|
Bratschenköpfe
The Bratschenköpfe, consisting of the ''Großer Bratschenkopf'' () and ''Kleiner Bratschenkopf'' (), are two peaks in the Hochkönig massif in the Berchtesgaden Alps. The lie in the district of St. Johann im Pongau in the Austrian state of Salzburg. The Großer Bratschenkopf may be climbed on a trackless route from the north from the crossing between the Arthurhaus and the Matrashaus (grade: easy). The Kleiner Bratschenkopf to the east may be reached from the same route (grade I). Across the south face of the Großer Bratschenkopfs runs the climbing route known as ''Freier als Paul Preuß'' by Albert Precht (first climb, 1986, free solo Free solo climbing, or free soloing, is a form of rock climbing where the climber (or ''free soloist'') climbs Solo climbing, solo (or alone) without Climbing rope, ropes or other Rock climbing equipment#Protection devices, protective equipmen ..., grade VII, face height 900 metres). Literature * * Albert Precht: ''Alpenvereinsfüh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hochkönig (massif)
The Hochkönig is a mountain group containing the highest mountain (Hochkönig) in the Berchtesgaden Alps, Salzburgerland, Austria. The Berchtesgaden Alps form part of the Northern Limestone Alps. Location It lies to the west of the town of Bischofshofen in the Austrian state of Salzburg, 42 km due south of the city of Salzburg. Hochkönig is separated from the rest of the Berchtesgaden Alps, and more specifically from the Steinernes Meer (''stone ocean'') by the mountain pass '' Torscharte'' at 2246 m. The summit itself is at the southern edge of a large limestone plateau, which is covered by the glacier known as the " Übergossene Alm", however this glacier is currently shrinking at a rate of 6.2% per year, and is likely to vanish in the relatively near future. The edge of the summit plateau is surrounded by an almost circular chain of mountains: * Hochseiler, * Lammkopf, * Hochkönig, * Großer Bratschenkopf, * Kleiner Bratschenkopf, * Torsäule, * Schoberköpfe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
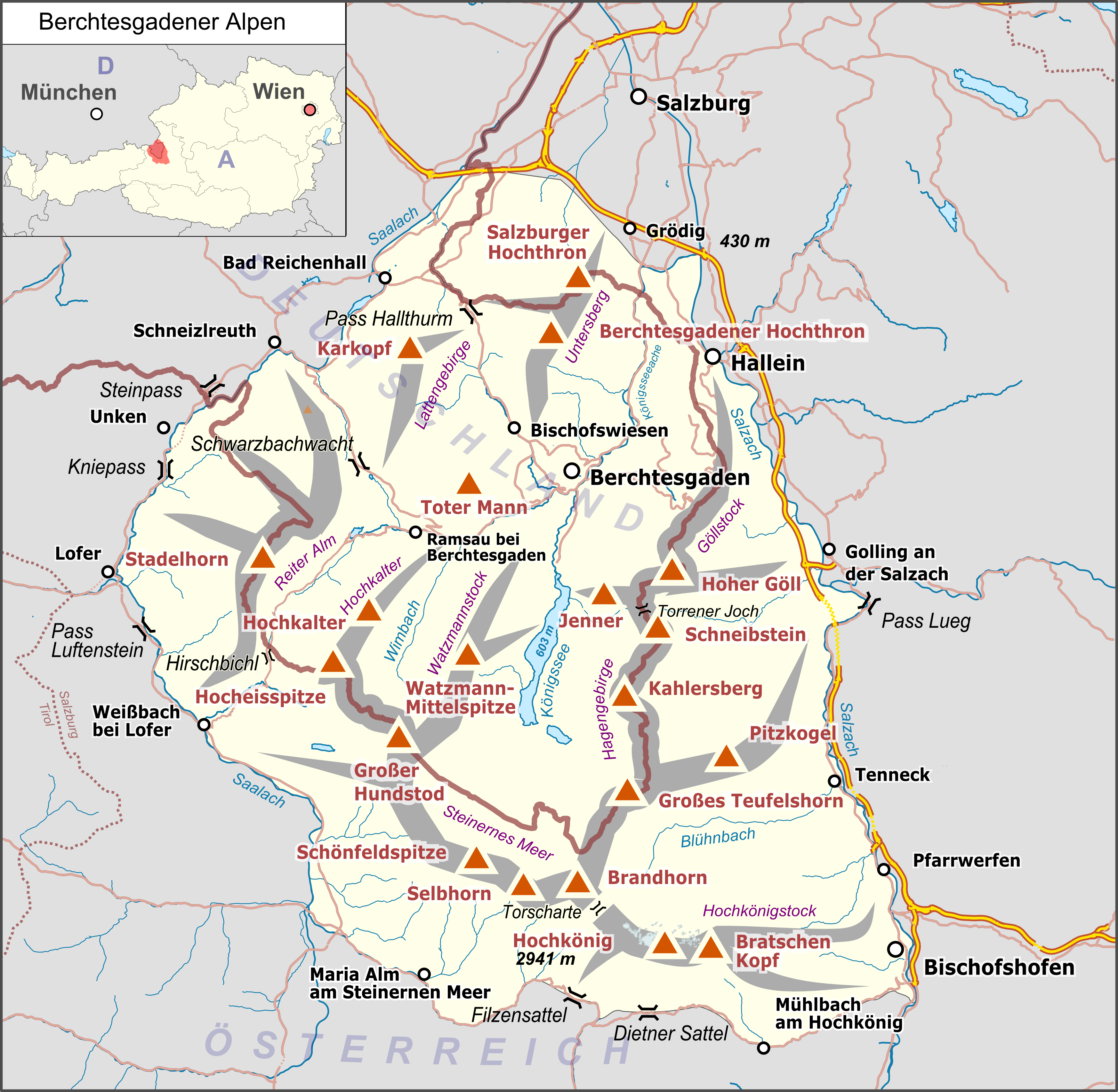
Berchtesgaden Alps
The Berchtesgaden Alps (, ) are a mountain range of the Northern Limestone Alps, named after the market town of Berchtesgaden located in the centre. It is crossed by the Austria–Germany border: the central part belongs to the Berchtesgadener Land district of southeastern Bavaria, Germany, while the adjacent area in the north, east and south is part of the Austrian state of Salzburg (state), Salzburg (''Salzburger Land''). Geography Mountains and lakes While the highest mountain of the Berchtesgaden Alps is the Hochkönig () located in the Austrian part, the best known peak is the Watzmann massif, the third-highest mountain of Germany at . The range also comprises the Obersalzberg slope east of Berchtesgaden, known for the former Berghof (residence), Berghof residence of Adolf Hitler. The picturesque heart is formed by the glacial Königssee lake with the famous St. Bartholomew's Church, Berchtesgaden, St. Bartholomew's pilgrimage church and the smaller Obersee (Königssee), O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Purtscheller
Ludwig Purtscheller (6 October 1849 – 3 March 1900) was an Austrian mountaineering, mountaineer and teacher. Purtscheller pioneered climbing without a mountain guide, who in the 19th century did all the route finding and lead climbing. By the end of his life he had recorded climbing over 1,700 mountains. A celebrated climb was the traverse of the Meije together with the Emil Zsigmondy, Zsigmondy brothers in 1885, which to this date is considered a classic alpine route. He is best known as the first European to ascend Kilimanjaro in 1889, together with the German mountaineer Hans Meyer (geologist), Hans Meyer. After a descent of the Aiguille du Dru with G. Löwenbach and Jakob Oberhollenzer on 25 August 1899, an ice axe broke and the rope team fell into a bergschrund. Purtscheller was injured and he was transferred to a hospital in Geneva and later Bern. After several months of recovery, he contracted pneumonia and died on the approximate date of his planned return home. In a e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bezirk St
The German term (; pl. ; derived from , "circle") translated as "district" can refer to the following types of administrative divisions: * , a subdivision of a city in the sense of a borough (e.g. in Berlin, Hamburg or Vienna), often again subdivided into several quarters and neighbourhoods. According to German ''Gemeindeordnung'' codes, the city council resolves upon the implementation by municipal by-law (''Satzung''). In some cities the have limited powers delegated to them by the city's local government, including an assembly resulting from local elections and an own 'mayor' (''Bürgermeister''). In the German states of Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate any municipality is authorized to implement ''Ortsbezirke'' with own advisory councils and local administrators. The state law in North Rhine-Westphalia commits the municipal administration of an independent city to subdivide the urban area into . * In Austria, the word is used with different meanings in three different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city and state. Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has Austrians, a population of around 9 million. The area of today's Austria has been inhabited since at least the Paleolithic, Paleolithic period. Around 400 BC, it was inhabited by the Celts and then annexed by the Roman Empire, Romans in the late 1st century BC. Christianization in the region began in the 4th and 5th centuries, during the late Western Roman Empire, Roman period, followed by the arrival of numerous Germanic tribes during the Migration Period. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; , also known as ''Salzburgerland''; ) is an Austrian federal state. In German it is called a , a German-to-English dictionary translates that to ''federal state'' and the European Commission calls it a ''province''. In German, its official name is , to distinguish it from its eponymous capital Salzburg. For centuries, it was an independent Prince-Bishopric of the Holy Roman Empire. It borders Germany and Italy. Geography Location Salzburg State covers an area of . It stretches along its main river — the Salzach – which rises in the Central Eastern Alps in the south to the Alpine foothills in the north. It is located in the north-west of Austria, close to the border with the German state of Bavaria; to the northeast lies the federal state Upper Austria; to the east the federal state Styria; to the south the federal states Carinthia and Tyrol. With 561,714 inhabitants, it is one of the country's smaller federal states in terms of population. Running through the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climbing Grade
Many climbing routes have grades for the technical difficulty, and in some cases for the risks, of the route. The first ascensionist can suggest a grade but it will be amended for the ''consensus view'' of subsequent ascents. While many countries with a tradition of climbing developed their own grading systems, a small number of grading systems have become internationally dominant for each type of climbing, and which has led to the standardization of grading worldwide. Over the years, grades have consistently risen in all forms of climbing, helped by improvements in climbing technique and equipment. In free climbing (i.e. climbing rock routes with no aid), the most popular grading systems are the French numerical or sport system (e.g. f7c+), the American YDS system (e.g. 5.13a), and latterly the UIAA scale (e.g. IX+). These systems grade technical difficulty being the main focus of the lower-risk activity of sport climbing. The American system adds an R/X suffix to tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climbing Route
A climbing route () is a path by which a Climbing, climber reaches the top of a mountain, a rock face or an ice-covered obstacle. The details of a climbing route are recorded in a climbing guidebook and/or in an online climbing-route database. Details recorded will include elements such as the type of climbing route (e.g. bouldering route, sport climbing route, traditional climbing route, ice climbing route, and alpine climbing route, etc.), the Grade (climbing), difficulty grade of the route–and beta (climbing), beta on its crux (climbing), crux(es)–and any risk or commitment grade, the length and number of pitch (climbing), pitches of the route, and the climbing equipment (e.g. climbing protection gear) that is needed to complete the route. There are definitions as to what is a valid ascent of a route (e.g. the redpoint (climbing), redpoint in rock climbing), and the class or style of ascent (e.g. onsighted, flash (climbing), flashed). The coveted first ascent (FA), first f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Preuß
Paul Preuss (spelled Preuß in German; pronounced ''Proyce'') (19 August 1886 – 3 October 1913) was an Austrian alpinist who achieved recognition for his bold solo ascents and for his advocacy of an ethically "pure" alpinism. He is an important figure in the history of rock climbing. Early years Paul Preuss was born in the mountain town of Altaussee, Austria, on 19 August 1886. His father, Eduard, a Hungarian of Jewish descent, taught music; his mother, Caroline Lauchheim, an Alsatian, had been a private tutor for a baron. They met when Eduard was engaged to give Caroline's wards music lessons. Based in Vienna, Eduard Preuss and his family (including two older sisters, Sophie and Mina) spent summers in Altaussee, following the migratory patterns of the vacationing Viennese upper class that employed him. As a boy, Preuss would often accompany his father, an amateur botanist, on his rambles throughout the local mountains of Altaussee. Never a robust child, at the age of six, Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Solo
Free solo climbing, or free soloing, is a form of rock climbing where the climber (or ''free soloist'') climbs Solo climbing, solo (or alone) without Climbing rope, ropes or other Rock climbing equipment#Protection devices, protective equipment, using only their climbing shoes and their liquid chalk, climbing chalk. Free soloing is the most dangerous form of climbing, and, unlike bouldering, free soloists climb above safe heights, where a fall can be fatal. Though many climbers have free soloed Grade (climbing), climbing grades they are very comfortable on, only a tiny group free solo regularly, and at grades closer to the limit of their abilities. Some climbers' profiles have been increased by free soloing (e.g. Alex Honnold and John Bachar), but others question the ethics of this, and whether the risks they are undertaking should be encouraged and commercially rewarded. "Free solo" was originally a term of climber slang, but after the popularity of the 2018 Academy Awards, Os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |