|
Brachioradialis Muscle
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way of the brachioradialis tendon, and to the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus. Structure The brachioradialis is a superficial, fusiform muscle on the lateral side of the forearm. It originates proximally on the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus. It inserts distally on the radius, at the base of its styloid process. Near the elbow, it forms the lateral limit of the cubital fossa, or elbow pit. Nerve supply Despite the bulk of the muscle body being visible from the anterior aspect of the forearm, the brachioradialis is a posterior compartment muscle and consequently is innervated by the radial nerve. Of the muscles that receive innervation from the radial nerve, it is one of only four that receive input directly from the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Supracondylar Ridge
The lateral supracondylar ridge is a prominent, rough margin on the lower part of the lateral border of the humerus. It presents an anterior lip for the origin of forearm extensors, including the brachioradialis muscle above, and the extensor carpi radialis longus muscle below. It also presents a posterior lip for the triceps brachii, and an intermediate ridge for the attachment of the lateral intermuscular septum. Clinical significance The lateral supracondylar ridge may be broken in a supracondylar humerus fracture, common in children A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking .... References External links * Image at u-szeged.hu Humerus {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
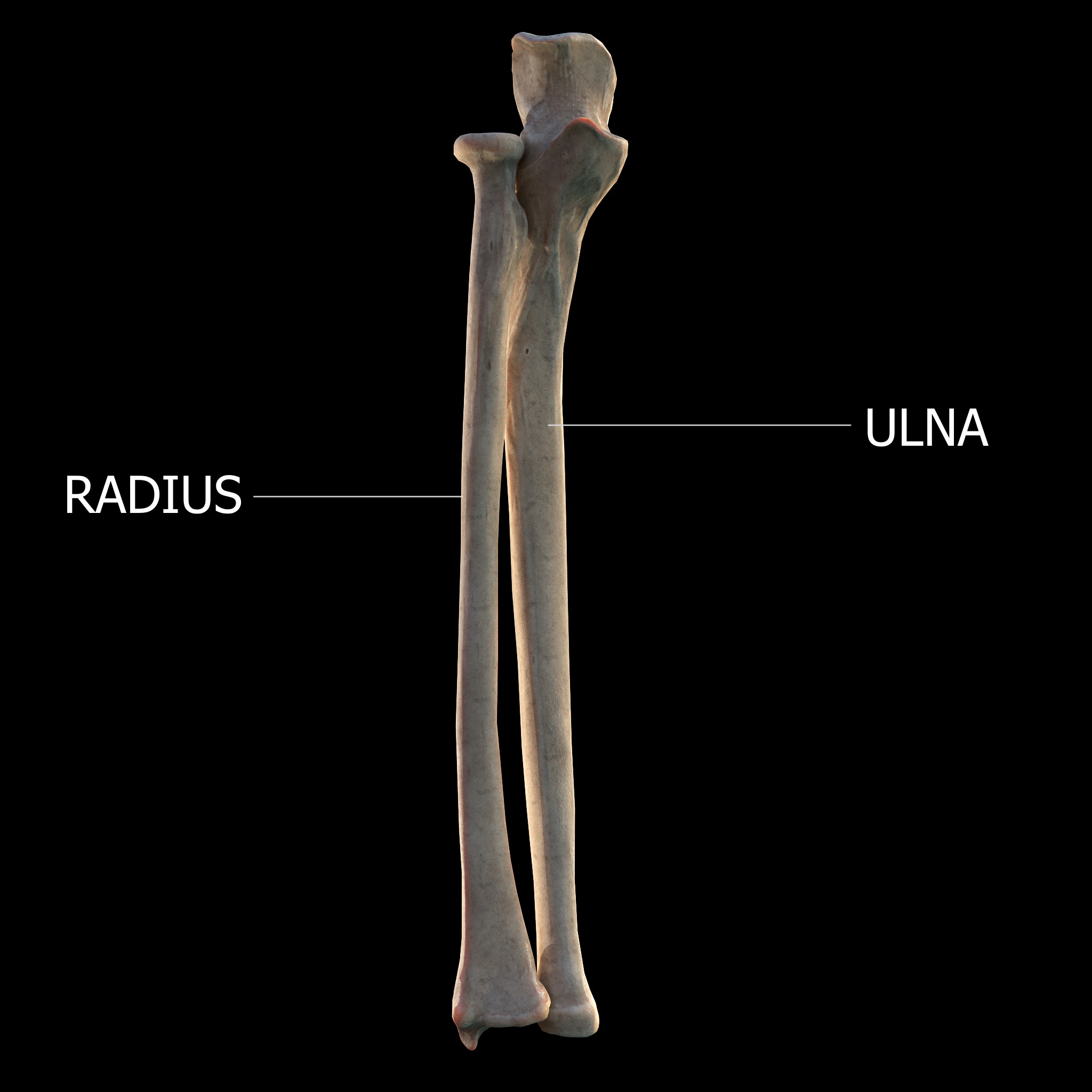
Radial Styloid Process
The radial styloid process is a projection of bone on the lateral surface of the distal radius bone. Structure The radial styloid process is found on the lateral surface of the distal radius bone. It extends obliquely downward into a strong, conical projection. The tendon of the brachioradialis attaches at its base. The radial collateral ligament of the wrist attaches at its apex. The lateral surface is marked by a flat groove for the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis. Clinical significance Breakage of the radius at the radial styloid is known as a Chauffeur's fracture; it is typically caused by compression of the scaphoid bone of the hand against the styloid. De Quervain syndrome causes pain over the styloid process of the radius. This is due to the passage of the inflamed extensor pollicis brevis tendon and abductor pollicis longus tendon around it. The styloid process of the radius is a useful landmark during arthroscopic resec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forearm Pronators
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the forearm can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbow Flexors
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates it is not used. In those cases, forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the humerus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachialis
The brachialis (brachialis anticus) is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow. It lies beneath the biceps brachii, and makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa (elbow pit). It originates from the anterior aspect of the distal humerus; it inserts onto the tuberosity of the ulna. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, and commonly also receives additional innervation from the radial nerve."Brachialis Muscle." Kenhub. Kenhub, Aug. 2001 The brachialis is the prime mover of elbow flexion generating about 50% more power than the biceps.Saladin, Kenneth S, Stephen J. Sullivan, and Christina A. Gan. Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. 2015. Print. Structure Origin The brachialis originates from the anterior surface of the distal half of the humerus, near the insertion of the deltoid muscle, which it embraces by two angular processes. Its origin extends below to within 2.5 cm of the margin of the articular surface of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . Just as a linear force is a push or a pull applied to a body, a torque can be thought of as a twist applied to an object with respect to a chosen point; for example, driving a screw uses torque to force it into an object, which is applied by the screwdriver rotating around its axis to the drives on the head. Historical terminology The term ''torque'' (from Latin , 'to twist') is said to have been suggested by James Thomson and appeared in print in April, 1884. Usage is attested the same year by Silvanus P. Thompson in the first edition of ''Dynamo-Electric Machinery''. Thompson describes his usage of the term as follows: Today, torque is referred to using d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximal Radioulnar Articulation
The proximal radioulnar articulation, also known as the proximal radioulnar joint (PRUJ), is a synovial pivot joint between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. Structure The proximal radioulnar joint is a synovial pivot joint. It occurs between the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament. The interosseous membrane of the forearm and the annular ligament stabilise the joint. A number of nerves run close to the proximal radioulnar joint, including: *median nerve The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has cont ... * musculocutaneous nerve * radial nerve See also * Distal radioulnar articulation * Supination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Motion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biceps Brachii
The biceps or biceps brachii (, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle belly which is attached to the upper forearm. While the long head of the biceps crosses both the shoulder and elbow joints, its main function is at the elbow where it flexes and supinates the forearm. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps screws in the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out (flexion). Structure The biceps is one of three muscles in the anterior compartment of the upper arm, along with the brachialis muscle and the coracobrachialis muscle, with which the biceps shares a nerve supply. The biceps muscle has two heads, the short head and the long head, distinguished according to their origin at the coracoid process and supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, respectively. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Branch Of The Radial Nerve
The radial nerve divides into a superficial (sensory) and deep (motor) branch at the cubital fossa. The deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the supinator In human anatomy, the supinator is a broad muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm, curved around the upper third of the radius (bone), radius. Its function is to supination, supinate the forearm. Structure The supinator consists of tw ..., and is prolonged downward between the superficial and deep layers of muscles, to the middle of the forearm. The deep branch provides motor function to the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm, which is mostly the extensor muscles of the hand. The radial nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The posterior cord takes nerves from the upper, lower, and middle trunk, so ultimately the radial nerve is formed from the anterior rami of C5 through T1. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
The extensor carpi radialis longus is one of the five main muscles that control movements at the wrist. This muscle is quite long, starting on the lateral side of the humerus, and attaching to the base of the second metacarpal bone (metacarpal of the index finger). Structure It originates from the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus, from the lateral intermuscular septum, and by a few fibers from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. The fibers end at the upper third of the forearm in a flat tendon, which runs along the lateral border of the radius, beneath the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis; it then passes beneath the dorsal carpal ligament, where it lies in a groove on the back of the radius common to it and the extensor carpi radialis brevis, immediately behind the styloid process. One of the three muscles of the radial forearm group, it initially lies beside the brachioradialis, but becomes mostly tendon early on. Passing between the brachi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anconeus Muscle
The anconeus muscle (or anconaeus/anconæus) is a small muscle on the posterior aspect of the elbow joint. Some consider anconeus to be a continuation of the triceps brachii muscle. Some sources consider it to be part of the posterior compartment of the arm, while others consider it part of the posterior compartment of the forearm. The anconeus muscle can easily be palpated just lateral to the olecranon process of the ulna. Structure Anconeus originates on the posterior surface of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts distally on the superior posterior surface of the ulna and the lateral aspect of the olecranon. Innervation Anconeus is innervated by a branch of the radial nerve (cervical roots 7 and 8) from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus called the nerve to the anconeus. The somatomotor portion of radial nerve innervating anconeus bifurcates from the main branch in the radial groove of the humerus. This innervation pattern follows the rules of innervat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |