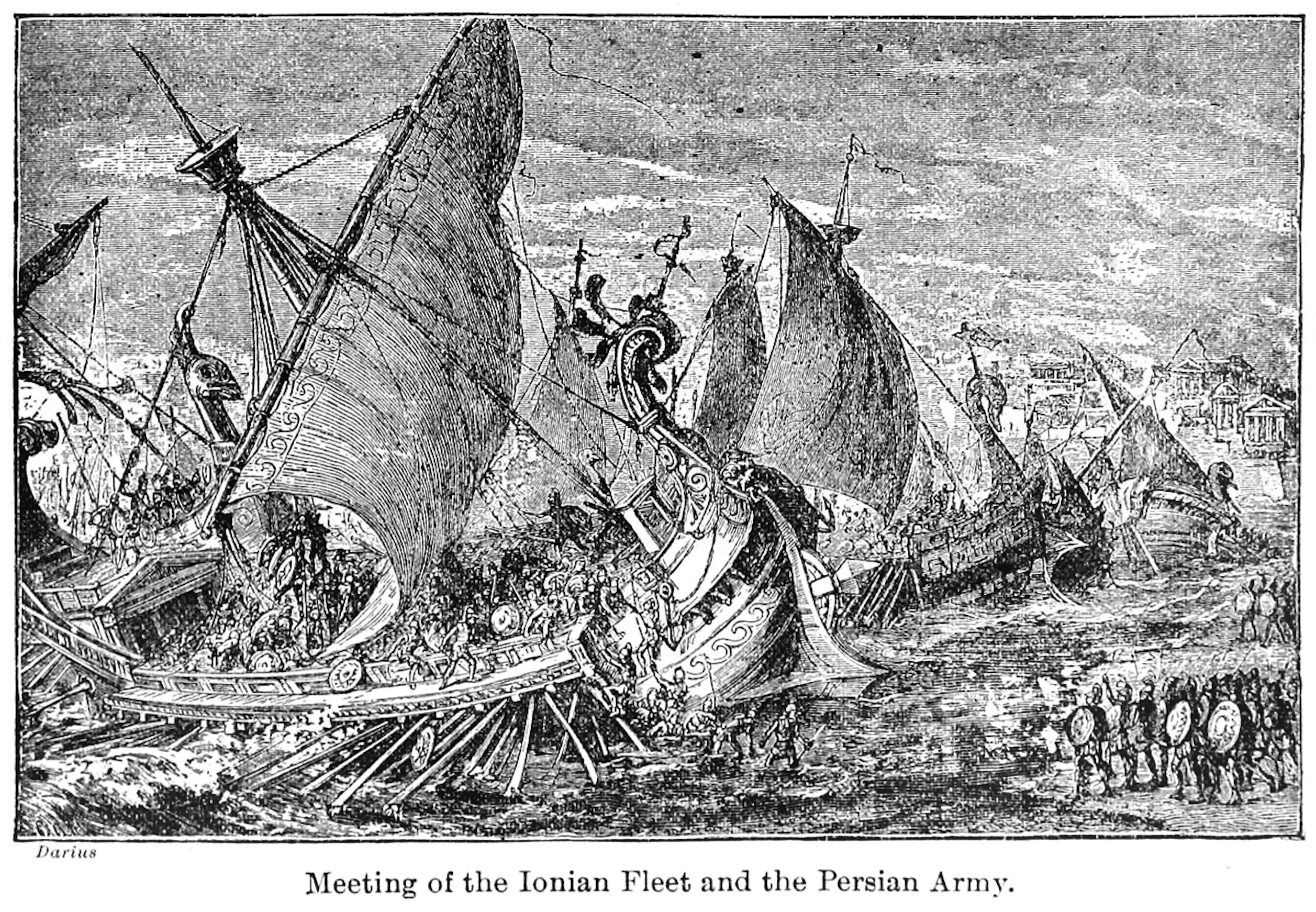
European Scythian Campaign Of Darius I
The Scythian campaign of Darius I was a military expedition into parts of European Scythia by Darius I, the king of the Achaemenid Empire, in 513 BC. The Scythians were an East Iranian-speaking people who had invaded Media, revolted against Darius and threatened to disrupt trade between Central Asia and the shores of the Black Sea as they lived between the Danube and Don Rivers and the Black Sea. The campaigns took place in parts of what is now the Balkans, Ukraine, and southern Russia. The Scythians managed to avoid a direct confrontation with the Persian army due to their mobile lifestyle and lack of any settlement (except Gelonus), while the Persians suffered losses due to the Scythians' scorched earth tactic. However, the Persians conquered much of their cultivated lands and damaged their allies, forcing the Scythians to respect the Persian force. Darius halted the advance to consolidate his gains, and built a defence line. The campaign Darius crossed the Black Sea at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspecies. A 2022 revision of the genus elevated five of the subspecies to species (see Taxonomy below). They have a circumpolar distribution and are native to the Arctic, sub-Arctic, tundra, boreal forest, and mountainous regions of northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. Reindeer occur in both migratory and sedentary populations, and their herd sizes vary greatly in different regions. The tundra subspecies are adapted for extreme cold, and some are adapted for long-distance migration. Reindeer vary greatly in size and color from the smallest species, the Svalbard reindeer (''R. t. platyrhynchus''), to the largest subspecies, Osborn's caribou (''R. t. osborni''). Although reindeer are quite numerous, some species and subspecies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper, and Don. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea covers (not including the Sea of Azov), has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end of the Balkan Mountains; and the Dobruja Plateau considerably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper
} The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth- longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. It is approximately long, with a drainage basin of . In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat, immediately above that tributary's confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and is connected by the Dnieper� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zbigniew Gołąb
Zbigniew Gołąb (16 March 1923, in Nowy Targ – 24 March 1994, in Chicago) was a Polish-American linguist and Slavist. He was described as "one of the world's greatest experts on the Macedonian language and the leading expert on Macedonian– Arumanian contact." He was active during the World War II Resistance Movement, after which he joined the guerrilla war against the Germans in 1944. He was imprisoned that same year, but managed to escape prior to the liberation of Kraków by the Red Army. In 1948–49 he was imprisoned for one year by the communist authorities, but was eventually released.Browne 1994 He received his M.A. from the University of Wrocław in 1947 and his Ph.D. at the Jagiellonian University in 1958. He served as a professor at the John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin during 1952–1961, and also at the Slavic Institute of the Polish Academy of Learning (1955–1961). Afterward he emigrated to the United States where he taught Slavic languages at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the Attested language, unattested, linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium B.C. through the 6th century A.D. As with most other proto-languages, no attested writings have been found; scholars have reconstructed the language by applying the comparative method to all the attested Slavic languages and by taking into account other Indo-European languages. Rapid development of Slavic speech occurred during the Proto-Slavic period, coinciding with the massive expansion of the Slavic-speaking area. Dialectal differentiation occurred early on during this period, but overall linguistic unity and mutual intelligibility continued for several centuries, into the 10th century or later. During this period, many sound changes diffused across the entire area, often uniformly. This makes it inconvenient to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exonym And Endonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, or linguistic community in question; it is their self-designated name for themselves, their homeland, or their language. An exonym (from Greek: , 'outer' + , 'name'; also known as xenonym) is an established, ''non-native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used only outside that particular place, group, or linguistic community. Exonyms exist not only for historico-geographical reasons but also in consideration of difficulties when pronouncing foreign words. For instance, is the endonym for the country that is also known by the exonym ''Germany'' in English, in Spanish and in French. Naming and etymology The terms ''autonym'', ''endonym'', ''exonym'' and ''xen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubor Niederle
Lubor Niederle (September 20, 1865 – June 14, 1944) was a Czech archeologist, anthropologist and ethnographer. He is seen as one of the founders of modern archeology in Czech lands. He was born in Klatovy. He studied at the Charles University in Prague from 1883 to 1887. He was initially interested in classical archaeology, then studied anthropology, sociology and ethnology. Later, he studied in Munich under professor Johannes Rank (1889) and in Paris under professor Léonce Manouvriere at the École d’anthropologie. Niederle also travelled in several Slavic countries, studying archaeological findings and historical documents. In 1898 Niederle was named professor at the Charles University. As archaeologist he had represented the "university school" (''univerzitní škola''), opposed to the "museum school" (''muzejní škola'') represented by archaeologist Josef Ladislav Píč. During 1907–08 Niederle served as a dean of Faculty of Philosophy, during 1908–09 as a vice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavel Jozef Šafárik
Pavel Jozef Šafárik ( sk, Pavol Jozef Šafárik; 13 May 1795 – 26 June 1861) was an ethnic Slovak philologist, poet, literary historian, historian and ethnographer in the Kingdom of Hungary. He was one of the first scientific Slavists. Family His father Pavol Šafárik (1761–1831) was a Protestant clergyman in Kobeliarovo and before that a teacher in Štítnik, where he was also born. His mother, Katarína Káresová (1764–1812) was born in a poor lower gentry family in Hanková and had several jobs in order to help the family in the poor region of Kobeliarovo. P.J. Šafárik had two elder brothers and one elder sister. One brother, Pavol Jozef as well, died before Šafárik was born. In 1813, after Katarína's death, Šafárik's father married the widow Rozália Drábová, although Šafárik and his brothers and sister were against this marriage. The local teacher provided Šafárik with Czech books. On 17 June 1822, when he was in Novi Sad (see below), P. J. Šafá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poltava
Poltava (, ; uk, Полтава ) is a city located on the Vorskla River in central Ukraine. It is the capital city of the Poltava Oblast (province) and of the surrounding Poltava Raion (district) of the oblast. Poltava is administratively incorporated as a city of oblast significance and does not belong to the raion. It has a population of History It is still unknown when Poltava was founded, although the town was not attested before 1174. However, for reasons unknown, municipal authorities chose to celebrate the city's 1100th anniversary in 1999. The settlement is indeed an old one, as archeologists unearthed a Paleolithic dwelling as well as Scythian remains within the city limits. Middle Ages The present name of the city is traditionally connected to the settlement Ltava which is mentioned in the Hypatian Chronicle in 1174. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic People
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic language, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably dive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |