|
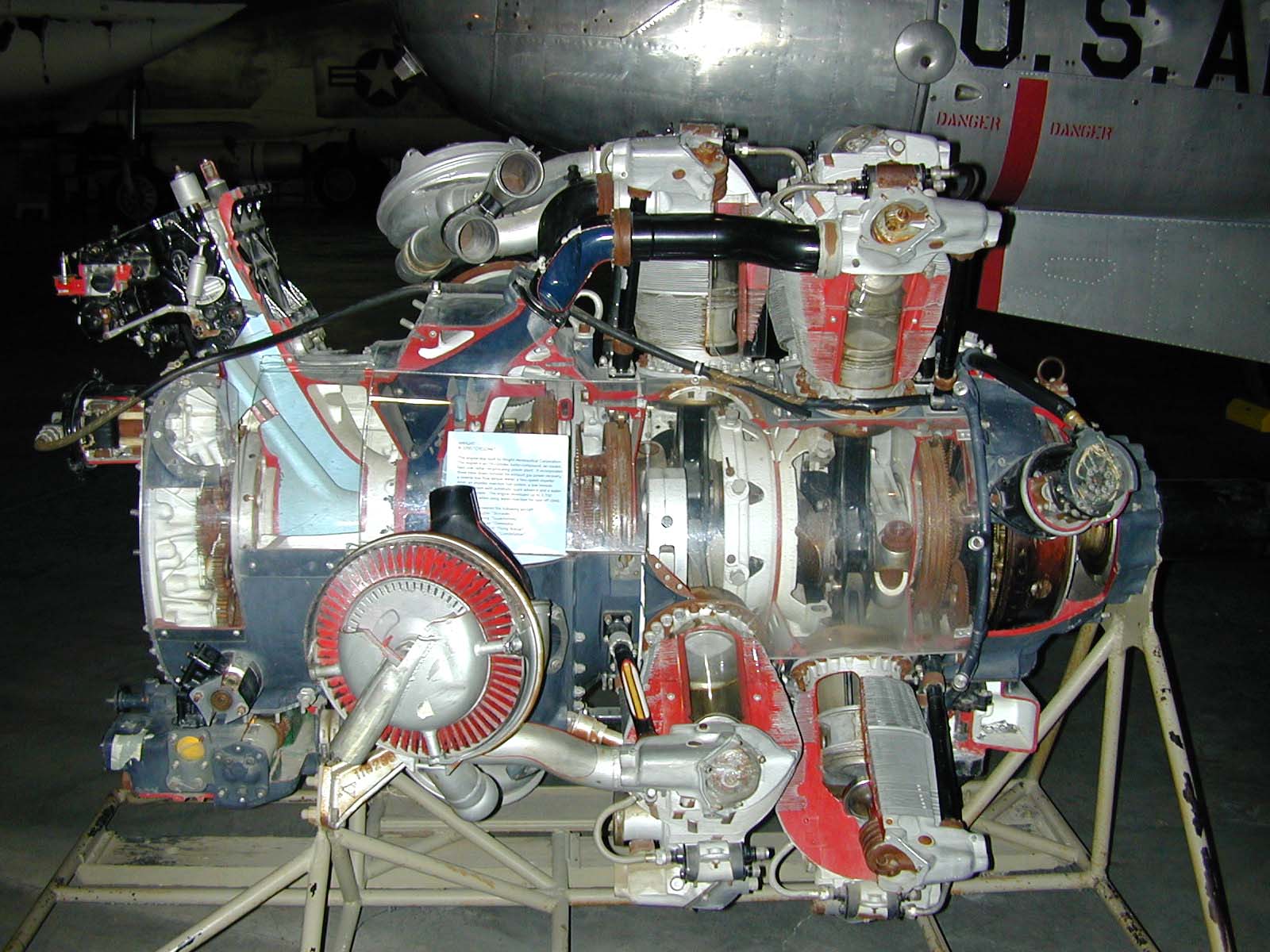
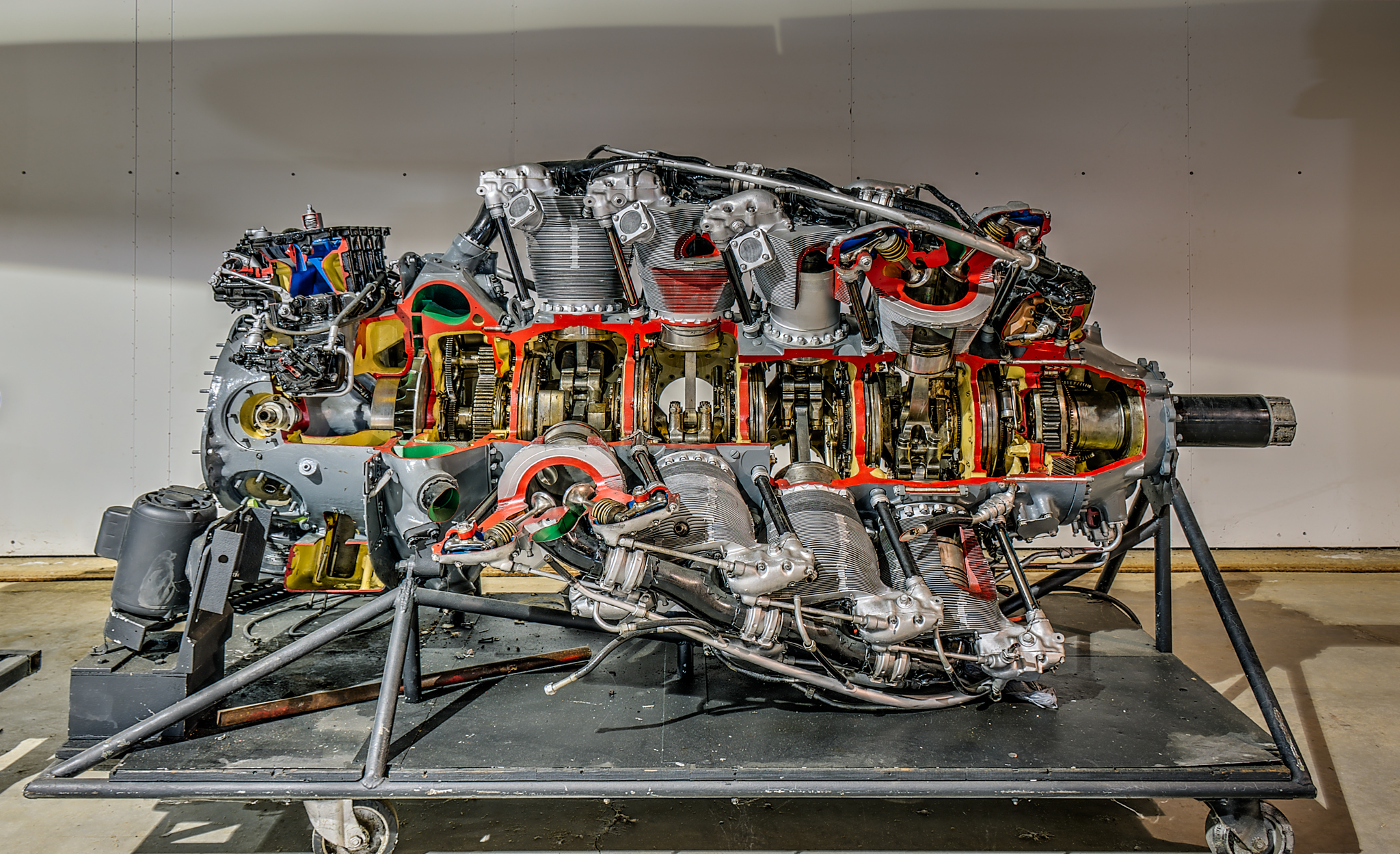
Bristol Centaurus
The Centaurus was the final development of the Bristol Engine Company's series of sleeve valve radial aircraft engines. The Centaurus is an 18-cylinder, two-row design that eventually delivered over . The engine was introduced into service late in the Second World War and was one of the most powerful aircraft piston engines to see service. Design and development Like other Bristol sleeve valve engines, the Centaurus was based on the design knowledge acquired from an earlier design, in this case the Bristol Perseus cylinder. The Centaurus used 18 Perseus cylinders. The same cylinder was in use in the contemporary 14-cylinder Hercules, which was being brought into production when the design of the Centaurus started. The Centaurus had a cylinder swept volume of , nearly as much as the American Wright R-3350 ''Duplex-Cyclone'' large radial, making the Centaurus one of the largest aircraft piston engines to enter production, while that of the Hercules was . The nearly 40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone
The Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone is an American twin-row, supercharged, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine with 18 cylinders displacing nearly . Power ranged from , depending on model. Developed before World War II, the R-3350's design required a long time to mature, and was still experiencing problems with reliability when used to power the Boeing B-29 Superfortress. After the war, the engine had matured sufficiently to be used in many civilian airliners, notably in its turbo-compound forms, and was used in the Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation airliners into the 1950s. Its main rival was the , Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major, which first ran some seven years after the Duplex-Cyclone. The engine is commonly used on Hawker Sea Fury and Grumman F8F Bearcat Unlimited Class Racers at the Reno Air Races. Design and development In 1927, Wright Aeronautical introduced its "Cyclone" engine, which powered a number of designs in the 1930s. After merging with Curtiss to become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Aircraft Establishment
The Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) was a British research establishment, known by several different names during its history, that eventually came under the aegis of the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), UK Ministry of Defence (MoD), before finally losing its identity in mergers with other institutions. The British Army Balloon Factory was established on Farnborough Common in the early 1900s. By 1912 it had come under civilian control and was the Royal Aircraft Factory (RAF) In 1918 it was renamed Royal Aircraft Establishment to prevent confusion with the newly created Royal Air Force. The first site was at Farnborough Airfield ("RAE Farnborough") in Hampshire to which was added a second site RAE Bedford (Bedfordshire) in 1946. On 1 May 1988 it was renamed the Royal Aerospace Establishment (RAE) before merging with other research entities to become part of the new Defence Research Agency in 1991. History In 1904–1906 the Army Balloon Factory, which was part of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impeller
An impeller, or impellor, is a driven rotor used to increase the pressure and flow of a fluid. It is the opposite of a turbine, which extracts energy from, and reduces the pressure of, a flowing fluid. Strictly speaking, propellers are a sub-class of impellers where the flow both enters and leaves axially, but in many contexts the term "impeller" is reserved for ''non''-propeller rotors where the flow enters axially and leaves radially, especially when creating suction in a pump or compressor. In pumps An impeller is a rotating component of a centrifugal pump that accelerates fluid outward from the center of rotation, thus transferring energy from the motor that drives the pump to the fluid being pumped. The acceleration generates output pressure when the outward movement of the fluid is confined by the pump casing. An impeller is usually a short cylinder with an open inlet (called an eye) to accept incoming fluid, vanes to push the fluid radially, and a splined, keyed, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octane Rating
An octane rating, or octane number, is a standard measure of a liquid fuel, fuel's ability to withstand Compression ratio, compression in an internal combustion engine without causing engine knocking. The higher the octane number, the more compression the fuel can withstand before detonating. Octane rating does not relate directly to the power output or the energy content of the fuel per unit mass or volume, but simply indicates the resistance to detonating under pressure without a spark. Whether a higher octane fuel improves or impairs an engine's performance depends on the design of the engine. In broad terms, fuels with a higher octane rating are used in higher-compression Petrol engine, gasoline engines, which may yield higher power for these engines. The added power in such cases comes from the way the engine is designed to compress the air/fuel mixture, and not directly from the rating of the gasoline. In contrast, fuels with lower octane (but higher cetane numbers) are idea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement (engine), displacement. It is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and increase power outputs, especially with reduced engine dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major
The Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major is an American 28-cylinder four-row radial engine, radial reciprocating engine, piston aircraft engine designed and built during World War II. At , it is the largest-displacement aviation piston engine to be mass-produced in the United States, and at the most powerful. First run in 1944, it was the last of the Pratt & Whitney Pratt & Whitney Wasp series, Wasp family, and the culmination of its maker's piston engine technology. The war was over before it could power airplanes into combat. It powered many of the last generation of large piston-engined aircraft before turbojets, but was supplanted by equivalent (and superior) powered turboprops (such as the Allison T56). Its main rival was the twin-row, 18-cylinder, nearly displacement, up to Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, first run some seven years earlier (May 1937). Design and development The R-4360 was a 28-cylinder (engine), cylinder four-row air-cooled radial engine. Each row of seven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
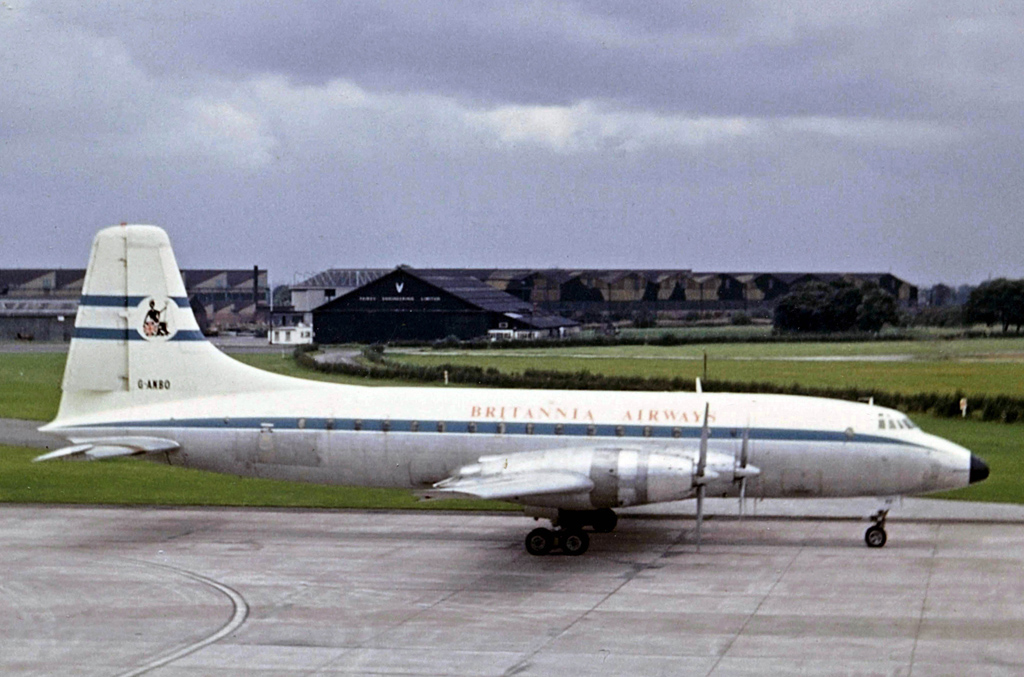
Bristol Orion
The Bristol Orion aero engine is a two-shaft turboprop intended for use in later marks of the Bristol Britannia and the Canadair CL-44. Although the engine was built and underwent a development program, the BE.25 Orion project was cancelled in 1958 by the British Ministry of Supply in favour of the Rolls-Royce Tyne.Turbojet History And Development 1930-1960 - Volume 1 Great Britain and Germany, Antony L. Kay 2007, The Crowood Press Ltd., , p.149 In addition, interest in turboprop-powered aircraft was beginning to wane, because of the successful introduction of the Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8 jetliners into airline service. The Orion gas generator had been chosen by French aircraft designer Wibault to power a vectored thrust aircraftPegasus The Heart of the Harrier, Andrew Dow, Pen & Sword Aviation 2009, , p.71/73 which ultimately became the Hawker Siddeley P.1127 but with a Bristol Siddeley Orpheus gas generator which had a compressor derived from the Orion low pressure compre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roy Fedden
Sir Alfred Hubert Roy Fedden MBE, FRAeS (6 June 1885 – 21 November 1973) was an engineer who designed most of Bristol Engine Company's successful piston aircraft engine designs. Early life Fedden was born in the Bristol area to fairly wealthy and influential parents. His older brother was the artist Romilly Fedden. Fedden's family was the first in the area to own a car, an interesting parallel with fellow engine designer, Harry Ricardo. This early influence almost certainly led to his future career. Fedden attended Clifton College, but did not do well scholastically and was known primarily for sports. After leaving, he declined to enter the Army, and announced he would apprentice as an engineer. Apprenticeship His apprenticeship was completed in 1906, and he immediately designed a complete car. He managed to convince the local firm of Brazil Straker to hire him, and the design was produced as the successful Shamrock. He remained at Brazil Straker over the following years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Proteus
The Bristol Proteus was the Bristol Engine Company's first mass-produced gas turbine engine design, a turboprop that delivered just over 4,000 hp (3,000 kW). The Proteus was a reverse-flow gas turbine. Because the second turbine drove no compressor stages, but only the propeller, this engine was classified as a Free-turbine turboshaft, free-turbine. It powered the Bristol Britannia airliner, small naval patrol craft, hovercraft and electrical generating sets. It was also used to power a land-speed record car, the Bluebird-Proteus CN7. After the merger of Bristol with Armstrong Siddeley the engine became the Bristol Siddeley Proteus, and later the Rolls-Royce Proteus. The Proteus was to have been superseded by the Bristol Orion which would have given a Britannia a 75% increase in power for cruising faster. Design and development The Proteus was to power a very large airliner for use after the war. Design work started in September 1944 with its free turbine and propelle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
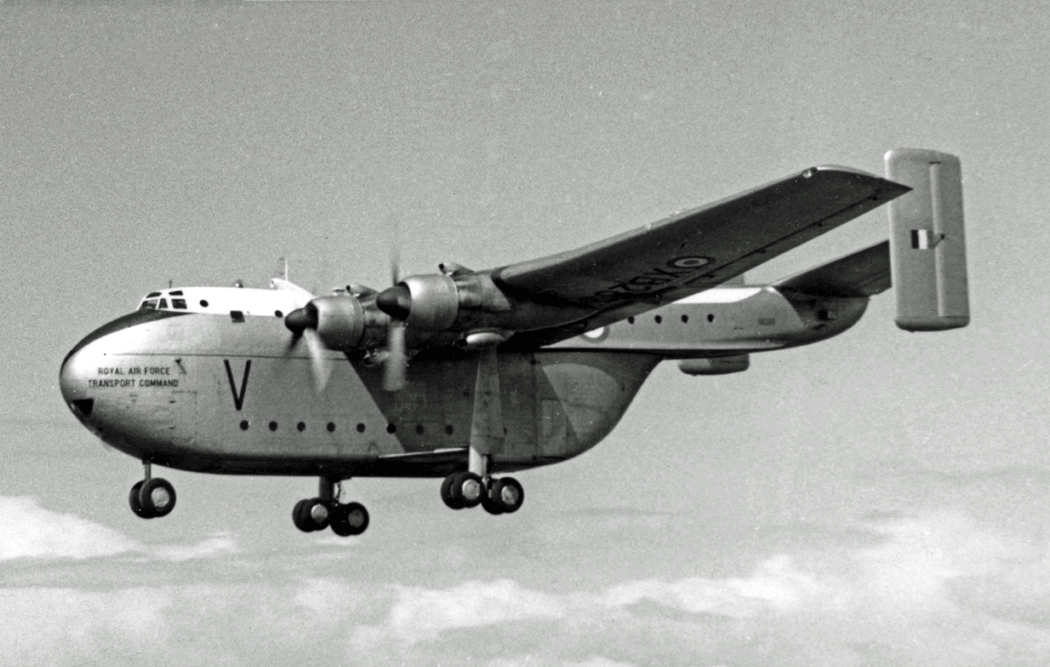
Blackburn Beverley
The Blackburn B-101 Beverley is a heavy transport aircraft produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Blackburn Aircraft. It was notably the only land-based transport aeroplane built by Blackburn, a company that otherwise specialised in producing naval fighter aircraft. The Beverley was originally designed by General Aircraft as the ''GAL.60 Universal Freighter'', reflecting its intended use by both military and civil operators. The design process had started during the Second World War, and drew upon the General Aircraft Hamilcar glider. A major design study was conducted in 1945, ahead of Specification C.3/46 being released by the Air Ministry. The company's proposal was accepted and the Air Ministry placed an order for one prototype. General Aircraft was absorbed by Blackburn during the late 1940s, who continued the project. On 20 June 1950, the first prototype conducted its maiden flight from the company's Brough facility; it was Britain's second largest landplane a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackburn Firebrand
The Blackburn Firebrand was a British single-engine strike fighter for the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy designed during World War II by Blackburn Aircraft. Originally intended to serve as a pure fighter aircraft, fighter, its unimpressive performance and the priority allocation by the Minister of Aircraft Production, Ministry of Aircraft Production of Napier Sabre engines to the Hawker Typhoon caused it to be redesigned with an alternative engine as a strike fighter to take advantage of its load-carrying capability. Development was slow and the first production aircraft was not delivered until after the end of the war. Only a few hundred were built before it was withdrawn from front-line service in 1953. Development In general, the Fleet Air Arm had required fighters that were capable of navigating long ranges over sea and speed differential over attackers was not critical. Defence of British naval bases was a RAF commitment but provision had not been made for this and so t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |