|
Bragny-sur-Saône
Bragny-sur-Saône (, literally ''Bragny on Saône'') is a commune in the Saône-et-Loire department in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France. History BC From 530 to 450 or 440 BC there was considerable trade conducted in this area between the Hallstatt people and the Greeks. Mediterranean pottery, including amphorae from Massalia, as well as artefacts from Attica, and polychrome glass have all been found in large numbers here. Trade eased up for a while in the early 5th century BC but soon sprung back into life. Artefacts from northern Italy, as well as Golaseccan pottery were found from this time onwards, along with more Massiliot amphorae. 17th Century In August 1636, the soldiers of Matthias Gallas burned the village center, church, and part of the château. Rebuilding was needed, and it was the Count of Thiard who had most of it done since the population were too poor. By 1690, most residents lived in small brick and mud houses, roofed with tile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of The Saône-et-Loire Department
The following is a list of the 563 communes of the Saône-et-Loire department of France France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan .... The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Périmètre des groupements en 2025 BANATIC. Accessed 28 May 2025. * Communauté urbaine Creusot Montceau * Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontus De Tyard
Pontus de Tyard (also Thyard, Thiard) (c. 1521 – 23 September 1605) was a French poet and priest, a member of " La Pléiade". Life He was born at Bissy-sur-Fley in Burgundy, of which he was ''seigneur'', but the exact year of his birth is uncertain. He became a friend of Antoine Héroet and Maurice Scève. His first published work, ''Erreurs amoureuses'' 1549, was augmented with other poems in successive editions till 1573. His work anticipated that of Pierre de Ronsard and Joachim du Bellay. He was one of the first to write sonnets in the French language (preceded by Clément Marot and Mellin de Saint-Gelais). He is also said to have introduced the ''sestina'', originally a Provençal invention, into French poetry. Tyard contributed to the poetic and metaphysical program of La Pléiade by elaborating, in his ''Solitaire Premier, ou Prose des Muses, et de la fureur poétique'' (1552), a full theory of divine fury, derived in large part from the Latin translations an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
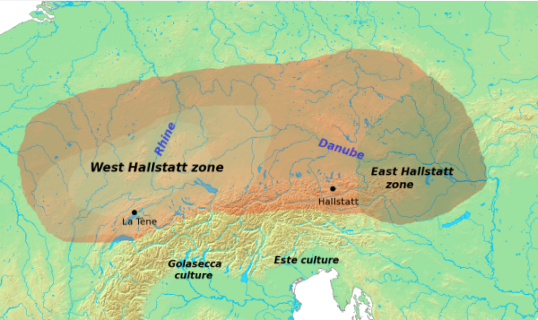
Hallstatt Culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe (Hallstatt C, Hallstatt D) from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC (Bronze Age Europe, Late Bronze Age) and followed in much of its area by the La Tène culture. It is commonly associated with Proto-Celtic speaking populations. It is named for its type site, Hallstatt, a lakeside village in the Austrian Salzkammergut southeast of Salzburg, Austria, Salzburg, where there was a rich salt mine, and some 1,300 burials are known, many with fine artifacts. Material from Hallstatt has been classified into four periods, designated "Hallstatt A" to "D". Hallstatt A and B are regarded as Late Bronze Age and the terms used for wider areas, such as "Hallstatt culture", or "period", "style" and so on, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attica
Attica (, ''Attikḗ'' (Ancient Greek) or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the entire Athens metropolitan area, which consists of the city of Athens, the capital city, capital of Greece and the core city of the metropolitan area, as well as its surrounding suburban cities and towns. It is a peninsula projecting into the Aegean Sea, bordering on Boeotia to the north and Megaris to the west. The southern tip of the peninsula, known as Laurion, Lavrio, was an important Mines of Laurion, mining region. The history of Attica is closely linked with that of Athens. In ancient times, Attica corresponded with the Athens city-state. It was the most prominent region in Ancient Greece, specifically during the Golden Age of Athens in the Classical Greece, classical period. Classical Athens, Ancient Attica (the classical Classical Athens, Athens city-state) was divided into deme, demoi, or municipalities, from the reform of Cleisthenes in 508/7 BC, gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château
A château (, ; plural: châteaux) is a manor house, or palace, or residence of the lord of the manor, or a fine country house of nobility or gentry, with or without fortifications, originally, and still most frequently, in French-speaking regions. Nowadays, a ''château'' may be any stately residence built in a French style; the term is additionally often used for a winegrower's estate, especially in the Bordeaux region of France. Definition The word château is a French word that has entered the English language, where its meaning is more specific than it is in French. The French word ''château'' denotes buildings as diverse as a medieval fortress, a Renaissance palace and a fine 19th-century country house. Care should therefore be taken when translating the French word ''château'' into English, noting the nature of the building in question. Most French châteaux are "palaces" or fine " country houses" rather than "castles", and for these, the word "château" is appropr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthias Gallas
Matthias Gallas, Graf von Campo und Herzog von Lucera (Count of Campo, Duke of Lucera) (Matteo Gallasso; 17 October 1588 in Trento – 25 April 1647 in Vienna) was an Italian professional soldier during the Thirty Years' War. He distinguished himself in the first half of the war in service of the Catholic League (German), Catholic League, in the War of the Mantuan Succession, and as one of Albrecht von Wallenstein's Generals. After carrying out the dismissal and elimination of Wallenstein, Gallas became acting supreme commander of the Imperial Army of the Holy Roman Emperor, Imperial Army three times between 1634 and 1647 but he never held the function or authority of a Generalissimo. He was a principal architect of the Battle of Nördlingen (1634), victory of Nördlingen 1634 but his following campaigns were less successful. After leading ineffective offensives against France, he managed to end Swedish attacks on Electorate of Saxony, Saxony and to drive them back to the Baltic S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golasecca Culture
The Golasecca culture (9th – 4th centuries BC) was a Prehistoric Italy#Bronze Age, Late Bronze Age/Prehistoric Italy#Iron Age, Early Iron Age culture in northern Italy, whose type-site was excavated at Golasecca in the province of Varese, Lombardy, where, in the area of Monsorino at the beginning of the 19th century, Abbot Giovanni Battista Giani made the first findings of about fifty graves with pottery and metal objects. The culture's material evidence is scattered over a wide area of 20,000 km2Raffaele de Marinis, ''Liguri e Celto-Liguri'' in ''Italia. Omniun terrarum alumna'', Garzanti-Scheiwiller, 1988. south of the Alps, between the rivers Po (river), Po, Serio (river), Serio and Sesia, and bordered on the north by the Alpine passes. Archaeological sources The name of the Golasecca culture comes from the first findings that were discovered from excavations conducted from 1822 at several locations in the Comune of Golasecca, by the antiquarian abbot Father Giovann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land border, as well as List of islands of Italy, nearly 800 islands, notably Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares land borders with France to the west; Switzerland and Austria to the north; Slovenia to the east; and the two enclaves of Vatican City and San Marino. It is the List of European countries by area, tenth-largest country in Europe by area, covering , and the third-most populous member state of the European Union, with nearly 59 million inhabitants. Italy's capital and List of cities in Italy, largest city is Rome; other major cities include Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo, Bologna, Florence, Genoa, and Venice. The history of Italy goes back to numerous List of ancient peoples of Italy, Italic peoples—notably including the ancient Romans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychrome
Polychrome is the "practice of decorating architectural elements, sculpture, etc., in a variety of colors." The term is used to refer to certain styles of architecture, pottery, or sculpture in multiple colors. When looking at artworks and architecture from antiquity and the European Middle Ages, people tend to believe that they were monochrome. In reality, the pre-Renaissance past was full of colour, and Greco-Roman sculptures and Gothic cathedrals, that are now white, beige, or grey, were initially painted in a variety of colours. As André Malraux stated: "Athens was never white but her statues, bereft of color, have conditioned the artistic sensibilities of Europe ..the whole past has reached us colorless." Polychrome was and is a practice not limited only to the Western world. Non-Western artworks, like Chinese temples, Oceanian Uli figures, or Maya ceramic vases, were also decorated with colours. Ancient Near East Similarly to the ancient art of other regions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
A () is a level of administrative divisions of France, administrative division in the France, French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipality, municipalities in Canada and the United States; ' in Germany; ' in Italy; ' in Spain; or civil parishes in the United Kingdom. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlet (place), hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the Municipal arrondissem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massalia
Massalia (; ) was an ancient Greek colonisation, Greek colony (''apoikia'') on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast, east of the Rhône. Settled by the Ionians from Phocaea in 600 BC, this ''apoikia'' grew up rapidly, and its population set up many outposts for trading in modern-day Spain, Corsica and Liguria. Massalia persisted as an independent colony until the Roman campaign in Gaul in the 1st Century BC. The ruins of Massalia still exist in the contemporary city of Marseille, which is considered the oldest city of France and one of Europe's oldest continuously inhabited settlements. History Massalia was established ca. 600 BC by Ionian Greeks, Ionian Greek settlers from Phocaea, in Western Anatolia. After the capture of Phocaea by the Persians in 545 BC, a new wave of settlers fled towards the colony. A creation myth telling the meeting between the Greeks and the local population is given by Aristotle and Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus, Pompeius Trogus (see founding myth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saône
The Saône ( , ; ; ) is a river in eastern France (modern Regions of France, region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté). It is a right tributary of the Rhône, rising at Vioménil in the Vosges (department), Vosges Departments of France, department and joining the Rhône in Lyon, at the southern end of the Presqu'île. Terminology The name derives from that of the Celtic mythology, Gallic river goddess Souconna (mythology), Souconna, which has also been connected with a local Celts, Celtic tribe, the Sequani, Sequanes. Monk, Monastic copyists progressively transformed ''Souconna'' to ''Saoconna'', which ultimately gave rise to . The other recorded ancient names for the river were and . The name ''Arar'' later gave rise to specific regional terms in historiography, created to designate various northern parts of History of Burgundy, historical Burgundy in relation to the river Saône. Depending on the point of view of a particular author, northern Burgundian lands were thus designated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |