|
Botond (warrior)
Botond (''Bothond'' or ''Bontond'') was a Hungarian legendary warrior and folk hero in the 10th century, a participant of the Hungarian invasions of Europe. According to a legend, he took part in a Hungarian campaign against the Byzantine Empire in 958 or 959. At the walls of Constantinople, he broke down the Golden Gate with an axe and defeated a Greek warrior in wrestling. Social status Botond's name and deeds are preserved by narrative sources only which were compiled centuries later, therefore the circumstances of his existence and military career are unclear and questionable. The anonymous author of the ''Gesta Hungarorum'' (early 13th century) writes that Botond was a tribal chieftain, thus a member of the upper elite, whose father Kölpény (''Culpun'') was the uncle of Tas, one of the seven chieftains of the Magyars. Anonymus claims that Grand Prince Árpád handed over the area of Bodrog along the river Vajas in the southern lands to Tas and Kölpény during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicon Pictum P036 Botond Monda
In historiography, a ''chronicon'' is a type of chronicle or annals. Examples are: * ''Chronicon'' (Eusebius) * ''Chronicon'' (Jerome) *''Chronicon Abbatiae de Evesham'' *'' Chronicon Burgense'' *'' Chronicon Ambrosianum'' *''Chronicon Compostellanum'' *'' Chronicon Gothanum'' *''Chronicon Helveticum'' *''Chronicon Holtzatiae'' *''Chronicon Iriense'' *''Chronicon Lethrense'' *''Chronicon Lusitanum'' *''Chronicon Paschale'' *''Chronicon Pictum'' *''Chronicon Roskildense'' *''Chronicon Salernitanum'' *''Chronicon Scotorum'' *''Chronicon complutense'' *''Chronicon terrae Prussiae ''Chronicon terræ Prussiæ'' () is a chronicle of the Teutonic Knights, by Peter of Dusburg, finished in 1326. The manuscript is the first major chronicle of the Teutonic Order in Prussia and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, completed some 100 yea ...'' Chronicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicon Pictum
The ''Chronicon Pictum'' or ''Illuminated Chronicle'' (, , , also referred to as the ''Illustrated Chronicle'', ''Chronica Hungarorum'', ''Chronicon Hungarie Pictum'', ''Chronica Picta'' or ''Chronica de Gestis Hungarorum'') is a medieval illustrated chronicle from the Kingdom of Hungary from the 14th century. It represents the artistic style of the royal court of King Louis I of Hungary. The codex is a unique source of art, medieval and cultural history. The chronicle's full name is: ''Chronicon Pictum – Marci de Kalt Chronica de Gestis Hungarorum'' (Illustrated Chronicle – Mark of Kalt's Chronicle About the Deeds of the Hungarians). History of the chronicle King Louis I of Hungary commissioned the ''Chronicon Pictum'' and the ''Secretum Secretorum'', which were both produced in a Hungarian workshop. Miklόs Meggyesi, son of Hertul the court painter of Louis, has traditionally been identified as the illuminator, though there is no real evidence for this. The Illuminated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taksony Of Hungary
Taksony (, also Taxis or Tocsun; before or around 931 – early 970s) was the Grand Prince of the Hungarians after their catastrophic defeat in the 955 Battle of Lechfeld. In his youth he had participated in plundering raids in Western Europe, but during his reign the Hungarians only targeted the Byzantine Empire. The ''Gesta Hungarorum'' recounts that significant Muslim and Pecheneg groups settled in Hungary under Taksony. Early life Taksony was the son of Zoltán, according to the ''Gesta Hungarorum'' (written around 1200). The same source adds that Taksony's mother was an unnamed daughter of Menumorut, a local ruler defeated by the conquering Hungarians shortly before 907. Its unknown author also says that Taksony was born "in the year of Our Lord's incarnation 931". The ''Gesta Hungarorum'' reports that Zoltán abdicated in favor of Taksony in 947, three years before his own death. However, modern historians have challenged existing information on Taksony's early li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Musala, , in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria. The concept of the Balkan Peninsula was created by the German geographer August Zeune in 1808, who mistakenly considered the Balkan Mountains the dominant mountain system of southeastern Europe spanning from the Adriatic Sea to the Black Sea. In the 19th century the term ''Balkan Peninsula'' was a synonym for Rumelia, the parts of Europe that were provinces of the Ottoman E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine VII
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Byzantine emperor of the Macedonian dynasty, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Karbonopsina, and the nephew of his predecessor Alexander. Most of his reign was dominated by co-regents: from 913 until 919 he was under the regency of his mother, while from 920 until 945 he shared the throne with Romanos Lekapenos, whose daughter Helena he married, and his sons. Constantine VII is best known for the '' Geoponika'' (τά γεοπονικά), an important agronomic treatise compiled during his reign, and three, perhaps four, books; (bearing in Greek the heading Πρὸς τὸν ἴδιον υἱὸν Ῥωμανόν), (Περὶ τῆς Βασιλείου Τάξεως), '' De Thematibus'' (Περὶ θεμάτων Άνατολῆς καὶ Δύσεως), and '' Vita Basilii'' (Βίος Βασιλείου), though his authorship of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Byzantine Emperors
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the List of Byzantine usurpers, various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title. The following list starts with Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor, who rebuilt the city of Byzantium as an imperial capital, Constantinople, and who was regarded by the later emperors as the model ruler. Modern historians distinguish this later phase of the Roman Empire as Byzantine due to the imperial seat moving from Rome to Byzantium, the Empire's integration of Christianity, and the predominance of Greek instead of Latin. The Byzantine Empire was the direct legal continuation of the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
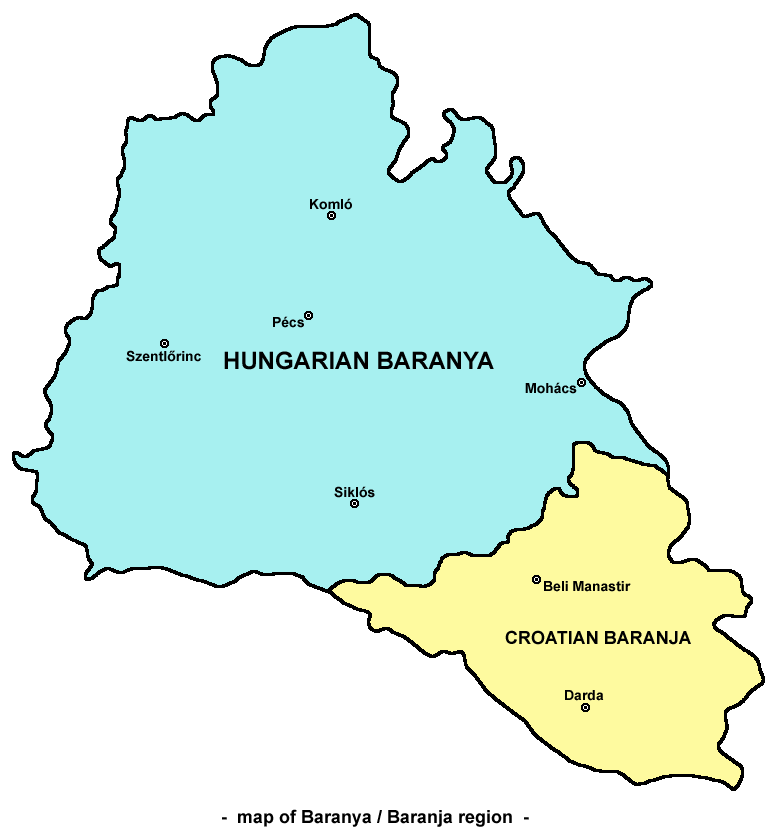
Baranya (region)
Baranya or Baranja (, ; , ) is a geographical and list of historical regions of Central Europe, historical region between the Danube and the Drava rivers located in the Pannonian Plain. Its territory is divided between Hungary and Croatia. In Hungary, the region is included in Baranya (county), Baranya county, while in Croatia, it is part of Osijek-Baranja county. Name The name of the region come from the Slavic languages, Slavic word 'bara', which means 'marsh', 'bog', thus the name of Baranya means 'marshland'. Even today large parts of the region are swamps, such as the natural reservation Kopački Rit in its southeast. Another theory states that the name of the region comes from the , an adaptation of Proto-Slavic language, Proto-Slavic 'ram'. History Historically, the region of Baranya was part of the Roman Empire, the Huns, Hunnic Empire, the Kingdom of the Ostrogoths, the Kingdom of the Lombards, the Avars (Carpathians), Avar Kingdom, the Frankish Empire, the Balaton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyula Moravcsik
Gyula (Julius) Moravcsik (Budapest, 29 January 1892 – Budapest, 10 December 1972), who usually wrote just as Gy. Moravcsik, was a Hungarian professor of Greek philology and Byzantine history who in 1967 was awarded the Pour le Mérite for Sciences and Arts. Scholarship Moravcsik explored in depth the relationship between Byzantium and the Turkic peoples, broadly defined and so including Hungarians, and this was reflected in the two volumes of ''Byzantinoturcica'' and the 1953 ''Bizánc és a Magyarság'' (Byzantium and the Magyars).Ritoók, Zsigmond. (1997"The contribution of Hungary to international classical scholarship" '' Hungarian Studies'', 12Archived here./ref> With R.J.H. Jenkins, he produced the critical and translated edition of Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus' '' De Administrando Imperio''. That work was first published in Budapest, 1949, and later at Dumbarton Oaks. Moravcsik also contributed to the later ''Commentary'', also in the Dumbarton Oaks series. Family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drava
The Drava or Drave (, ; ; ; ; ), historically known as the Dravis or Dravus, is a river in southern Central Europe.''Utrata Fachwörterbuch: Geographie - Englisch-Deutsch/Deutsch-Englisch'' by Jürgen Utrata (2014). Retrieved 10 Apr 2014. With a length of ,Joint Drava River Corridor Analysis Report , 27 November 2014 or , if the length of its Sextner Bach source is added, it is the fifth or sixth longest tributary of the |
Bálint Hóman
Bálint Hóman (29 December 1885 – 2 June 1951) was a Hungarian scholar and politician who served as Minister of Religion and Education twice: between 1932 and 1938 and between 1939 and 1942. He died in prison in 1951 for his support of the fascistic invasion of the Soviet Union and antisemitic legislation activity as part of the Axis alliance in World War II. Academic career He was born into a Roman Catholic family. He finished his studies in Budapest. He started his career when he was still a student, working for the University Library of Budapest. He was appointed director of the National Széchényi Library in 1922, and of the Hungarian National Museum in 1923, a position he held until 1932. Hóman produced several serious scholarly works. The centre of his research was the history of the Hungarian nation during the Middle Ages. Initially he dealt with economic history, social history and the auxiliary sciences of history. He wrote about Hungarian towns during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kylfings
The Kylfings (Old Norse ''Kylfingar''; Finnic languages, Estonian ''Kalevid''; Hungarian language, Hungarian ''Kölpények''; Old East Slavic Колбяги, ''Kolbiagi''; Byzantine Greek Κουλπίγγοι, ''Koulpingoi''; Arabic ''al-Kilabiyya'') were a people of uncertain origin active in Northern Europe during the Viking Age, roughly from the late ninth century to the early twelfth century. They could be found in areas of Lapland (Sweden), Lapland, Russia, and the Byzantine Empire that were frequented by Scandinavian traders, raiders and mercenaries. Scholars differ on whether the Kylfings were ethnically Finnic languages, Finnic or Norsemen, Norse. Also disputed is their geographic origin, with Denmark, Sweden and the Eastern Baltic region, Baltic all put forward as candidates. Whether the name Kylfing denotes a particular tribal, socio-political, or economic grouping is also much debated. They are mentioned on the Viking runestones, the sagas of Icelanders (most notably in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kupinovo
Kupinovo ( sr-Cyrl, Купиново, Glagolitic script: Ⰽⱆⱂⰻⱀⱁⰲⱁ) is a village located in the municipality of Pećinci, Serbia. As of 2011 census, the village has 1,866 inhabitants. It is near the famous biodiversity area, the Obedska bara. This contains several insects and other life forms unique to the area. Name In Serbian, the village is known as ''Kupinovo'' ( sr-Cyrl, Купиново, Glagolitic script: Ⰽⱆⱂⰻⱀⱁⰲⱁ), formerly also ''Kupinik'' ( sr-Cyrl, Купиник, link=no, Glagolitic script: Ⰽⱆⱂⱀⰻⰽ); in Croatian as ''Kupinovo''; and in Hungarian as ''Kölpény'' or ''Kelpény''. The name of the village derived from Serbian word "kupina" ("blackberry" in English). History In the Middle Ages, Kupinik was a notable city and was a residence of Serbian Despots in Syrmia in the 15th and 16th century. The oldest mention of Kupinik is in the two charters by the Hungarian King Sigismund, from the second half of 14th century (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |