|
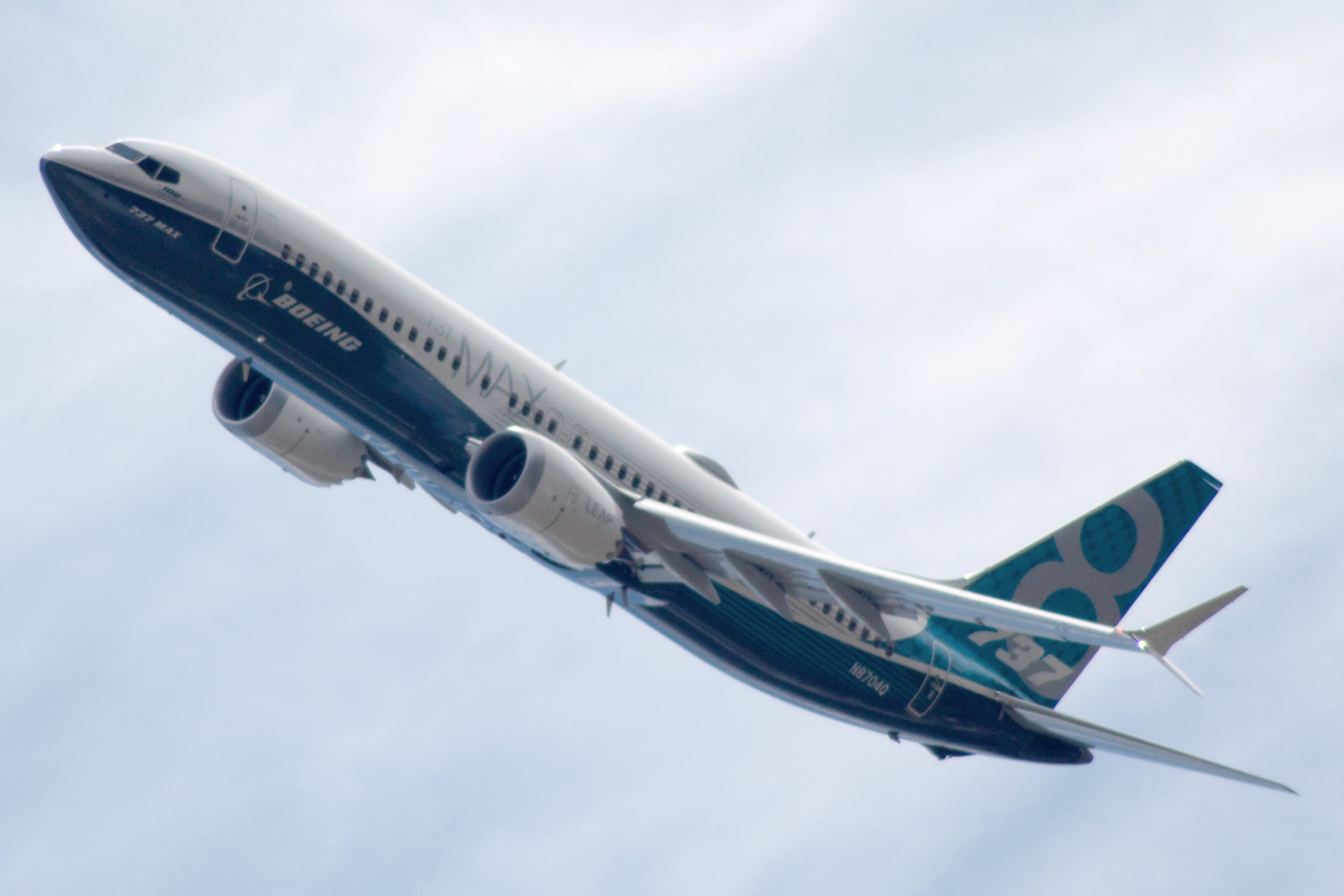
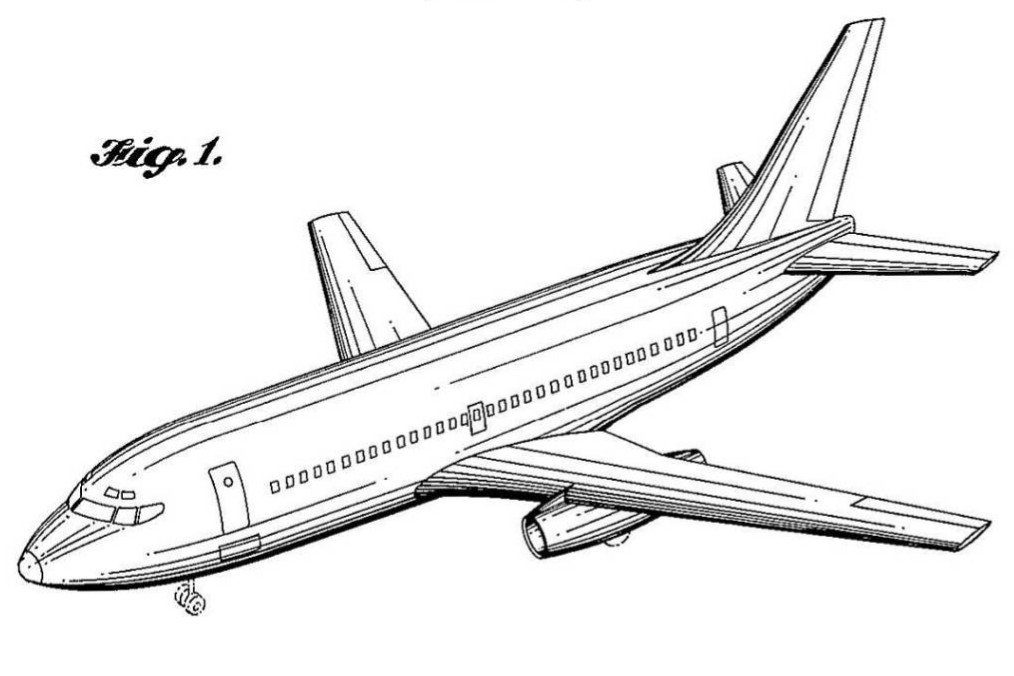
Boeing 737 Next Generation
The Boeing 737 Next Generation, commonly abbreviated as 737NG, or 737 Next Gen, is a twinjet, twin-engine narrow-body aircraft produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. Launched in 1993 as the third-generation derivative of the Boeing 737, it has been produced since 1997. The 737NG is an upgrade of the Boeing 737 Classic, 737 Classic (–300/–400/–500) series. Compared to the 737 Classic, it has a redesigned wing with a larger area, a wider wingspan, greater fuel capacity, and higher maximum takeoff weights (MTOW) and longer range. It has CFM International CFM56#CFM56-7 series, CFM International CFM56-7 series engines, a glass cockpit, and upgraded and redesigned interior configurations. The series includes four variants, the –600/–700/–800/–900, seating between 108 and 215 passengers. The 737NG's primary Competition between Airbus and Boeing, competition is the Airbus A320 family. , a total of 7,126 737NG aircraft had been ordered, of which 7,116 had been delivered, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing 737
The Boeing 737 is an American narrow-body aircraft, narrow-body aircraft produced by Boeing at its Boeing Renton Factory, Renton factory in Washington (state), Washington. Developed to supplement the Boeing 727 on short and thin routes, the twinjet retained the Boeing 707, 707 fuselage width and six abreast seating but with two underwing Pratt & Whitney JT8D low-bypass turbofan engines. Envisioned in 1964, the initial 737-100 made its first flight in April 1967 and entered service in February 1968 with Lufthansa. The lengthened 737-200 entered service in April 1968, and evolved through four generations, offering several variants for 85 to 215 passengers. The First Generation 737-100/200 variants were powered by Pratt & Whitney JT8D low-bypass turbofan engines and offered seating for 85 to 130 passengers. Launched in 1980 and introduced in 1984, the Second Generation Boeing 737 Classic, 737 Classic -300/400/500 variants were re-engine, upgraded with more fuel-efficient CFM In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailstrike
In aviation, a tailstrike or tail strike occurs when the tail or empennage of an aircraft strikes the ground or other stationary object. This can happen with a fixed-wing aircraft with tricycle undercarriage, in both takeoff where the pilot rotates the nose up too rapidly, or in landing Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying animal, aircraft, or spacecraft returns to the ground. When the flying object returns to water, the process is called alighting, although it is commonly called "landing", "touchdown" or " spl ... where the pilot raises the nose too sharply during final approach, often in attempting to land too near the runway threshold. It can also happen during helicopter operations close to the ground, when the tail inadvertently strikes an obstacle. A minor tailstrike incident may not be dangerous in itself, but the aircraft may still be weakened and must be thoroughly inspected and repaired if a more disastrous accident is to be avoided later in it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Brake (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, air brakes, or speed brakes, are a type of flight control surface used on an aircraft to increase the Drag (physics), drag on the aircraft. When extended into the airstream, air brakes cause an increase in the drag on the aircraft. When not in use, they conform to the local streamlined profile of the aircraft in order to help minimize drag. Air brakes differ from Spoiler (aeronautics), spoilers in that air brakes are designed to increase Aerodynamic drag, drag while making little change to Lift (force), lift, whereas spoilers reduce the lift-to-drag ratio and require a higher angle of attack to maintain lift, resulting in a higher stall speed. However, flight spoilers are routinely referred to as "speed brakes" on transport aircraft by pilots and manufacturers, despite significantly reducing lift. History In the early decades of powered flight, air brakes were flaps mounted on the wings. They were manually controlled by a lever in the cockpit, and mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading-edge Slats
A slat is an aerodynamic surface on the leading edge of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. When retracted, the slat lies flush with the rest of the wing. A slat is deployed by sliding forward, opening a slot between the wing and the slat. Air from below the slat flows through the slot and replaces the boundary layer that has travelled at high speed around the leading edge of the slat, losing a significant amount of its kinetic energy due to skin friction drag. When deployed, slats allow the wings to operate at a higher angle of attack before stalling. With slats deployed an aircraft can fly at slower speeds, allowing it to take off and land in shorter distances. They are used during takeoff and landing and while performing low-speed maneuvers which may take the aircraft close to a stall. Slats are retracted in normal flight to minimize drag. Slats are high-lift devices typically used on aircraft intended to operate within a wide range of speeds. Trailing-edge flap systems run ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc. is a Major airlines of the United States, major airline in the United States headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, operating nine hubs, with Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport being its largest in terms of total passengers and number of departures. With its regional subsidiaries and contractors operating under the brand name Delta Connection, Delta has over 5,400 flights daily and serve 325 destinations in 52 countries on six continents. Delta is a founding member of the SkyTeam airline alliance which helps to extend its global network. It is the oldest operating U.S. airline and the List of airlines by foundation date, seventh-oldest operating worldwide. Delta ranks first in revenue and brand value among the world's largest airlines, and second by number of passengers carried, passenger miles flown, and fleet size. Listed 70th on the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list, Delta has topped ''The Wall Street Journal's'' annua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
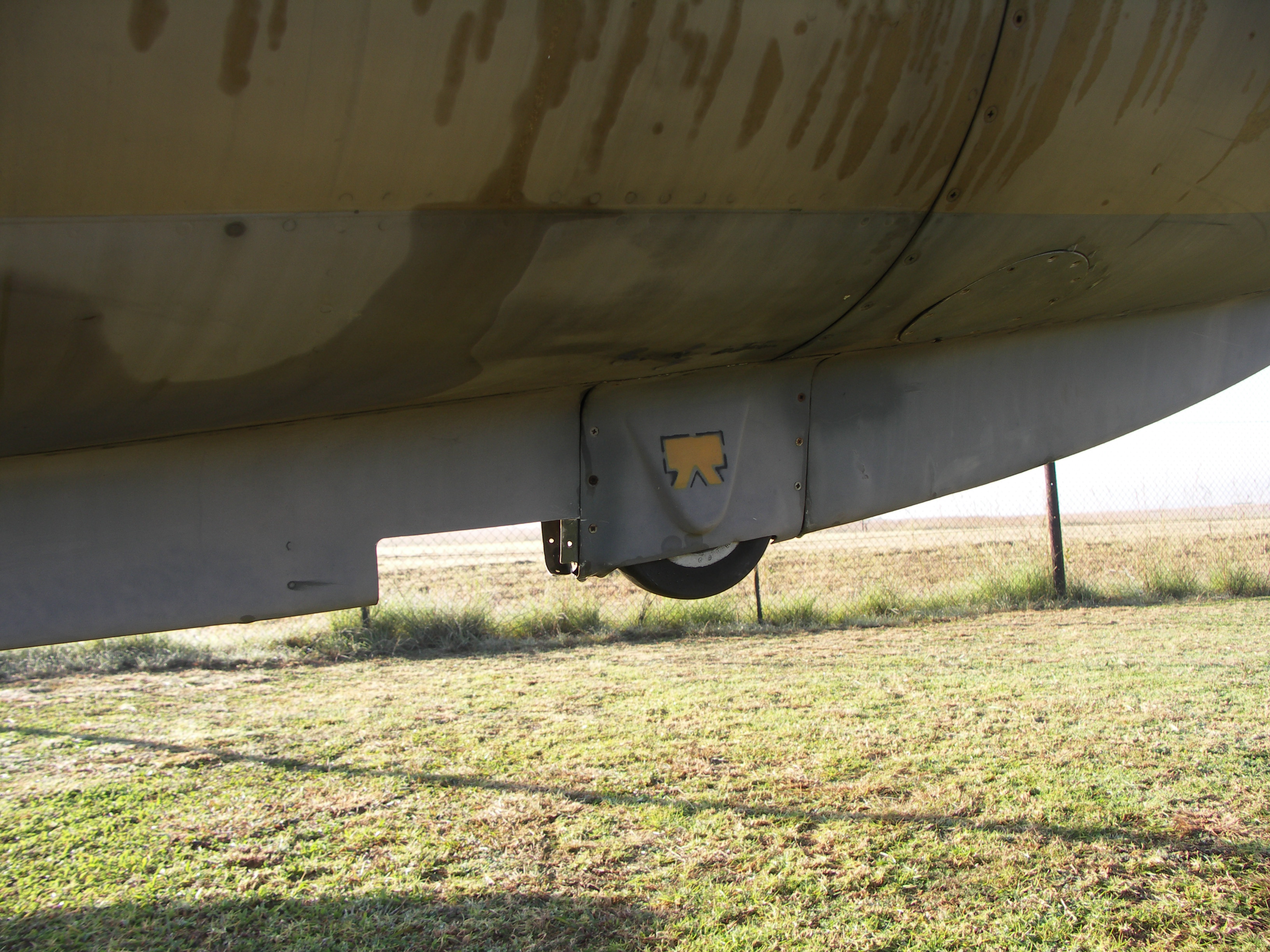
Messier-Bugatti-Dowty
Safran Landing Systems, formerly Messier-Bugatti-Dowty, is the world's largest manufacturer of aircraft landing gear, and is involved in the design, development, manufacture and customer support of all types of aircraft landing gear, wheels and brakes. The company is a wholly owned subsidiary of Safran SA. It is based in Vélizy, France, and was founded in 2011. The company can be traced to the establishment of a 50/50 joint venture in 1995 between France's Messier and the United Kingdom's Dowty Group, then owned by TI Group. Messier-Dowty was purchased outright from TI Group by the SNECMA group in 1998. The 2005 merger of SAGEM and SNECMA made Messier-Dowty part of the new ''Safran'' company. In May 2011, ''Messier-Bugatti-Dowty'' was formed through the merger of three Safran subsidiaries: Messier-Dowty, Messier-Bugatti and Messier Services. In May 2016, Messier-Bugatti-Dowty became ''Safran Landing Systems''. Safran Landing Systems operates a number of sites across the gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gol Transportes Aéreos
Gol or GOL may refer to: Places * * Gol, Gilan, a village in Gilan Province, Iran * Gol, South Khorasan, a village in South Khorasan Province, Iran * Gol, Bukan, a village in West Azerbaijan Province, Iran * Gol, Chaldoran, a village in West Azerbaijan Province, Iran * Gol, Naqadeh, a village in West Azerbaijan Province, Iran * Gol, Norway, a municipality in Buskerud * Göl, Vezirköprü, a municipality in Samsun Province, Turkey * Gol, Bhopal, a village in Madhya Pradesh, India * ''Gol'' is the Mongolian word for "river", and part of many river names, e.g. Khalkhyn Gol, Edsin Gol, Tamir gol,... People with the surname * Janusz Gol (born 1985), Polish footballer * Jean Gol (1942-1995), Belgian politician Other uses * GOL Sniper Magnum, a German sniper rifle * Gol Linhas Aéreas Inteligentes, a Brazilian airline company * GOL PLAY, a Spanish TV channel dedicated to football (soccer) * GOL TV, the first television network in the United States dedicated to soccer * Conw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fly-by-wire
Fly-by-wire (FBW) is a system that replaces the conventional aircraft flight control system#Hydro-mechanical, manual flight controls of an aircraft with an electronic interface. The movements of flight controls are converted to electronic signals, and flight control computers determine how to move the actuators at each control surface to provide the ordered response. Implementations either use Aircraft flight control system, mechanical flight control backup systems or else are fully electronic.Fly by Wire Flight Control Systems Sutherland Improved fully fly-by-wire systems interpret the pilot's control inputs as a desired outcome and calculate the control surface positions required to achieve that outcome; this results in various combinations of rudder, Elevator (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N707SA Southwest Airlines 1998 Boeing 737-7H4 (cn 27841-1) (5289274531)
N7 may refer to: Music and entertainment * ''N7'', 1995 film with Cliff Parisi * '' Never 7: The End of Infinity'', a Japanese video game Transport * London Buses route N7 * National Airlines (N7), an airline that operated from 1999 to 2002 under the IATA N7 * LNER Class N7, a class of British steam locomotives * Xiali N7, a Chinese SUV * Denza N7, an electric SUV by BYD Auto * Luxgen n7, an electric SUV * Nissan N7, an electric sedan Roads * N7 road (Bangladesh) * N7 road (Belgium), a road connecting Brussels and Doornik passing Halle and Ath * N7 road (France) * N7 road (Ireland) * N7 road (Luxembourg) * N7 road (Netherlands), part of Rijksweg 7 * N7 road (Senegal) * N7 road (South Africa), a road in South Africa connecting Cape Town to the Namibian border * N7 road (Switzerland) * Nebraska Highway 7, a state highway in the U.S. state of Nebraska N07 * ATC code N07 ''Other nervous system drugs'', a subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbus A320 Family
The Airbus A320 family is a series of narrow-body airliners developed and produced by Airbus. The A320 was launched in March 1984, first flew on 22 February 1987, and was introduced in April 1988 by Air France. The first member of the family was followed by the stretched A321 (first delivered in January 1994), the shorter A319 (April 1996), and the shortest variant, the A318 (July 2003). Final assembly takes place in Toulouse in France; Hamburg in Germany; Tianjin in China since 2009; and Mobile, Alabama, in the United States since April 2016. The twinjet has a six-abreast economy cross-section and came with either CFM56-5A or -5B, or IAE V2500 turbofan engines, except the A318. The A318 has either two CFM56-5B engines or a pair of PW6000 engines in place of the IAE V2500. The family pioneered the use of digital fly-by-wire and side-stick flight controls in airliners. Variants offer maximum take-off weights from , to cover a range. The 31.4 m (103 ft) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competition Between Airbus And Boeing
The competition between Airbus and Boeing has been characterized as a duopoly in the large jet airliner market since the 1990s. The duopoly resulted from a series of mergers within the global aerospace industry, with Airbus beginning as a pan-European consortium while the American Boeing absorbed its former arch-rival, McDonnell Douglas, in 1997. Other manufacturers, such as Lockheed Martin and Convair in the United States, and Fokker in Europe, were no longer able to compete and effectively withdrew from this market. British Aerospace (now BAE Systems) joined the consortium in 1979. In the 10 years from 2015 to 2024, Airbus received orders for 8,950 aircraft and delivered 7,043, while Boeing received net orders for 5,012 aircraft and delivered 5,312. During their period of intense competition, both companies regularly accused each other of receiving unfair state aid from their respective governments. In 2019, Airbus displaced Boeing as the largest aerospace company by revenu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |