|
Boudica
Boudica or Boudicca (, from Brittonic languages, Brythonic * 'victory, win' + * 'having' suffix, i.e. 'Victorious Woman', known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh language, Welsh as , ) was a queen of the Iceni, ancient British Iceni tribe, who led a Boudican revolt, failed uprising against the Roman Britain, conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. She is considered a British national heroine and a symbol of the struggle for justice and independence. Boudica's husband Prasutagus, with whom she had two daughters, ruled as a nominally independent ally of Rome. He left his kingdom jointly to his daughters and to the Roman emperor in his Will and testament, will. When he died, his will was ignored, and the kingdom was annexed and his property taken. According to the Roman historian Tacitus, Boudica was Flagellation, flogged and her daughters wartime sexual violence, raped. The historian Cassius Dio wrote that previous imperial donations to influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boudican Revolt
The Boudican revolt was an armed uprising by native Celtic Britons against the Roman Empire during the Roman conquest of Britain. It took place circa AD 60–61 in the Roman province of Britain, and it was led by Boudica, the Queen of the Iceni tribe. The uprising was motivated by the Romans' failure to honour an agreement they had made with Boudica's husband, Prasutagus, regarding the succession of his kingdom upon his death, and by the brutal mistreatment of Boudica and her daughters by the occupying Romans. Although heavily outnumbered, the Roman army led by Gaius Suetonius Paulinus decisively defeated the allied tribes in a final battle which inflicted heavy losses on the Britons. The location of this battle is not known. It marked the end of resistance to Roman rule in most of the southern half of Great Britain, a period that lasted until AD 410. Modern historians are dependent for information about the uprising and the defeat of Boudica on the narratives written by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
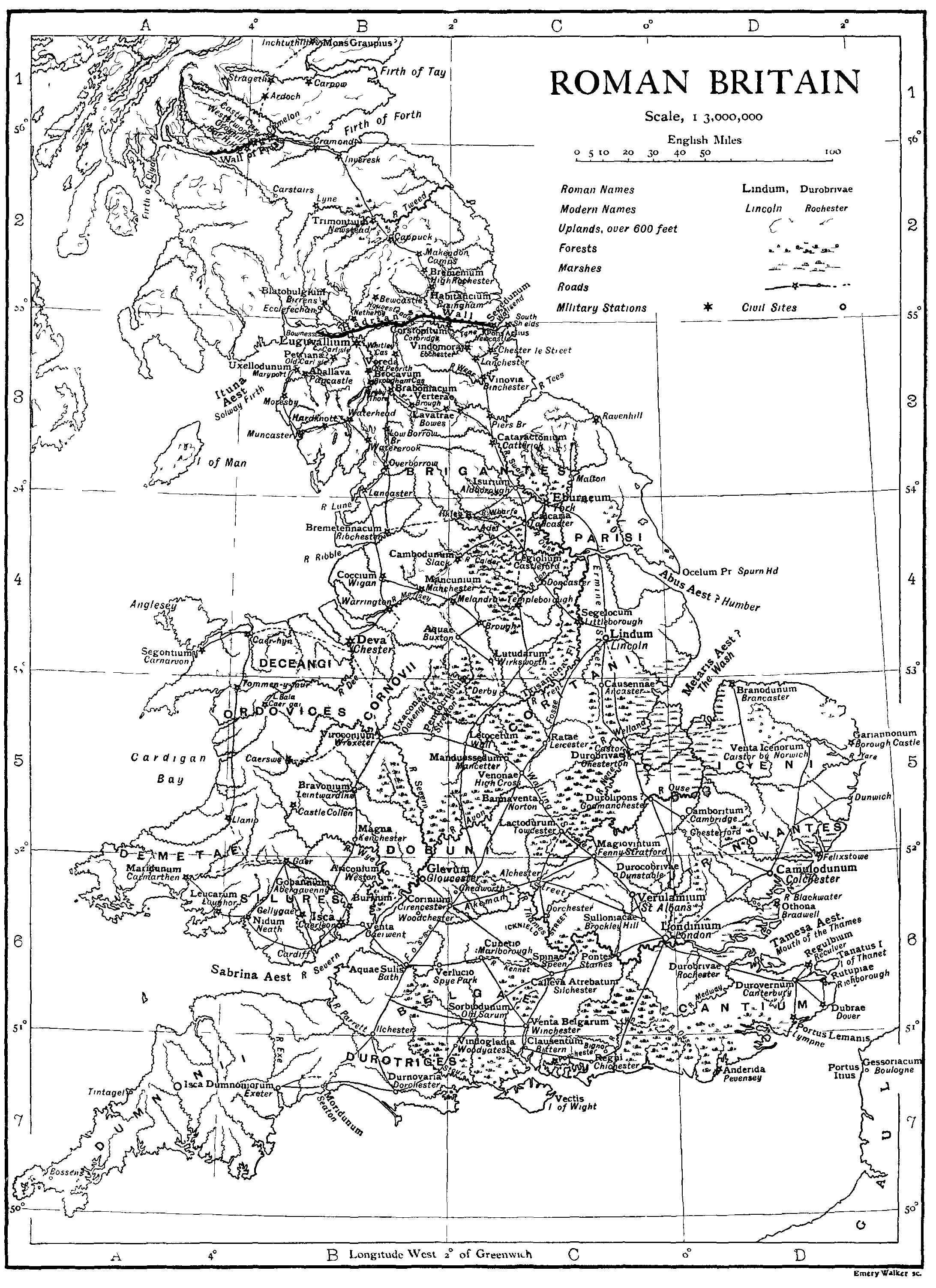
Camulodunum
Camulodunum ( ; ), the Roman Empire, Ancient Roman name for what is now Colchester in Essex, was an important Castra, castrum and city in Roman Britain, and the first capital of the province. A temporary "wikt:strapline, strapline" in the 1960s identifying it as the "oldest recorded town in Britain" has become popular with residents and is still used on heritage roadsigns on trunk road approaches.McWhirr, Alan (1988) Roman Crafts and Industries. Published by Shire Publications LTD. () Originally the site of the Brythonic-Celtic oppidum of Camulodunon (meaning "stronghold of Camulos"), capital of the Trinovantes and later the Catuvellauni tribes, it was first mentioned by name on coinage minted by the chieftain Tasciovanus some time between 20 and 10 BC. The Roman town began life as a Castra, Roman legionary base constructed in the AD 40s on the site of the Brythonic-Celtic fortress following its conquest by the Emperor Claudius. After the early town was destroyed during the Boudic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Londinium
Londinium, also known as Roman London, was the capital of Roman Britain during most of the period of Roman rule. Most twenty-first century historians think that it was originally a settlement established shortly after the Roman conquest of Britain, Claudian invasion of Britain, on the current site of the City of London, around 47–50 AD, but some defend an older view that the city originated in a defensive enclosure constructed during the Claudian invasion in 43 AD. Its earliest securely-dated structure is a timber drain of 47 AD. It had almost certainly been granted colony () status prior to the complete replanning of the city's street plan attending the erection of the great second forum around the year 120.Merrifieldp. 68./ref> By this time, Britain's provincial administration had also almost certainly been moved to Londinium from Camulodunum (now Colchester in Essex). The precise date of this change is unknown, and no surviving source explicitly states that Londinium w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceni
The Iceni ( , ) or Eceni were an ancient tribe of eastern Britain during the British Iron Age, Iron Age and early Roman Britain, Roman era. Their territory included present-day Norfolk and parts of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, and bordered the area of the Corieltauvi to the west, and the Catuvellauni and Trinovantes to the south. In the Roman period, their capital was Venta Icenorum at modern-day Caistor St Edmund. Julius Caesar does not mention the Iceni in his account of his Caesar's invasions of Britain, invasions of Britain in 55 and 54 BC, though they may be related to the Cenimagni, whom Caesar notes as living north of the River Thames at that time. The Iceni were a significant power in eastern Britain during Claudius' Roman conquest of Britain, conquest of Britain in AD 43, following which they allied with Rome. Increasing Roman influence on their affairs led to revolt in AD 47, though they remained nominally independent under king Prasutagus until his death around AD 60. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by the Belgae during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. The Belgae were the only Celtic tribe to cross the sea into Britain, for to all other Celtic tribes this land was unknown. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells () according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his death in AD 68. Nero was born at Antium in AD 37, the son of Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus (father of Nero), Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus and Agrippina the Younger (great-granddaughter of the emperor Augustus). Nero was three when his father died. By the time Nero turned eleven, his mother married Emperor Claudius, who then Adoption in ancient Rome, adopted Nero as his heir. Upon Claudius' death in AD 54, Nero ascended to the throne with the backing of the Praetorian Guard and the Senate. In the early years of his reign, Nero was advised and guided by his mother Agrippina, his tutor Seneca the Younger, and his praetorian prefect Sextus Afranius Burrus, but sought to rule independently and rid himself of restraining influences. The power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boadicea Haranguing The Britons
''Boadicea Haranguing the Britons'' is a 1793 history painting by the British artist John Opie. It depicts the Boudica the queen of the Ancient British Iceni tribe who led an ultimately unsuccessful uprising against the Roman Empire during the first century. She is portrayed in a white robe and red cloak, a bright figure in a dark composition. Her two daughters shelter behind her for protection as she rallies her supporters. Her poised aristocratic manner contrasts to the depiction of her as a battlefield warrior in Henry Courtney Selous's 1840 painting of the same title. An engraving based on Opie's painting produced by William Sharp is now in the National Portrait Gallery National Portrait Gallery may refer to: * National Portrait Gallery (Australia), in Canberra * National Portrait Gallery (Sweden), in Mariefred *National Portrait Gallery (United States), in Washington, D.C. *National Portrait Gallery, London ....https://www.npg.org.uk/collections/search/portrait/mw56 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Suetonius Paulinus
Gaius Suetonius Paulinus (fl. AD 40–69) was a Roman general best known as the commander who defeated Boudica and her army during the Boudican revolt. Early life Little is known of Suetonius' family, but it likely came from Pisaurum (modern Pesaro), a town on the Adriatic coast of Italy. Mauretanian campaign Having served as ''praetor'' in 40 AD, Suetonius was appointed governor of Mauretania (modern northern Morocco) the following year. In collaboration with Gnaeus Hosidius Geta, he suppressed the revolt led by Aedemon in the mountainous province that arose from the execution of the local ruler by Caligula. In 41 AD Suetonius was the first Roman commander to lead troops across the Atlas Mountains, and Pliny the Elder quotes his description of the area in his ''Natural History''. Governor of Britain In 58 AD, before being consul,A. R. Birley, "Suetonius Paullinus, Gaius (fl. c.AD 40–69)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prasutagus
Prasutagus (died AD 60 or 61) was king of the Iceni, a British Celtic tribe who inhabited roughly what is now Norfolk, in the 1st century AD. He is best known as the husband of Boudica. Prasutagus may have been one of the eleven kings who surrendered to Claudius following the Roman conquest in 43, or he may have been installed as king following the defeat of a rebellion of the Iceni in 47. As an ally of Rome his tribe were allowed to remain nominally independent, albeit disarmed, and to ensure this Prasutagus named the Roman emperor as co-heir to his kingdom, along with his two daughters. Tacitus says he lived a long and prosperous life, but when he died, the Romans ignored his will and took over, depriving the nobles of their lands and plundering the kingdom. Boudica was flogged and their daughters raped. Roman financiers called in their loans. All this led to the revolt of the Iceni, under the leadership of Boudica, in 60 or 61. Coins have been found in Suffolk inscribed SV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio IX Hispana
Legio IX Hispana ("9th Hispanian Legion"), also written as Legio VIIII Hispana, was a legion of the Imperial Roman army that existed from the 1st century BC until at least AD 120. The legion fought in various provinces of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. The nickname "Hispana" was gained when it was stationed in Hispania under Augustus. It was stationed in Britain following the Roman invasion in AD 43. The legion disappears from surviving Roman records after and there is no specific account of what happened to it. The unknown fate of the legion has been the subject of considerable research and speculation. One theory (per historian Theodor Mommsen) was that the legion was wiped out in action in northern Britain soon after AD 108, the date of the latest datable inscription of the Ninth found in Britain, perhaps during a rising of northern tribes against Roman rule. This view was popularised by the 1954 novel '' The Eagle of the Ninth'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history of ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the subsequent founding of Rome (753 BC), the formation of the Republic (509 BC), and the creation of the Empire (27 BC) up until 229 AD, during the reign of Severus Alexander. Written in Koine Greek over 22 years, Dio's work covers approximately 1,000 years of history. Many of his books have survived intact, alongside summaries edited by later authors such as Xiphilinus, a Byzantine monk of the 11th century, and Zonaras, a Byzantine chronicler of the 12th century. Biography Lucius Cassius Dio was the son of Cassius Apronianus, a Roman senator and member of the Cassia gens, who was born and raised at Nicaea in Bithynia. Byzantine tradition maintains that Dio's mother was the daughter or sister of the Greek orator and philosopher, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars. Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' (Latin: ) and the ''Histories'' (Latin: ), originally formed a continuous narrative of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus (14 AD) to the end of Domitian’s reign (96 AD). The surviving portions of the Annals focus on the reigns of Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). Tacitus's other writings discuss oratory (in dialogue format, see ), Germania (in ''De origine et situ Germanorum''), and the life of his father-in-law, Agricola (the general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain), mainly focusing on his campaign in Britannia ('' De vita et moribus Iulii Agricolae''). Tacitus's ''Histories'' offers insights into Roman attitudes towards Jews, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |