|
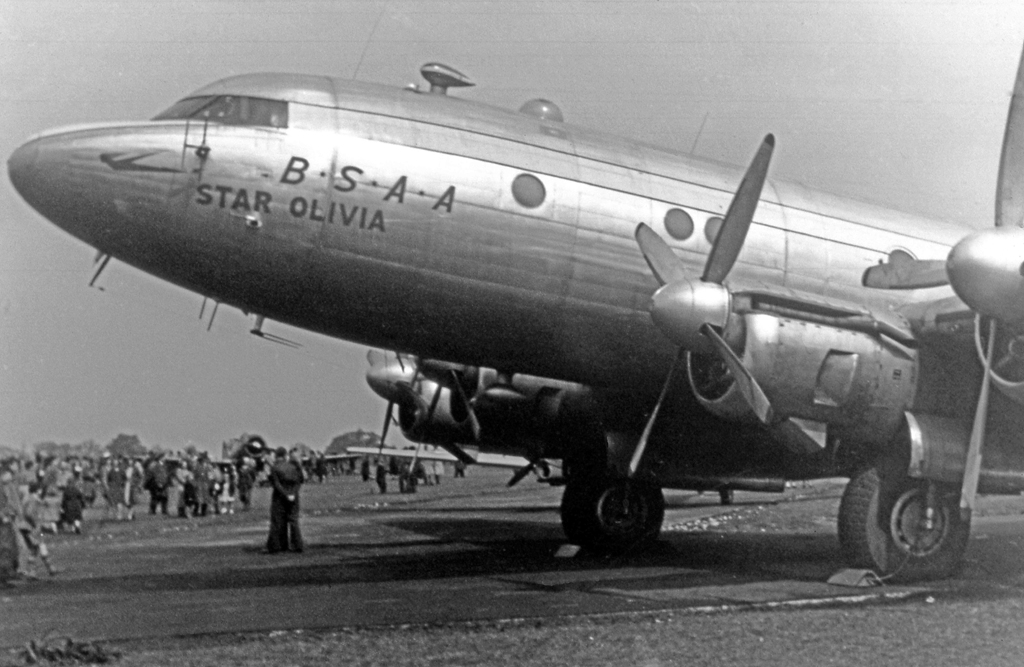
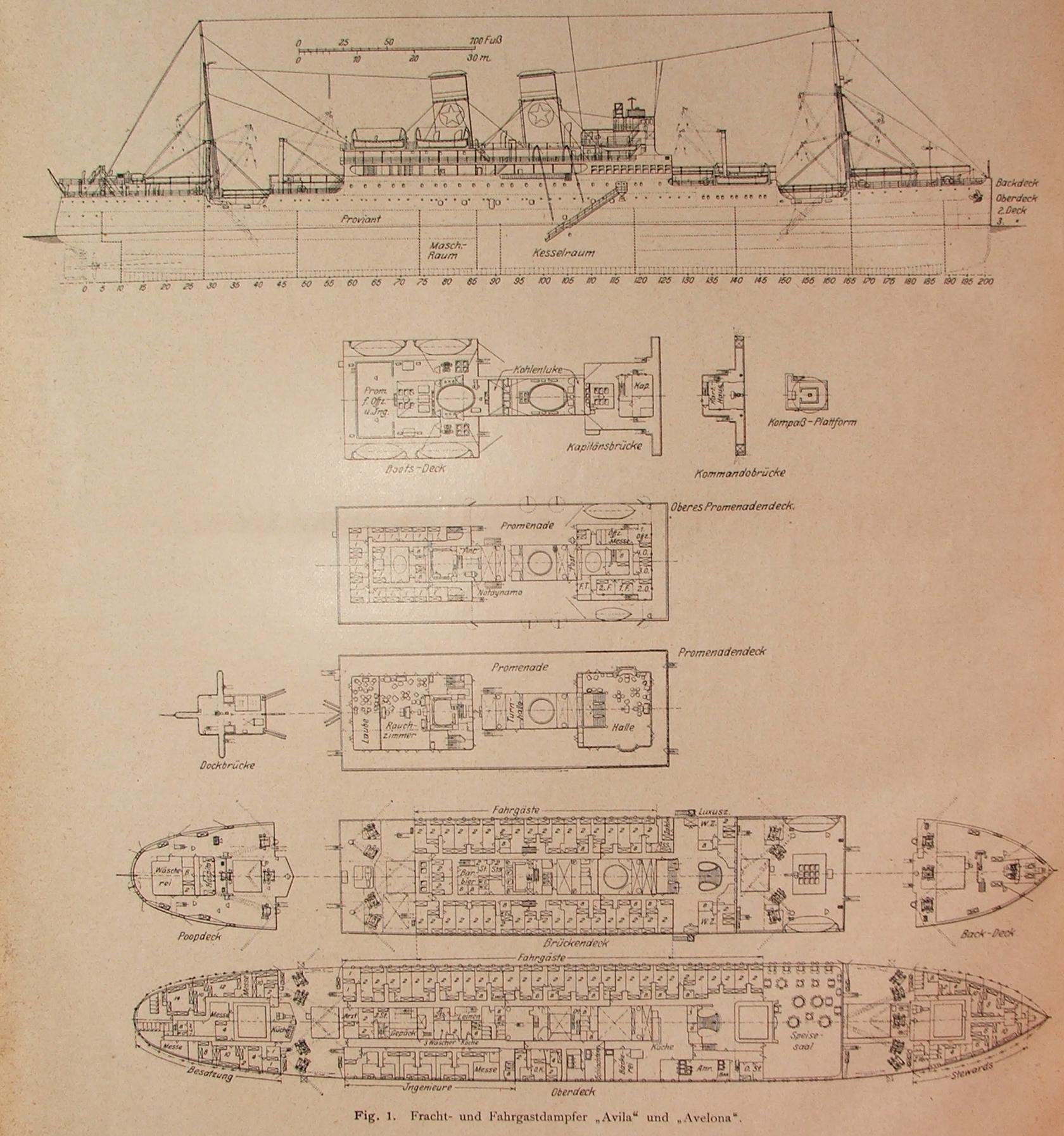
British South American Airways
British South American Airways (BSAA) was a state-run airline of the United Kingdom in the mid-to-late 1940s responsible for services to the Caribbean and South America. Originally named British Latin American Air Lines, it was renamed before services started in 1946. BSAA operated mostly Avro aircraft: Yorks, Lancastrians and Tudors and flew to Bermuda, the West Indies, Mexico and the western coast of South America. After two high-profile aircraft disappearances it was merged into the British Overseas Airways Corporation at the end of 1949. Most of BSAA's aircraft were given individual aircraft names beginning with "Star", which have long been used in long-range celestial navigation. History British Latin American Air Lines (BLAIR) was formed on 25 January 1944 by shipping interests ( Royal Mail Lines, Pacific Steam Navigation Company, Lamport & Holt Line, Booth Steamship Company and Blue Star Line) to complement the companies' shipping services to South America; at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Langley Airfield
Langley, also known as Langley Marish, is an area of Slough in Berkshire, England. It is east of Slough town centre and west of Charing Cross in Central London. It was a separate civil parish and village until the 1930s, when the built-up part of Langley was incorporated into Slough. Langley was in the historic county of Buckinghamshire, being transferred to the administrative county of Berkshire in 1974. Etymology The place-name Langley derives from the Middle English word ''lang'', meaning long, and '' lea'', a wood or clearing. Langley was formed of a number of clearings: George Green, Horsemoor Green, Middle Green, Sawyers Green and Shreding Green. They became the sites for housing which merged into one village centred on the parish church in St Mary's Road. The clearings are remembered in the names of streets or smaller green fields. ''Marish'' or ''Maries'' commemorates Christiana de Marecis who held the manor for a short time in the reign of Edward I. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
British Overseas Airways Corporation
British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) was the United Kingdom, British state-owned national airline created in 1939 by the merger of Imperial Airways and British Airways Ltd. It continued operating overseas services throughout World War II. After the passing of the Civil Aviation Act 1946, European and South American services passed to two further state-owned airlines, British European Airways (BEA) and British South American Airways (BSAA). BOAC absorbed BSAA in 1949, but BEA continued to operate British domestic and European routes for the next quarter century. The Civil Aviation Act 1971 merged BOAC and BEA, effective 31 March 1974, forming today's British Airways. History War years On 24 November 1939, BOAC was created by the (2 & 3 Geo. 6. c. 61) to become the British state airline, formed from the merger of Imperial Airways and British Airways Ltd. The companies had been operating together since war was declared on 3 September 1939, when their operations were eva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aerial Refueling
Aerial refueling ( en-us), or aerial refuelling ( en-gb), also referred to as air refueling, in-flight refueling (IFR), air-to-air refueling (AAR), and tanking, is the process of transferring aviation fuel from one aircraft (the tanker) to another (the receiver) while both aircraft are in flight. The two main refueling systems are '' probe-and-drogue'', which is simpler to adapt to existing aircraft and the '' flying boom'', which offers faster fuel transfer, but requires a dedicated boom operator station. The procedure allows the receiving aircraft to remain airborne longer, extending its range or loiter time. A series of air refuelings can give range limited only by crew fatigue/physical needs and engineering factors such as engine oil consumption. Because the receiver aircraft is topped-off with extra fuel in the air, air refueling can allow a takeoff with a greater payload which could be weapons, cargo, or personnel: the maximum takeoff weight is maintained by carrying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Civil Aviation Act 1946
Civil may refer to: *Civility, orderly behavior and politeness *Civic virtue, the cultivation of habits important for the success of a society *Civil (journalism) ''The Colorado Sun'' is an online news outlet based in Denver, Colorado. It launched on September 10, 2018, to provide long-form, in-depth coverage of news from all around Colorado. It was started with two years of funding from blockchain ventu ..., a platform for independent journalism * Civil (surname) See also * {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Heathrow Airport
Heathrow Airport , also colloquially known as London Heathrow Airport and named ''London Airport'' until 1966, is the primary and largest international airport serving London, the capital and most populous city of England and the United Kingdom. It is the largest of the six international airports in the London airport system (the others being Gatwick, Stansted, Luton, City and Southend). The airport is owned and operated by Heathrow Airport Holdings. In 2024, Heathrow was the busiest airport in Europe, the fifth-busiest airport in the world by passenger traffic and the second-busiest airport in the world by international passenger traffic. Heathrow was the airport with the most international connections in the world in 2024. Heathrow was founded as a small airfield in 1930 but was developed into a much larger airport after World War II. It lies west of Central London on a site that covers . It was gradually expanded over 75 years and now has two parallel east–west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pathfinder (RAF)
The Pathfinders were target-marking Squadron (aviation), squadrons in RAF Bomber Command during World War II. They located and marked targets with flares, at which a main bomber force could aim, increasing the accuracy of their bombing. The Pathfinders were normally the first to receive new blind-bombing aids such as Gee (navigation), Gee, Oboe (navigation), Oboe and the H2S radar. The early Pathfinder Force (PFF) squadrons were expanded to become a group, No. 8 Group RAF, No. 8 (Pathfinder Force) Group, in January 1943. The initial Pathfinder Force was five squadrons, whilst No 8 Group ultimately grew to a strength of 19 squadrons. Whereas the majority of Pathfinder squadrons and personnel were from the Royal Air Force, the group also included No 405 Squadron of the Royal Canadian Air Force as well as many individual airmen from the air forces of other Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth countries. History Background At the start of the Second World War in September 1939 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
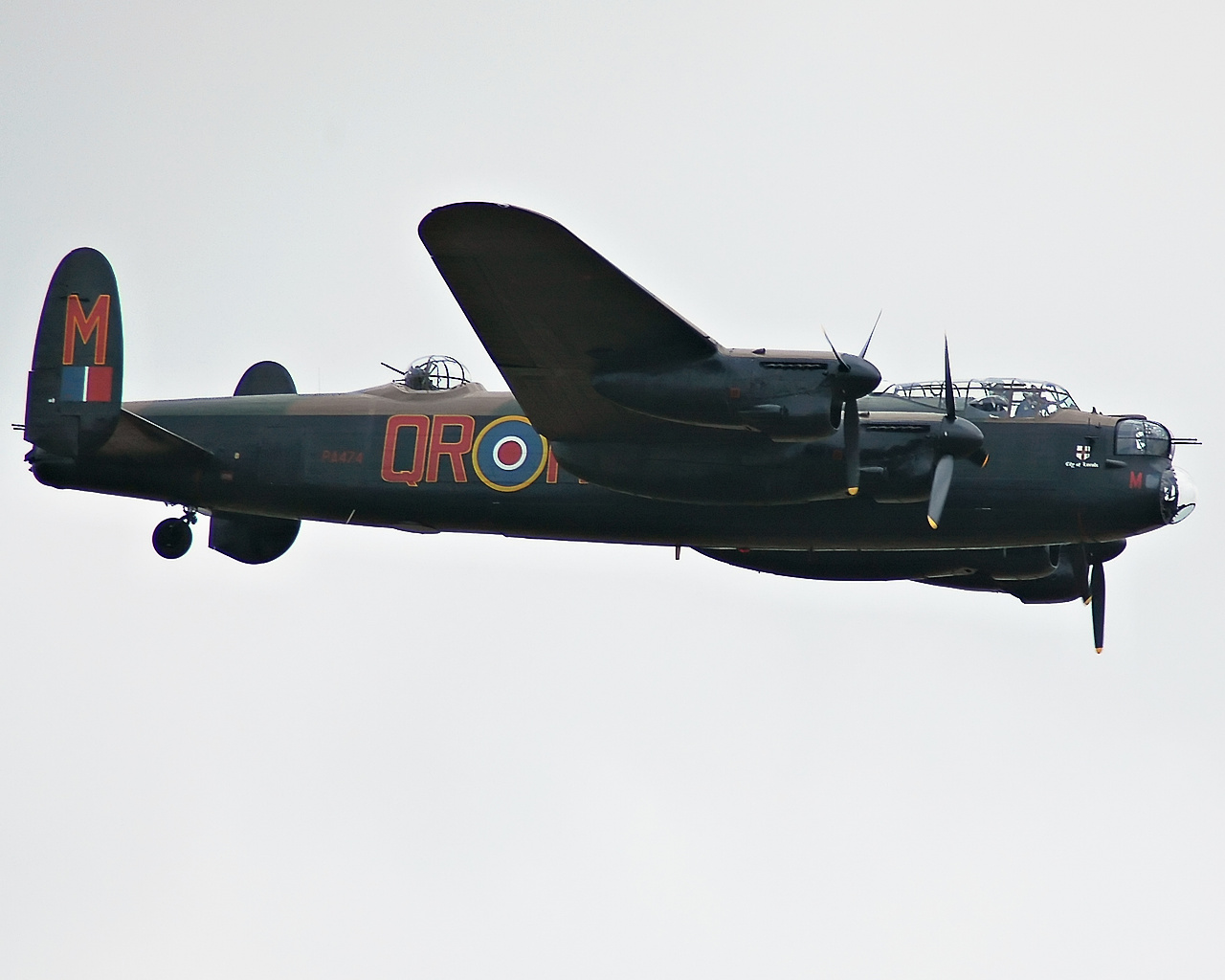
Avro Lancaster
The Avro Lancaster, commonly known as the Lancaster Bomber, is a British World War II, Second World War heavy bomber. It was designed and manufactured by Avro as a contemporary of the Handley Page Halifax, both bombers having been developed to the same specification, as well as the Short Stirling, all three aircraft being four-engined heavy bombers adopted by the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the same era. The Lancaster has its origins in the twin-engine Avro Manchester which had been developed during the late 1930s in response to the Air Ministry List of Air Ministry specifications, Specification P.13/36 for a medium bomber for "world-wide use" which could carry a torpedo internally, and make shallow dive-bombing attacks. Originally developed as an evolution of the Manchester (which had proved troublesome in service and was retired in 1942), the Lancaster was designed by Roy Chadwick and powered by four Rolls-Royce Merlins and in one of the versions, Bristol Hercules engines. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper ''The Sunday Times'' (founded in 1821), are published by Times Media, since 1981 a subsidiary of News UK, in turn wholly owned by News Corp. ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'' were founded independently and have had common ownership only since 1966. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. ''The Times'' was the first newspaper to bear that name, inspiring numerous other papers around the world. In countries where these other titles are popular, the newspaper is often referred to as or , although the newspaper is of national scope and distribution. ''The Times'' had an average daily circulation of 365,880 in March 2020; in the same period, ''The Sunday Times'' had an average weekly circulation of 647,622. The two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Blue Star Line
The Blue Star Line was a Merchant Navy (United Kingdom), British passenger and cargo shipping company formed in 1911, being in operation until 1998. Formation Blue Star Line was formed as an initiative by the Vestey Brothers, a Liverpool-based butchers company, who had founded the Union Cold Storage Company to take advantage of refrigeration practices. They developed a large importation business, shipping frozen meat from South America to Britain, initially from Argentina on ships of the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company, and other shipping lines that called at South American ports. The high prices charged for transport by these companies led the Vestey brothers to start to operate their own ships. They chartered their first ships from 1904, and began to buy their own ships from 1909 onwards. The Blue Star Line was officially inaugurated on 28 July 1911, initially using second-hand ships. They ordered their first new ship in 1914, and by the outbreak of the First World War were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Booth Steamship Company
Alfred Booth and Company was a British trading and shipping company, founded in 1866 and traded for more than a century. It was founded in Liverpool, England, by two brothers, Alfred and Charles Booth to export English light leather to the US. It grew into a significant merchant shipping company with its head office in Liverpool and interests in the United States and South America. The group was broken up in 1964 and the last Booth company from the group was sold in 1986. History Alfred and Charles Booth were cousins of William James Lamport, co-founder of the Liverpool shipping company Lamport and Holt Line, and worked in the company's office. In 1851 Lamport transferred minority shareholdings in a cargo steamship, the ''Nile'', to several associates including Charles Booth and George Holt. In 1854 Lamport, Holt, Booth and Holt's father, also called George Holt, all took minority shares in a new ship, the ''Orontes''. At the time it was common for a merchant ship to be in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lamport And Holt
Lamport and Holt was a UK merchant shipping line. It was founded as a partnership in 1845, reconstituted as a limited company in 1911 and ceased trading in 1991. From 1845 until 1975 Lamport and Holt was headquartered in Liverpool. The founders of Booth Line and Blue Funnel Line had family links with the original partners in Lamport and Holt, and worked for them before founding their own steamship lines in the 1860s. Lamport and Holt was an independent partnership until 1911, when it became a limited company and the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company (RMSP) took it over. RMSP collapsed as a result of the Royal Mail Case in 1931 but was reconstituted as Royal Mail Lines in 1932. Vestey Group bought Lamport and Holt in 1944 and absorbed it into its Blue Star Line subsidiary in 1991. For much of its history Lamport and Holt traded with the east coast of South America, operating liner services there to and from New York, Britain and mainland Europe. from 1902 to 1928 it operated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pacific Steam Navigation Company
The Pacific Steam Navigation Company () was a British commercial shipping company that operated along the Pacific coast of South America, and was the first to use steam ships for commercial traffic in the Pacific Ocean. At one point in the 1870s, it had the world's largest merchant steamship fleet. The company continued in business until 1965, when it was purchased by another company, but it survived in name through a succession of ownership changes until at least the 1980s. History The company was founded by William Wheelwright in London in 1838 and began operations in 1840 when two steam ships ''Chile'' and ''Peru'' were commissioned to carry mail. Early ports of call were Valparaíso, Coquimbo, Huasco, Copiapó, Cobija, Iquique, Arica, Islay Province, Islay, Pisco, Peru, Pisco and Callao. In 1846 the company expanded its routes to include Huanchaco, Lambayeque, Peru, Lambayeque, Paita, Guayaquil, Buenaventura, Valle del Cauca, Buenaventura and Panama City. The company eventu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |