|
Boris Sheremetev
Count Boris Petrovich Sheremetev (; – ) was a Russian diplomat and field marshal (Russian Empire), general field marshal during the Great Northern War. He became the first Russian count in 1706. His children included Pyotr Sheremetev and Natalia Sheremeteva. Early life In his youth, Sheremetyev was a page to Tsar Alexis I of Russia, Alexis I before starting his military career. From 1671 he served at the imperial court. In 1681 he was a leader at Tambov, commanding the armies fighting the Crimean Khanate, and from 1682 he was a boyar. From 1685 to 1687 he participated in negotiations and the conclusion of the "Eternal Peace of 1686" with Poland and the allied treaty with Austria. From the end of 1687 he commanded the armies in Belgorod defending Russia's southern border, and participated in the Crimean campaigns of 1687 and 1689, Crimean campaigns. After Peter I of Russia, Peter I gained power in 1689, he joined him as a fellow campaigner. He participated along with Mazepa i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheremetev
The House of Sheremetev () was one of the wealthiest and most influential Russian noble families, descending from Feodor Koshka. History The family held many high commanding ranks in the Russian military, governorships and eventually the rank of Count of the Russian Empire. Notable members * Yelena Sheremeteva, third wife of Tsarevich Ivan Ivanovich (1554–1581), son of Ivan the Terrible. * Fedor Sheremetev (1570–1650) cousin of Tsar Michael I and head of government in 1613–18 and 1642–46 * Vasily Borisovich Sheremetev (1622–1682) fought in Ukraine * Count Boris Sheremetev (1652–1719) military leader and diplomat during the Great Northern War * Count Pyotr Borisovich Sheremetev (1713—1788) son of Boris; courtier and noted patron of Russian theater * Princess Natalia Borisovna Dolgorukova, daughter of Boris and wife of Prince Ivan Dolgorukov * Count Nikolai Petrovich Sheremetev (1751–1809) son of Pyotr; noted patron of Russian theater * Praskovia Kova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
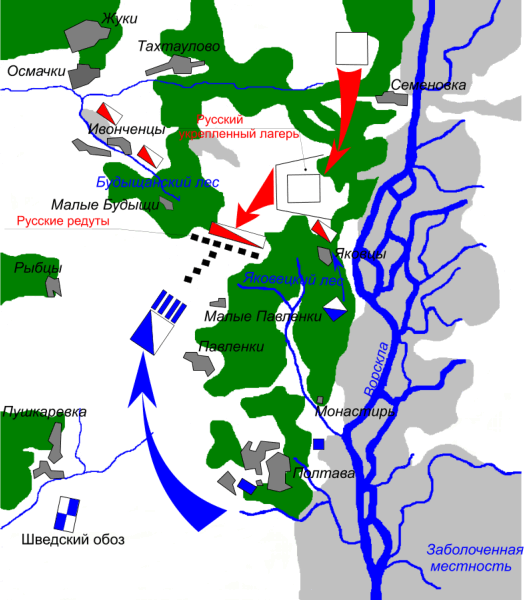
Battle Of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava took place 8 July 1709, was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. The Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeated the Swedish army commanded by Carl Gustaf Rehnskiöld. The battle would lead to the Swedish Empire losing its status as a European great power and also marked the beginning of Russian supremacy in eastern Europe. During the course of six years in the initial stages of the war, King Charles XII and the Swedish Empire had defeated almost all participants in the anti-Swedish coalition, which initially consisted of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Denmark-Norway and the Tsardom of Russia. The latter, under , was the only one still fighting. Charles therefore chose to invade Russia in the autumn of 1707 and march towards Moscow with a large Swedish army. However, the campaign was complicated by harsh weather conditions and by Russian scorched earth tactics and surprise attacks, which forced Charles to interr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tambov
Tambov ( , ; rus, Тамбов, p=tɐmˈbof) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Tambov Oblast, Central Federal District, central Russia, at the confluence of the Tsna River (Moksha basin), Tsna and Studenets River, Studenets rivers, about south-southeast of Moscow. With a population of 261,803 as of 2021, Tambov is the largest city, and historical center, of the Tambov Oblast as a whole. Etymology The name "Tambov" originates from a Moksha language, Mokshan word (). Geography Urban layout In terms of its layout, Tambov was no different from other fortified cities – the Kremlin, the prison and a small settlement. The chosen place was in full compliance with the requirements of the fortification. From the north and east, the new fortress was washed by rivers, and from the west and south it was protected by artificial ditches filled with water by the Studenets River. The Kremlin was surrounded by a six-meter wooden wall with 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexis I Of Russia
Alexei Mikhailovich (, ; – ), also known as Alexis, was Tsar of all Russia from 1645 until his death in 1676. He was the second Russian tsar from the House of Romanov. He was the first tsar to sign laws on his own authority and his council passed the '' Sobornoye Ulozheniye'' of 1649, which strengthened the bonds between autocracy and the lower nobility. In religious matters, he sided closely with Patriarch Nikon during the schism in the Russian Orthodox Church which saw unpopular liturgical reforms. While finding success in foreign affairs, his reign saw several wars with Iran, Poland (from whom left-bank Ukraine and Smolensk were annexed) and Sweden, as well as internal instabilities such as the Salt Riot in Moscow and the Cossack revolt of Stenka Razin in southern Russia. At the time of his death, Russia spanned almost . Early life and reign Alexis was born on , in Moscow, to Tsar Michael and Eudoxia Streshneva. At the age of sixteen, he acceded to the throne after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, цар, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official—but was usually considered by Western Europeans to be equivalent to "king". Tsar and its variants were the official titles in the First Bulgarian Empire (681–1018), Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1396), the Kingdom of Bulgaria (1908–1946), the Serbian Empire (1346–1371), and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721). The first ruler to adopt the title ''tsar'' was Simeon I of Bulgaria. Simeon II, the last tsar of Bulgaria, is the last person to have held this title. Meaning in Slavic languages The title tsar is derived from the Latin title for the Roman emperors, ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natalia Sheremeteva
Princess Natalia Borisovna Dolgorukova (née Countess Sheremeteva; , née ; 17 January, 1714 – 3 July, 1771) was one of the first Russian women writers. She has been called the most accomplished Russian memoirist of the 18th century. D.S. Mirsky. ''A history of Russian literature from its beginnings to 1900''. Northwestern University Press, 1999. Page 60. Natalia's father was Count Boris Sheremetev, Russia's first native field marshal. He died when she was 4. She was betrothed to Prince Ivan Dolgorukov, an intimate friend of the young Peter II of Russia and his brother-in-law. After the Emperor's sudden death, Dolgorukov fell into disgrace, but Natalia did not desert her lover, and insisted on getting married. She was 16 at the time. Several days after the wedding, the entire Dolgorukov family was exiled to Beryozov, a remote Arctic town. She gave birth to two sons in exile but was allowed to return to Moscow ten years later, after her husband's execution. She took the veil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyotr Sheremetev
Pyotr Borisovich Sheremetev () (1713–1788) was a Russian nobleman and courtier, the richest man in Russia aside from the tsar; he was the son of Boris Sheremetev. When his father Boris died in 1719, tsar Peter promised to be "like a father" to Boris's children, and young Pyotr was brought up at court as a companion to the heir to the throne, who became tsar Peter II. After a teenage career in the Guards, Sheremetev became a chamberlain to the Empress Anna, and then to the Empress Elizabeth. Under Catherine the Great, he became a senator and was the first elected Marshal of the Nobility. Unlike other court favourites, who rose and fell with the change of sovereign, Sheremetev remained in office for six consecutive reigns. ... He was one of Russia's first noblemen to be independent in the European sense.Orlando Figes, ''Natasha's Dance'' (Picador, 2002), p. 19. He was a lover of art and theater, using his vast wealth to remodel the Sheremetev Palace (known as the "Fountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: Barnes & Noble, 1992. p. 73. . Especially in earlier medieval periods the term often implied not only a certain status, but also that the ''count'' had specific responsibilities or offices. The etymologically related English term " county" denoted the territories associated with some countships, but not all. The title of ''count'' is typically not used in England or English-speaking countries, and the term ''earl'' is used instead. A female holder of the title is still referred to as a ''countess'', however. Origin of the term The word ''count'' came into English from the French ', itself from Latin '—in its accusative form ''comitem''. It meant "companion" or "attendant", and as a title it indicated that someone was delegated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Marshal (Russian Empire)
Field marshal (''General-feldmarshal'', ''General-fel'dmarshal'', General field marshal, or simply Fieldmarshal; ) was, with the exception of ''Generalissimo'', the Highest military ranks, highest military rank of the Russian Empire. It was a Ranks and insignia of the Imperial Russian Armed Forces, military rank of the 1st class in the Imperial Russian Army and equal to those of Chancellor (Russia), Chancellor and Active Privy Councillor, 1st class in civil service, and General admiral#Russian Empire, General Admiral in the Imperial Russian Navy. After the Russian Revolution of 1917 the rank was Decree on the Abolition of Estates and Civil Ranks, abolished, alongside the Table of Ranks. In 1935 however, the Red Army introduced the equivalent rank of "Marshal of the Soviet Union" () as the highest Military ranks of the Soviet Union, military rank of the Soviet Union, when ranks were restored under History of the Soviet Union (1927–1953), Stalin's rule. Russian field marshals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Black Eagle
The Order of the Black Eagle () was the highest order of chivalry in the Kingdom of Prussia. The order was founded on 17 January 1701 by Elector Friedrich III of Brandenburg (who became Friedrich I of Prussia, Friedrich I, King in Prussia, the following day). In his Dutch exile after World War I, deposed Emperor Wilhelm II of Germany, Wilhelm II continued to award the order to his family. He made his second wife, Hermine Reuss of Greiz, Princess Hermine Reuss of Greiz, a Lady in the Order of the Black Eagle. Overview The statutes of the order were published on 18 January 1701, and revised in 1847. Membership in the Order of the Black Eagle was limited to a small number of knights, and was divided into two classes: members of reigning houses (further divided into members of the House of Hohenzollern and members of other houses, both German and foreign) and capitular knights. Before 1847, membership was limited to nobles, but after that date, capitular knights who were not noble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The White Eagle (Poland)
The Order of the White Eagle () is the highest honour of the Poland, Republic of Poland and formerly the Second Polish Republic and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and one of the oldest state decorations in the world still in use. It was officially instituted on 1 November 1705 by Augustus II the Strong, King of Poland and Elector of Saxony, and bestowed on eight of his closest diplomatic and political supporters. It has since been awarded to the most distinguished Polish people, Poles for their merits and occasionally to the heads of state of foreign countries. The Order of the White Eagle is attached to an azure sash slung over the left shoulder to the right side. The star of the Order, formerly embroidered, is worn on the left side of the chest. Unlike other Polish high decorations, the Order of the White Eagle does not have different classes or crosses. History The badge of the Order of the White Eagle was originally a red vitreous enamel, enamel oval gold medal wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of St
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to: * A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica * Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood * Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of different ways * Hierarchy, an arrangement of items that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another * an action or inaction that must be obeyed, mandated by someone in authority People * Orders (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Order'' (film), a 2005 Russian film * ''Order'' (album), a 2009 album by Maroon * "Order", a 2016 song from '' Brand New Maid'' by Band-Maid * ''Orders'' (1974 film), a film by Michel Brault * "Orders" (''Star Wars: The Clone Wars'') Business * Blanket order, a purchase order to allow multiple delivery dates over a period of time * Money order or postal orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |