|
Borna Manci Mičević
Borna may refer to: People * Borna (given name), a Croatian masculine given name * Borna (duke), the Duke of the Duchy of Littoral Croatia (Dalmatian Croatia) c. 810–821, a vassal of the Frankish Empire * Bertin Borna (1930–2007), a Beninese politician Places * Borna, Leipzig, a town in Saxony, Germany * Borna, Bahretal, a subdivision of the Bahretal municipality, Saxony, Germany * Borna Dam, an earthfill dam on Borna river near Ambejogai, Beed district, Maharashtra, India Other uses * Borna disease, an infectious neurological syndrome ** Bornaviridae, a family of viruses associated with Borna disease ** Borna disease virus * Borna language (Democratic Republic of the Congo), a spurious language description now retired from ISO 639-3 * Borna language (Ethiopia), a North Omotic language spoken in western Ethiopia * Borna snakehead, ''Channa amphibeus'', an extremely rare species of snakehead fish See also *Boma (other) *Borne (other) {{disambiguation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borna (given Name)
Borna () is a masculine Croatian given name. It is also a masculine Persian given name, (). Borna in Persian language means young. Notable people with the name include: *Borna (duke) (died 821), Duke of Dalmatia *Borna Barišić (born 1992), Croatian football player *Borna Ćorić (born 1996), Croatian tennis player *Borna Franić (born 1975), Croatian handball player *Borna Gojo (born 1998), Croatian tennis player *Borna Rendulić (born 1992), Croatian ice hockey player *Borna Sosa (born 1998), Croatian football player {{given name Croatian masculine given names Masculine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borna (duke)
Borna was the duke of Croatia (''Dalmatia and Liburnia'') from to 821 and vassal of the Frankish Empire. He is mentioned in the Royal Frankish Annals (''Annales regni Francorum'') in entries regarding 818–821. His titles were "Duke of the Guduscani" (a tribe from Lika and northern Dalmatia) in 818; "Duke of Dalmatia" in 819; "Duke of Dalmatia and Liburnia" in 821. Historiography treats him as a ruler of Duchy of Croatia. Etymology In the name of Borna scholars have seen similarity with the name of Saxons count Bernus (father of Gottschalk of Orbais), and Burgundian names Bornus, Borno and Bornonus. Petar Skok, besides supporting possibility of being a Frankish name (''borns'' meaning "son"), also proposed Slavic etymology from Proto-Slavic *''born-'' which with liquid metathesis could be related to Slavic personal names Branimir, Branislav and others. History Borna is documented in the "Royal Frankish Annals" (''Annales regni Francorum''). He is first mentioned regardin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Littoral Croatia
The Duchy of Croatia (Modern ; also Duchy of the Croats, Modern ; ; ) was a medieval state that was established by White Croats who migrated into the area of the former Roman province of Dalmatia 7th century AD. Throughout its existence the Duchy had several seats – namely, Klis, Solin, Knin, Bijaći and Nin. It comprised the ''littoral –'' the coastal part of today's Croatia ''–'' except Istria, and included a large part of the mountainous hinterland as well. The Croats settled in Dalmatia after defeating the Pannonian Avars, during the time of Byzantine emperor Heraclius I. The Duchy was in the center of competition between the Byzantine Empire and the Carolingian Empire for rule over the area. Croatian rivalry with Venice emerged in the first decades of the 9th century and would continue through the following centuries. Croatia also waged battles with the Bulgarian Empire (founded ; Bulgar-Croatian relations improved greatly afterwards) and with the Arabs; it also sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertin Borna
Bertin Borna Babiliba (20 November 1930 – 15 June 2007) was a Beninese politician. He served as Minister of Finance. He was born on 20 November 1930 in Tanguiéta and received an international education. Borna attended the Parakou Congress of 1957 and aligned himself with Hubert Maga. Borna served as vice president of the National Assembly from 1959 to 1960. He was minister of public works from 1958 to 1960. That year, he was named finance minister, a post he held until the coup in 1963. Christophe Soglo brought him back as finance minister in 1966, but his appointment led to agitations that resulted in the 1967 coup. Borna was accused of being involved in the 1975 coup attempt and was sentenced to death in absentia on 7 March 1975. Remaining in Abidjan and Lomé, Berta remained active in international trade. He became a UN director for the Sahel The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
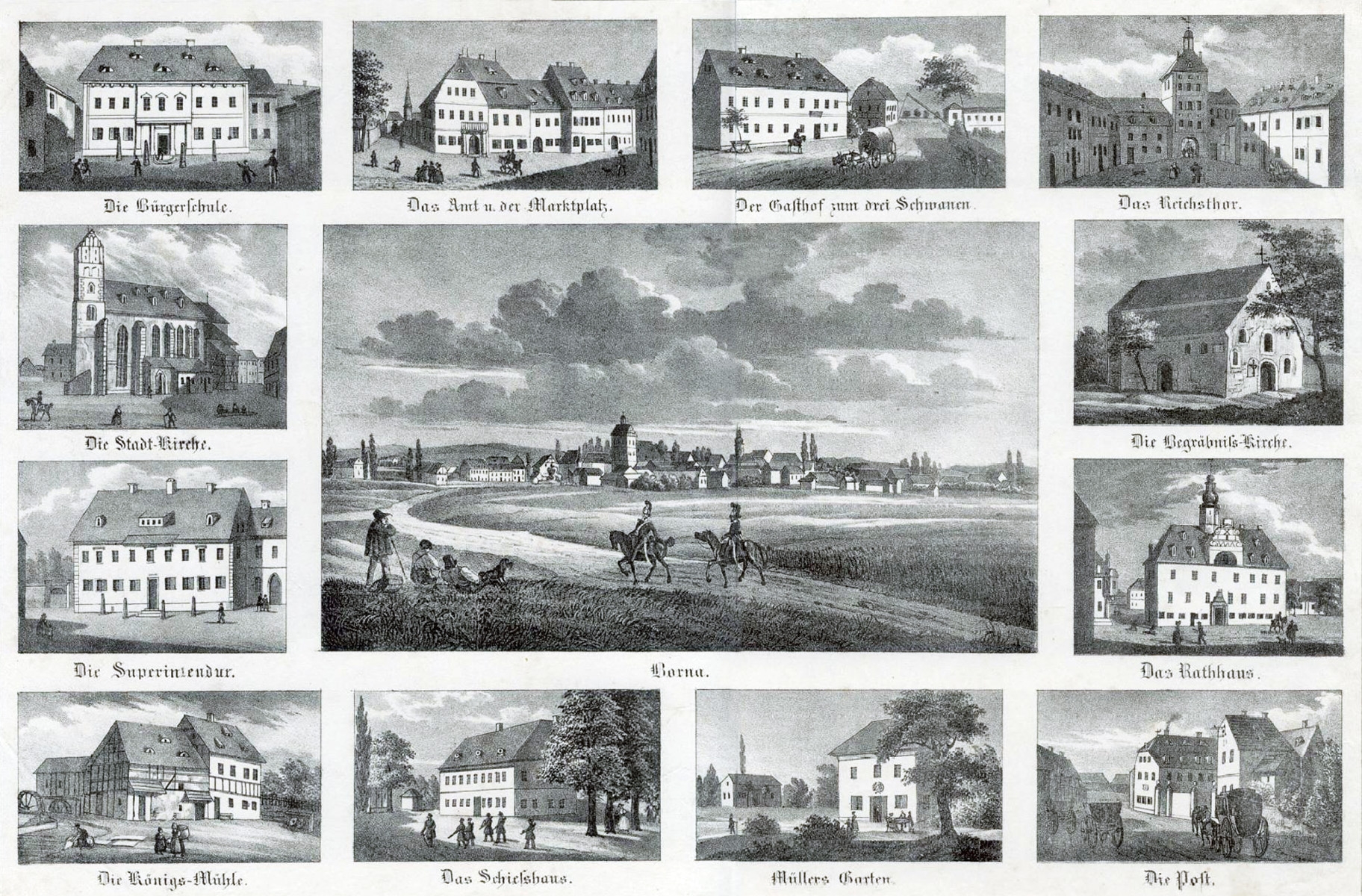
Borna, Leipzig
Borna () is a town in Saxony, Germany, capital of the Leipzig (district), Leipzig district. It is situated approximately 30 km southeast of Leipzig city. It has approx. 19,000 inhabitants. The town is the district seat of the Leipzig (district), district of Leipzig. Geography Borna is located about south of Leipzig. The river Wyhra flows through the town. The surrounding landscape has been influenced by open-cast coal mining. The town lies in the middle of Central German Metropolitan Region, with Leipzig distant, Gera , Chemnitz , Halle , and Dresden . Neighboring large towns are Altenburg, away, Grimma, and Zeitz . History Pre-history and Middle Ages The current site of Borna town was originally two settlements; Altstadt (the old town) and Wenigborn. Before the foundation of the town, there had been a water castle since the 9th Century. The first written mention of the town of Borna was recorded in 1251. Borna was burnt to the ground five times during the wars of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borna, Bahretal
Bahretal is a municipality in the Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge district in Saxony, Germany. It is situated in the northeastern foothills of the Ore Mountains, between Bad Gottleuba-Berggießhübel and Dohna. It consists of several small villages, situated in the valleys of the rivers Bahre and Seidewitz as well as on the heights between the valleys. The municipality is named after the small river Bahre which flows through it. Its source is located 1.5 km north of Breitenau in Bad Gottleuba-Berggießhübel at 505 m. It flows into the Seidewitz near Zuschendorf. In order to prevent flooding, a retention basin was built between Borna-Gersdorf and Friedrichswalde-Ottendorf in 1970. Municipality subdivisions Bahretal consists of the following villages: *Borna *Friedrichswalde *Gersdorf *Göppersdorf *Nentmannsdorf *Niederseidewitz *Ottendorf *Wingendorf History Borna Borna () probably belonged to the castle of Dohna at first. In the beginning of the 15th century it became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borna Dam
Borna Dam, is an earthfill dam on Borna river near Ambejogai, Beed district in state of Maharashtra in India. Specifications The height of the dam above lowest foundation is while the length is . The volume content is and gross storage capacity is . Purpose * IrrigationSee also * *List of reservoirs and dams in India
This page shows the state-wise list of d ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borna Disease
Borna disease, also known as sad horse disease, is an infectious neurological syndrome of warm-blooded animals, caused by Borna disease viruses 1 and 2 (BoDV-1/2). BoDV-1/2 are neurotropic viruses of the species ''Orthobornavirus bornaense'', and members of the ''Bornaviridae'' family within the ''Mononegavirales'' order. Borna disease is a severe neurological illness that predominantly affects horses and sheep, but it has been observed in a wide range of mammals. The disease is characterised by ataxia and abnormal depressive behaviour, frequently culminating in death. There have been rare cases of human fatalities associated with encephalitis caused by Borna disease virus infection. Additionally, correlative evidence exists linking BoDV-1/2 infection with neuropsychiatric disorders such as bipolar disorder in humans. History Borna disease was first described in 1885, when all horses belonging to a cavalry regiment stationed near the city of Borna in Saxony, Germany, died f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bornaviridae
''Bornaviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, reptiles, and humans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with bornaviruses include Borna disease, a fatal neurologic disease of mammals restricted to central Europe; and Proventricular dilatation disease, proventricular dilatation disease (PDD) in birds. Bornaviruses may cause encephalitis in mammals like horses or sheep. The family contains four genera. History Borna disease was first identified in 1926 and its genome was isolated in 1990. The ICTV proposed the creation in 1996 of the family ''Bornaviridae'' along with the genus ''Bornaviru''s (today ''Orthobornavirus''). The viral family is named after the city of Borna, Leipzig, Borna in Saxony, Saxony, Germany, which is where many animals were lost to the sporadic encephalopathy caused by the viral disease. Structure Orthobornavirions are enveloped, with spherical geometries and he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
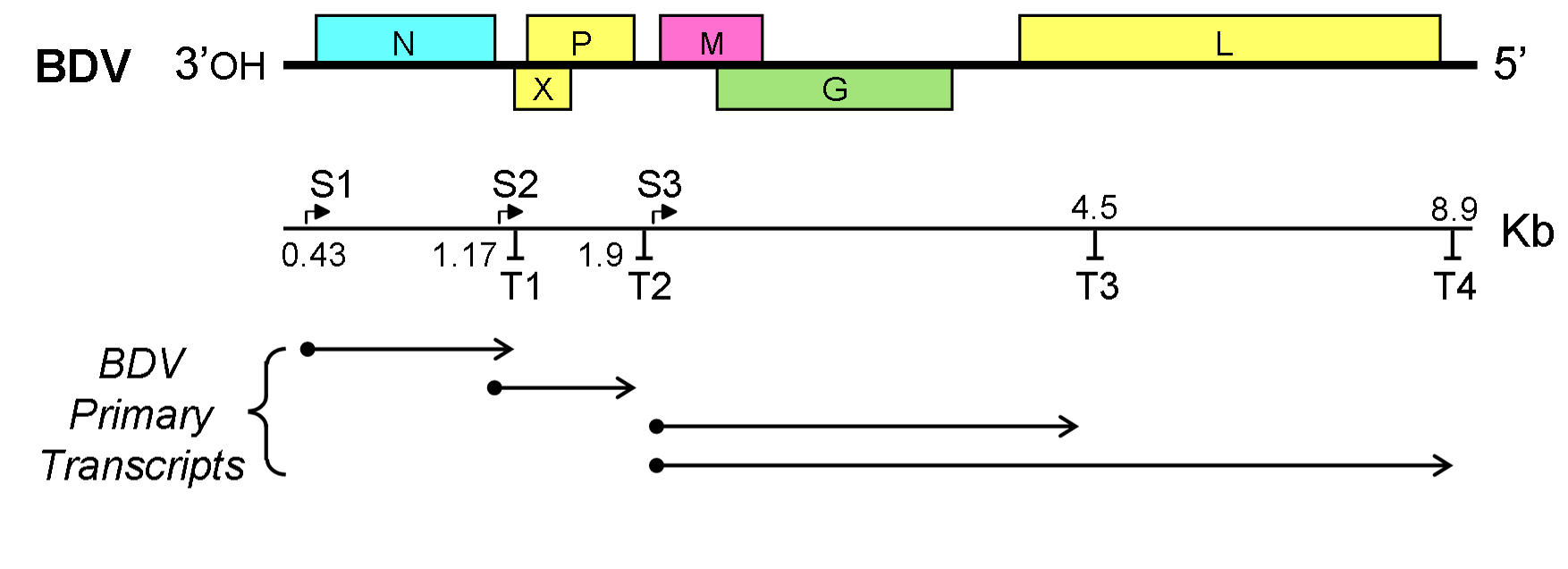
Borna Disease Virus
The Borna disease viruses 1 and 2 (BoDV-1 and BoDV-2) are members of the species ''Mammalian 1 orthobornavirus'' and cause Borna disease in mammals. Virology Genome BoDV-1/2 have the smallest genome (8.9 kilobases) of any ''Mononegavirales'' member and are unique within that order in their ability to replicate within the host cell nucleus. BoDV-1 was isolated from a diseased horse in the 1970s, but the virus particles were difficult to characterise. Nonetheless, the virus' genome has been characterised. It is a linear negative-sense single stranded RNA virus in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Several of the proteins encoded by the BoDV-1 genome have been characterised. The G glycoprotein is important for viral entry into the host cell. It has been suggested that the p10, or X, protein plays a role in viral RNA synthesis or ribonucleoprotein transport. The P40 nucleoprotein from BoDV-1 is multi-helical in structure and can be divided into two subdomains, each of which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borna Language (Democratic Republic Of The Congo)
Spurious languages are languages that have been reported as existing in reputable works, while other research has reported that the language in question did not exist. Some spurious languages have been proven to not exist. Others have very little evidence supporting their existence, and have been dismissed in later scholarship. Others still are of uncertain existence due to limited research. Below is a sampling of languages that have been claimed to exist in reputable sources but have subsequently been disproved or challenged. In some cases a purported language is tracked down and turns out to be another, known language. This is common when language varieties are named after places or ethnicities. Some alleged languages turn out to be hoaxes, such as the Kukurá language of Brazil or the Taensa language of Louisiana. Others are honest errors that persist in the literature despite being corrected by the original authors; an example of this is ', the name given in 1892 to two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borna Language (Ethiopia)
Shinasha, also known as Boro (Borna, Bworo) is a North Omotic language spoken in western Ethiopia by the Shinasha people. Its speakers live in scattered areas north of the Abay River: in the Dangur, Bullen, Dibate and Wenbera districts, which are parts of the Benishangul-Gumuz Region.Raymond G. Gordon Jr., ed. 2005"Boro, a language of Ethiopia", ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' 15th edition. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics. Notes References * Lamberti, Marcello (1993) ''Die Shinassha-Sprache – Materialien zum Boro''. Heidelberg. Universitätsverlag C. Winter. Further reading * Franz Rottland (1990), "A sketch of Shinasha morphology"''Omotic Language Studies'' Richard Hayward (editor), pp. 185–209. London: SOAS. * Idar Bergfjord (2013)''Issues in Borna Phonology'' MA thesis, University of Oslo External links * World Atlas of Language Structures The World Atlas of Language Structures (WALS) is a database of structural (phonological, gramma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |