|
Blundellsands
Blundellsands is an area of Crosby in the ceremonial county of Merseyside, England and in the historic county of Lancashire. The area was created as a suburb for wealthy businessmen from Liverpool by the Blundell family of Crosby Hall in the middle of the 19th century. It is part of the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton, and a Sefton council electoral ward. At the 2001 census the population was recorded as 11,514. This area was not measured in the 2011 Census. For current figures see Blundellsands (Ward). Description Blundellsands is an area north to the city of Liverpool and to the west of Crosby with Hightown and Little Crosby to the north, Great Crosby and Thornton to the east and Brighton-le-Sands and Waterloo to the south. The area is served by Blundellsands & Crosby and Hall Road railway stations. Its shoreline, the northern part of Crosby Beach, includes parts of the popular exhibit, ''Another Place'', designed by the sculptor Antony Gormley. Several of the Gor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blundellsands & Crosby Railway Station
Blundellsands & Crosby railway station is a railway station in the Blundellsands area of Merseyside, England. It also serves the adjacent town of Crosby. It is situated on the Northern Line of the Merseyrail network. History Blundellsands & Crosby railway station opened on 24 July 1848 as Crosby when the Liverpool, Crosby and Southport Railway (LC&SR) opened its line from to . The station was situated on the north side of Warren House lane (which became Mersey Road) which was crossed using a level crossing, In 1852, the station was moved north to the south side of the newly built Blundellsands Road which was also crossed via a level crossing. This station was constructed from some of the materials from the recently closed opening on 1 June. In 1850, the LC&SR had been authorised to lease, sell or transfer itself to the L&YR and on 14 June 1855 the L&YR purchased and took over the LC&SR. The station was relocated again in 1865 to the north side of Blundellsands Road whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2001 United Kingdom Census
A nationwide census, known as Census 2001, was conducted in the United Kingdom on Sunday, 29 April 2001. This was the 20th Census in the United Kingdom, UK census and recorded a resident population of 58,789,194. The 2001 UK census was organised by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA). Detailed results by region, council area, ward and ONS coding system, output area are available from their respective websites. Organisation Similar to previous UK censuses, the 2001 census was organised by the three statistical agencies, ONS, GROS, and NISRA, and coordinated at the national level by the Office for National Statistics. The Order in Council#Orders in Council as Statutory Instruments, Orders in Council to conduct the census, specifying the people and information to be included in the census, were made under the authority of the Census Act 1920 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Another Place (sculpture)
''Another Place'' is a piece of modern sculpture by British artist Antony Gormley located at Crosby Beach in Merseyside, England. It consists of 100 cast iron figures facing towards the sea. The figures are modelled on the artist's own naked body. The work proved controversial due to the naked statues but has increased tourism to the beach. After being exhibited at two other locations, it was put on display at Crosby on 1 July 2005. After some controversy, Sefton Metropolitan Borough Council decided on 7 March 2007 that the sculptures should be permanently installed at the beach. Construction and history The work consists of cast iron figures which face out to sea, spread over a stretch of beach between Waterloo and Blundellsands. Each figure is tall and weighs around . The figures are cast replicas of Gormley's own body. As the tides ebb and flow, the figures are revealed and submerged by the sea, and are subject to corrosion by seawater and colonisation by marine animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
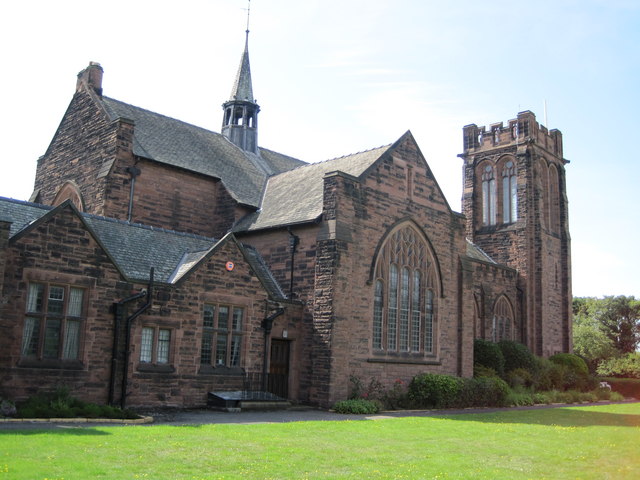
Listed Buildings In Blundellsands
Blundellsands is an area in Metropolitan Borough of Sefton, Sefton, Merseyside, England. It contains six buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England as designated listed buildings, all of which are listed at Grade II. This grade is the lowest of the three gradings given to listed buildings and is applied to "buildings of national importance and special interest". The area was created as a suburb for wealthy businessmen from Liverpool by the Blundell family of Crosby Hall in the middle of the 19th century. The listed buildings consist of domestic properties, two churches, and a drinking fountain. References Citations Sources * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Blundellsands Listed buildings in Merseyside Lists of listed buildings in Merseyside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anne Robinson
Anne Josephine Robinson (born 26 September 1944) is a British journalist and television presenter, best known as the host of BBC game show ''The Weakest Link'' from 2000 to 2012, and again in 2017 for a one-off celebrity special for ''Children in Need''. She presented the BBC consumer affairs programme '' Watchdog'' for a total of 15 years, from 1993 to 2001 and again from 2009 to 2015. Robinson hosted the Channel 4 game show '' Countdown'' from June 2021 to July 2022, taking over from Nick Hewer. She left the programme on 13 July 2022 after one year, recording a total of 265 episodes. Early life Robinson was born in Crosby, Lancashire, on 26 September 1944 and is of British and Irish descent."Memoirs of an Unfit Mother by Anne Robinson" – Post.ie – 11 November 2001 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idries Shah
Idries Shah (; , , ; 16 June 1924 – 23 November 1996), also known as Idris Shah, Indries Shah, né Sayyid, Sayed Idries el-Hashemite, Hashimi (Arabic: ) and by the pen name Arkon Daraul, was an Afghans, Afghan author, thinker and teacher in the Sufism, Sufi tradition. Shah wrote over three dozen books on topics ranging from psychology and spirituality to travelogues and culture studies. Born in British India, the descendant of a family of Afghans, Afghan nobles on his father's side and a Scottish people, Scottish mother, Shah grew up mainly in England. His early writings centred on magic (paranormal), magic and witchcraft. In 1960 he established a publishing house, Octagon Press, producing translations of Sufi classics as well as titles of his own. His seminal work was ''The Sufis'', which appeared in 1964 and was well received internationally. In 1965, Shah founded the Institute for Cultural Research, a London-based educational charity devoted to the study of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wicca
Wicca (), also known as "The Craft", is a Modern paganism, modern pagan, syncretic, Earth religion, Earth-centred religion. Considered a new religious movement by Religious studies, scholars of religion, the path evolved from Western esotericism, developed in England during the first half of the 20th century, and was Witchcraft Today, introduced to the public in 1954 by Gerald Gardner, a retired British civil servant. Wicca draws upon paganism, ancient pagan and Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, 20th-century Hermetic motif (folkloristics), motifs for theology, theological and ritual purposes. Doreen Valiente joined Gardner in the 1950s, further building Wicca's liturgical tradition of beliefs, principles, and practices, disseminated through published books as well as secret written and oral teachings passed along to Initiation, initiates. Many variations of the religion have grown and evolved over time, associated with a number of diverse lineages, sects, and Religious den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neopaganism
Modern paganism, also known as contemporary paganism and neopaganism, spans a range of new religious movements variously influenced by the Paganism, beliefs of pre-modern peoples across Europe, North Africa, and the Near East. Despite some common similarities, contemporary pagan movements are diverse, sharing no single set of beliefs, practices, or religious texts. Religious studies, Scholars of religion may study the phenomenon as a movement divided into different religions, while others study neopaganism as a decentralized religion with an array of Religious denomination, denominations. Adherents rely on Christianization, pre-Christian, folkloric, and ethnographic sources to a variety of degrees; many of them follow a spirituality that they accept as entirely modern, while others claim to adhere to Prehistoric religion, prehistoric beliefs, or else, they attempt to revive indigenous religions as accurately as possible. List of modern pagan movements, Modern pagan movements are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gardnerian Wicca
Gardnerian Wicca, or Gardnerian witchcraft, is a tradition in the neopagan religion of Wicca, whose members can trace initiatory descent from Gerald Gardner. The tradition is itself named after Gardner (1884–1964), a British civil servant and amateur scholar of magic. The term "Gardnerian" was probably coined by the founder of Cochranian Witchcraft, Robert Cochrane in the 1950s or 1960s, who himself left that tradition to found his own. Gardner claimed to have learned the beliefs and practices that would later become known as Gardnerian Wicca from the New Forest coven, who allegedly initiated him into their ranks in 1939. For this reason, Gardnerian Wicca is usually considered to be the earliest created tradition of Wicca, from which most subsequent Wiccan traditions are derived. From the supposed New Forest coven, Gardner formed his own Bricket Wood coven, and in turn initiated many Witches, including a series of High Priestesses, founding further covens and continu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Gardner
Gerald Brosseau Gardner (13 June 1884 – 12 February 1964), also known by the craft name Scire, was an English Wiccan, author, and amateur anthropology, anthropologist and archaeology, archaeologist. He was instrumental in bringing the Modern paganism, modern pagan religion of Wicca to public attention, writing some of its definitive religious texts and founding the tradition of Gardnerian Wicca. Born into an upper-middle-class family in Blundellsands, Lancashire, Gardner spent much of his childhood abroad in Madeira. In 1900, he moved to colonial Sri Lanka, Ceylon. In 1911, he relocated to British Malaya, Malaya, where he worked as a civil servant. Independently, he developed an interest in the native peoples, writing papers, and even a book about their magical practices. After his retirement in 1936, he travelled to Cyprus and penned the novel ''A Goddess Arrives'' before returning to England. Settling down near the New Forest, he joined an occult group, the Rosicrucian Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterloo R
Waterloo most commonly refers to: * Battle of Waterloo, 1815 battle where Napoleon's French army was defeated by Anglo-allied and Prussian forces * Waterloo, Belgium Waterloo may also refer to: Other places Australia *Waterloo, New South Wales * Waterloo, Queensland * Waterloo, South Australia *Waterloo Bay, now Elliston, South Australia *Waterloo, Victoria * Waterloo, Western Australia Canada * Waterloo, Nova Scotia *Regional Municipality of Waterloo, a region in Ontario **Waterloo, Ontario, a city **Waterloo (federal electoral district) **Waterloo (provincial electoral district) **Waterloo County, Ontario (1853–1973) * Waterloo, Quebec * Waterloo Village, a neighbourhood in Saint John, New Brunswick United Kingdom England *Waterloo, Dorset, England, a suburb of Poole * Waterloo, Huddersfield, England, a suburb *Waterloo, London, England, area around Waterloo Station * Waterloo Place, London, a street in the St James's area *Waterloo, Merseyside, England **Waterloo (UK P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Reformation
The English Reformation began in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away first from the authority of the pope and bishops Oath_of_Supremacy, over the King and then from some doctrines and practices of the Catholic Church. These events were part of the wider European Reformation: various religious and political movements that affected both the practice of Christianity in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe and relations between church and state. The English Reformation began as more of a political affair than a theological dispute. In 1527 Henry VIII requested an annulment of his marriage, but Pope Clement VII refused. In response, the English Reformation Parliament, Reformation Parliament (1529–1536) passed laws abolishing papal authority in England and declared Henry to be Supreme Head of the Church of England, head of the Church of England. Final authority in doctrinal disputes now rested with the monarch. Though a religious traditionalist hims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |