|
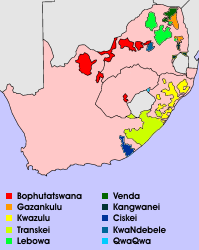
Bophuthatswana
Bophuthatswana (, ), officially the Republic of Bophuthatswana (; ), and colloquially referred to as the Bop and by outsiders as Jigsawland (In reference to its enclave-ridden borders) was a Bantustan (also known as "Homeland", an area set aside for members of a specific ethnicity) that was declared (nominally) independent by the apartheid regime of South Africa in 1977. However, like the other Bantustans of Ciskei, Transkei and Venda, its independence was not recognized by any country other than South Africa. Bophuthatswana was the second Bantustan to be declared an independent state by the Apartheid government, after Transkei. Its territory constituted a scattered patchwork of enclaves spread across what was then Cape Province, Orange Free State (province), Orange Free State and Transvaal (province), Transvaal. Its seat of government was Mmabatho, which is now a suburb of Mahikeng. On 27 April 1994, it was reintegrated into South Africa with the coming into force of the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1994 Bophuthatswana Crisis
The 1994 Bophuthatswana crisis was a major political crisis which began after Lucas Mangope, the president of Bophuthatswana, a nominally independent South African bantustan created under ''apartheid'', attempted to crush widespread labour unrest and popular demonstrations demanding the incorporation of the territory into South Africa pending non-racial elections later that year. Violent protests immediately broke out following President Mangope's announcement on 7 March that Bophuthatswana would boycott the South African general elections. This was escalated by the arrival of right-wing Afrikaner militias seeking to preserve the Mangope government. The predominantly black Bophuthatswana Defence Force and police refused to cooperate with the white extremists and mutinied, then forced the Afrikaner militias to leave Bophuthatswana. The South African military entered Bophuthatswana and restored order on 12 March. The Bophuthatswana Crisis highlighted the deep unpopularity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Bophuthatswana
This article lists the leaders of the TBVC states, the four Bantustans which were declared nominally independent by the government of the Republic of South Africa during the period of apartheid, which lasted from 1948 to 1994. Their independence was not recognized outside South Africa. The bantustans with nominal independence were namely: Transkei (1976), Bophuthatswana (1977), Venda (1979) and Ciskei (1981), hence the abbreviation TBVC. The TBVC states were reintegrated into South Africa in the wake of the first post-apartheid general election in April 1994.All Bantustans (both nominally independent and self-governing) were dismantled and their territories reincorporated into South Africa with effect from 27 April 1994, in terms of section 1(2) and Schedule 1 of the Constitution of the Republic of South Africa, 1993, the so-called "Interim Constitution" which abolished apartheid in South Africa. The text of this Interim Constitution, which came into force on 27 April 1994 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
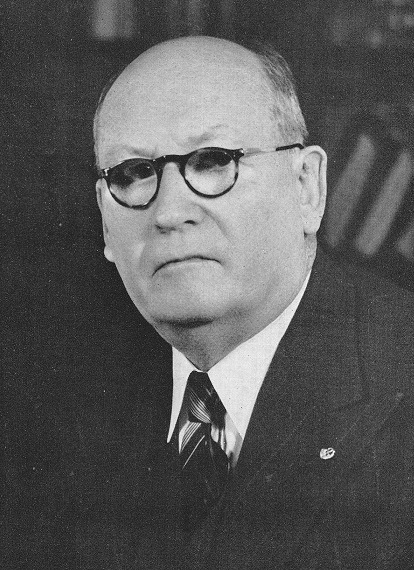
Lucas Mangope
Kgosi Lucas Manyane Mangope (27 December 1923 – 18 January 2018) was the leader of the Bantustan (homeland) of Bophuthatswana. The territory he ruled over was distributed between the Orange Free State – what is now Free State – and North West Province. He was also the founder and leader of the United Christian Democratic Party, a political party based in the North West of South Africa. Education Mangope attended an Anglican mission school for most of his school career. He matriculated from St. Peter's College, Rosetenville in Johannesburg in 1946. After matric, he registered for a Junior Teaching Diploma at the Diocesan Teachers' Training College in Polokwane (then called Pietersburg). He studied towards a Higher Primary Teacher’s Diploma at Bethel College in the Transvaal from 1951. After graduating he started teaching and specialised as an Afrikaans teacher. He taught at secondary schools in Mahikeng, Motswedi, Krugersdorp and Potchefstroom and was awarded in 1959 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantustan
A Bantustan (also known as a Bantu peoples, Bantu homeland, a Black people, black homeland, a Khoisan, black state or simply known as a homeland; ) was a territory that the National Party (South Africa), National Party administration of the Union of South Africa (1910–1961) and later the Republic of South Africa (1961–1994) set aside for People of Indigenous South African Bantu languages, black inhabitants of South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia), as a part of its policy of apartheid., "1. one of the areas in South Africa where black people lived during the apartheid system; 2. SHOWING DISAPPROVAL any area where people are forced to live without full civil and political rights." The term, first used in the late 1940s, was coined from ''Bantu'' (meaning "people" in some of the Bantu languages) and ''-stan'' (a suffix meaning "land" in Persian language, Persian and other Persian-influenced languages). It subsequently came to be regarded as a disparaging term by s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bophuthatswana Democratic Party
The Bophuthatswana Democratic Party (founded as the Bophuthatswana National Party) was the dominant party in Bantustan Bophuthatswana. It was founded around 1977. Under the leadership of Lucas Mangope Kgosi Lucas Manyane Mangope (27 December 1923 – 18 January 2018) was the leader of the Bantustan (homeland) of Bophuthatswana. The territory he ruled over was distributed between the Orange Free State – what is now Free State – and North ..., it launched a campaign to build hospitals, schools and sports stadia. The party was pro-apartheid. References Defunct political parties in Africa Defunct political parties in South Africa Bophuthatswana Tswana Organisations associated with apartheid {{SouthAfrica-party-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lefatshe Leno La Bo-rrarona
"Lefatshe leno la bo-rrarona" was the national anthem of Bophuthatswana, one of the black homelands in South Africa established under apartheid. The lyrics were written by J M Ntsime, a famous Setswana Tswana, also known by its native name Setswana, is a Bantu language indigenous to Southern Africa and spoken by about 8.2 million people. It is closely related to the Northern Sotho and Southern Sotho languages, as well as the Kgalaga ... novelist, dramatist and minister of education of Bophuthatswana. The vocal version could often be heard at the beginning of Bop TV, the official television station of Bophuthatswana. Lyrics References External linksBophuthatswana National Anthem National anthems Historical national anthems Bophuthatswana African anthems 1977 songs {{Anthem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahikeng
Mahikeng ( Tswana for "Place of Rocks"), formerly known as Mafikeng and alternatively known as Mafeking (, ), is the capital city of the North West province of South Africa. Close to South Africa's border with Botswana, Mafikeng is northeast of Cape Town and west of Johannesburg. In 2001 it had a population of 49,300. In 2007 Mafikeng was reported to have a population of 250,000, of which the CBD constituted between 69,000 and 75,000. It is built on the open veld at an elevation of , by the banks of the Upper Molopo River. The Madibi goldfields are some south of the town. History Establishment Molema's town was founded by Molema Tawana (c. 1822 – January 1882). In 1857 Molema led an advance guard to scout out the area along the Molopo River. This was a familiar area as they had previously lived in nearby Khunwana. Molema settled a town known in its early years as "Molema's town", while the main body of the Barolong under Montshiwa followed. But Montshiwa did not fee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apartheid
Apartheid ( , especially South African English: , ; , ) was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. It was characterised by an authoritarian political culture based on ''baasskap'' ( 'boss-ship' or 'boss-hood'), which ensured that South Africa was dominated politically, socially, and economically by the nation's minority White South Africans, white population. Under this minoritarianism, minoritarian system, white citizens held the highest status, followed by Indian South Africans, Indians, Coloureds and Ethnic groups in South Africa#Black South Africans, black Africans, in that order. The economic legacy and social effects of apartheid continue to the present day, particularly Inequality in post-apartheid South Africa, inequality. Broadly speaking, apartheid was delineated into ''petty apartheid'', which entailed the segregation of public facilities and social ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocky Malebane-Metsing
Peter Ishmael Rocky Malebana-Metsing (23 August 1949 – 23 November 2016) was a South African politician who was a member of the African National Congress in the 1990s. He was born in Rustenburg. In 1988, a coup ousted Lucas Mangope, the president of Bophuthatswana, and installed Malebane-Metsing, who at the time was leader of the Progressive People's Party, as president. Fifteen hours later, the South African government sent troops in and reinstated Mangope. In December 1991 Rocky Malebana-Metsing was elected into the National Executive Committee (NEC) of the ANC. After the 1994 elections, he was appointed MEC for Agriculture in North West Province North West ( ; ) is a province of South Africa. Its capital is Mahikeng. The province is located to the west of the major population centre and province of Gauteng and south of Botswana. History North West was incorporated after the end of ... of South Africa, but he resigned from the ANC, and consequently lost his seat o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mmabatho
Mmabatho (Tswana for "Mother of the People") is the former capital of the North-West Province of South Africa. During the apartheid era, it was the capital of the former "Bantustan" of Bophuthatswana, separated from the adjacent Mafeking which temporarily remained outside Bophuthatswana. Following the end of apartheid in 1994, Bophuthatswana was integrated into the newly established North-West Province and Mmabatho was proclaimed the provincial capital. However, Mmabatho's status as the provincial capital was short-lived. Later in 1994, the North West provincial legislature voted to rename the capital to Mahikeng (the town of Mafikeng having been merged with Mmabatho in 1980 and treated as a suburb of Mmabatho between 1980 and 1994), reducing Mmabatho to a suburb of Mafikeng. The city is an enclave within the latter. Mmabatho contains many provincial government buildings, a shopping complex called Mega City and a Sports Stadium formerly called the Independence Stadium. The N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language spoken in South Africa, Namibia and to a lesser extent Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe and also Argentina where there is a group in Sarmiento, Chubut, Sarmiento that speaks the Patagonian Afrikaans, Patagonian dialect. It evolved from the Dutch language, Dutch vernacular of South Holland (Hollandic dialect) spoken by the free Burghers, predominantly Dutch settlers and slavery in South Africa#Dutch rule, enslaved population of the Dutch Cape Colony, where it gradually began to develop distinguishing characteristics in the 17th and 18th centuries. Although Afrikaans has adopted words from other languages including German language, German, Malay language, Malay and Khoisan languages, an estimated 90 to 95% of the vocabulary of Afrikaans is of Dutch origin. Differences between Afrikaans and Dutch often lie in the more analytic language, analytic Morphology (linguistics), morphology and grammar of Afrikaans, and differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |