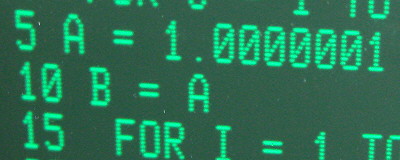|
Blanking (video)
In analog video, blanking occurs between horizontal lines and between frames. In raster scan equipment, an image is built up by scanning an electron beam from left to right across a screen to produce a visible trace of one scan line, reducing the brightness of the beam to zero (horizontal blanking), moving it back as fast as possible to the left of the screen at a slightly lower position (the next scan line), restoring the brightness, and continuing until all the lines have been displayed and the beam is at the bottom right of the screen. Its intensity is then reduced to zero again ( vertical blanking), and it is rapidly moved to the top left to start again, creating the next frame. In television, in particular, the vertical blanking interval In a raster scan display, the vertical blanking interval (VBI), also known as the vertical interval or VBLANK, is the time between the end of the final visible line of a frame or field and the beginning of the first visible line of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Video
Video is an Electronics, electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving picture, moving image, visual Media (communication), media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems, which, in turn, were replaced by flat-panel displays of several types. Video systems vary in display resolution, Display aspect ratio, aspect ratio, refresh rate, color capabilities, and other qualities. Analog and digital variants exist and can be carried on a variety of media, including radio broadcasts, magnetic tape, optical discs, Video file format, computer files, and Streaming media, network streaming. Etymology The word ''video'' comes from the Latin verb ''video,'' meaning to see or ''videre''. And as a noun, "that which is displayed on a (television) screen," History Analog video Video developed from facsimile systems developed in the mid-19th century. Early mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raster Scan
A raster scan, or raster scanning, is the rectangular pattern of image capture and reconstruction in television. By analogy, the term is used for raster graphics, the pattern of image storage and transmission used in most computer bitmap image systems. The word ''wiktionary:raster, raster'' comes from the Latin word ''wiktionary:rastrum, rastrum'' (a rake), which is derived from ''wiktionary:radere, radere'' (to scrape); see also rastrum, an instrument for drawing musical staff lines. The pattern left by the lines of a rake, when drawn straight, resembles the parallel lines of a raster: this line-by-line scanning is what creates a raster. It is a systematic process of covering the area progressively, one line at a time. Although often a great deal faster, it is similar in the most general sense to how one's gaze travels when one reads lines of text. In most modern graphics cards the data to be drawn is stored internally in an area of semiconductor memory called the framebuffer. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode Ray Tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms on an oscilloscope, a Film frame, frame of video on an Analog television, analog television set (TV), Digital imaging, digital raster graphics on a computer monitor, or other phenomena like radar targets. A CRT in a TV is commonly called a picture tube. CRTs have also been Williams tube, used as memory devices, in which case the screen is not intended to be visible to an observer. The term ''cathode ray'' was used to describe electron beams when they were first discovered, before it was understood that what was emitted from the cathode was a beam of electrons. In CRT TVs and computer monitors, the entire front area of the tube is scanned repeatedly and systematically in a fixed pattern called a raster scan, raster. In color devices, an image is produced by con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Blanking Interval
Horizontal blanking interval refers to a part of the process of displaying images on a computer monitor or television screen via raster scanning. CRT screens display images by moving beams of electrons very quickly across the screen. Once the beam of the monitor has reached the edge of the screen, it is switched off, and the deflection circuit voltages (or currents) are returned to the values they had for the other edge of the screen; this would have the effect of retracing the screen in the opposite direction, so the beam is turned off during this time. This part of the line display process is the Horizontal Blank. In detail, the Horizontal blanking interval consists of: * front porch – blank while still moving right, past the end of the scanline, * sync pulse – blank while rapidly moving left; in terms of amplitude, "blacker than black". * back porch – blank while moving right again, before the start of the next scanline. Colorburst occurs during the back porch, and un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Blanking Interval
In a raster scan display, the vertical blanking interval (VBI), also known as the vertical interval or VBLANK, is the time between the end of the final visible line of a frame or field and the beginning of the first visible line of the next frame or field. It is present in analog television, VGA, DVI and other signals. Here the term field is used in interlaced video, and the term frame is used in progressive video and there can be a VBI after each frame or field. In interlaced video a frame is made up of 2 fields. Sometimes in interlaced video a field is called a frame which can lead to confusion. In raster cathode-ray tube (CRT) displays, the blank level is usually supplied during this period to avoid painting the retrace line—see raster scan for details; signal sources such as television broadcasts do not supply image information during the blanking period. Digital displays usually will not display incoming data stream during the blanking interval even if present. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. The medium is capable of more than "radio broadcasting", which refers to an audio signal sent to radio receivers. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Blanking Interval
In a raster scan display, the vertical blanking interval (VBI), also known as the vertical interval or VBLANK, is the time between the end of the final visible line of a frame or field and the beginning of the first visible line of the next frame or field. It is present in analog television, VGA, DVI and other signals. Here the term field is used in interlaced video, and the term frame is used in progressive video and there can be a VBI after each frame or field. In interlaced video a frame is made up of 2 fields. Sometimes in interlaced video a field is called a frame which can lead to confusion. In raster cathode-ray tube (CRT) displays, the blank level is usually supplied during this period to avoid painting the retrace line—see raster scan for details; signal sources such as television broadcasts do not supply image information during the blanking period. Digital displays usually will not display incoming data stream during the blanking interval even if present. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Technology
The technology of television has evolved since its early days using a mechanical system invented by Paul Gottlieb Nipkow in 1884. Every television system works on the scanning principle first implemented in the rotating disk scanner of Nipkow. This turns a two-dimensional image into a time series of signals that represent the brightness and color of each resolvable element of the picture. By repeating a two-dimensional image quickly enough, the impression of motion can be transmitted as well. For the receiving apparatus to reconstruct the image, synchronization information is included in the signal to allow proper placement of each line within the image and to identify when a complete image has been transmitted and a new image is to follow. While mechanically scanned systems were experimentally used, television as a mass medium was made practical by the development of electronic camera tubes and displays. By the turn of the 21st century, it was technically feasible to replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |