|
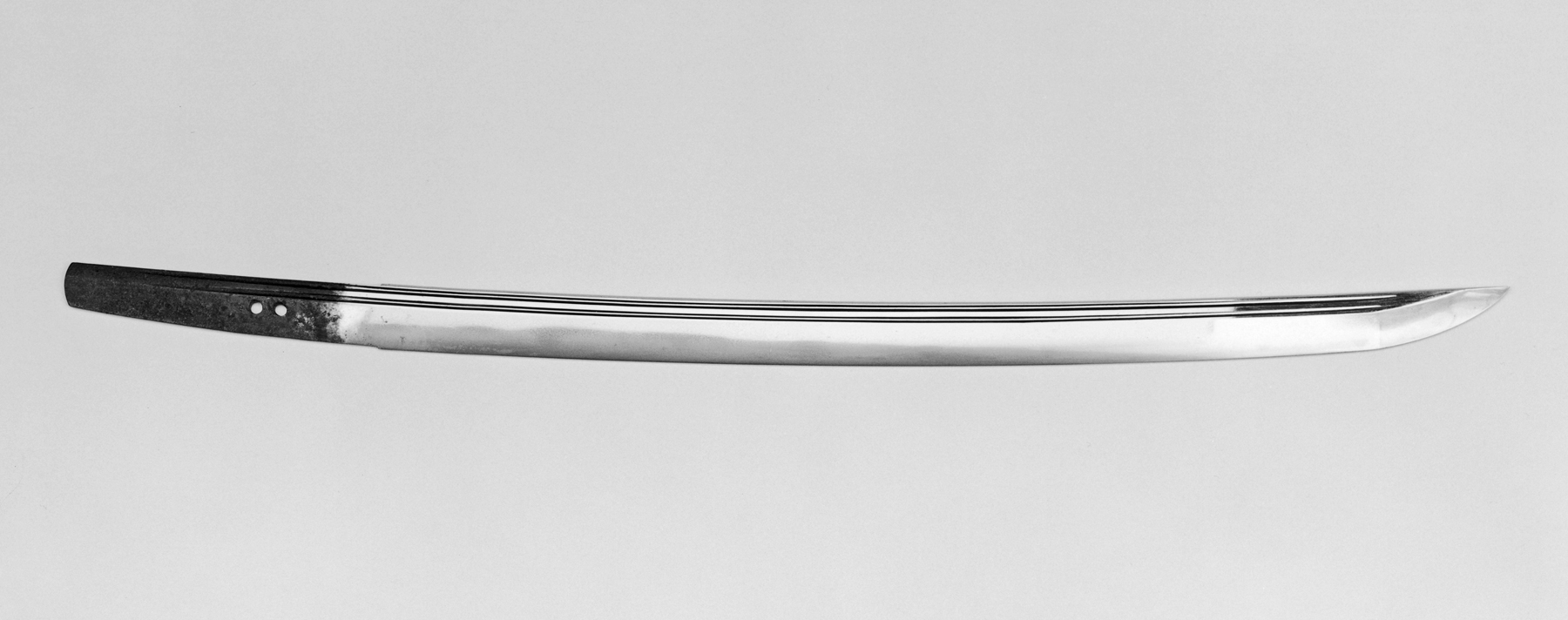
Blade Geometry
The term ''blade geometry'' refers to the physical properties of a sword blade: cross-section (or grind) and taper. Blade geometry Blade geometry is a crucial aspect of knife and sword design, influencing both the performance and usability of cutting tools. Cross-section The cross-section of a blade is the primary way of determining its function and place in history. Early Middle Ages Early Viking and medieval European blades tended to have a lenticular cross-section. This type of design lacks a strong central ridge in the middle of the blade. The flexibility these blades have illustrates the purpose that they served, as primarily cutting weapons, that could also be used with the thrust. Late Middle Ages With the improvement in the defensive capabilities of armor in the High and Late Middle Ages, the cross-section of the sword blade adapted to suit the needs of warriors. Swords began to favour rigidity over flexibility as more rigid blades allowed for the stronger thrusts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grind
A blade's grind is its cross-sectional shape in a plane normal to the edge. Grind differs from Blade#Knife blade profiles .28Patterns.29, blade profile, which is the blade's cross-sectional shape in the plane containing the blade's edge and the centre contour of the blade's back (meaning the shape of the blade when viewed from the side, i.e. clip point, spear point, etc.). The ''grind'' of a blade should not be confused with the bevel forming the sharpened edge; it more usually describes the overall cross-section of the blade, not inclusive of the beveled cutting edge which is typically of a different, less acute angle as the bevel ground onto the blade to give it a cross-sectional shape. For example, the famous Buck 110 hunting knife has a "hollow ground" blade, with concave blade faces (which aid in slicing through materials), but the cutting edge itself is a simple, flat-ground bevel of lesser angle. It would be difficult, if not impossible, to put a "hollow grind" onto th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blade
A blade is the Sharpness (cutting), sharp, cutting portion of a tool, weapon, or machine, specifically designed to puncture, chop, slice, or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are intended to cut. This includes early examples made from flaked stones like flint or obsidian, evolving through the ages into metal forms like copper, bronze, and iron, and culminating in modern versions made from steel or ceramics. Serving as one of humanity's oldest tools, blades continue to have wide-ranging applications, including in combat, cooking, and various other everyday and specialized tasks. Blades function by concentrating force at the cutting edge. Design variations, such as serrated edges found on bread knives and saws, serve to enhance this force concentration, adapting blades for specific functions and materials. Blades thus hold a significant place both historically and in contemporary society, reflecting an evolution i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden), who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9–22. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, North Africa, the Middle East, Greenland, and Vinland (present-day Newfoundland in Canada, North America). In their countries of origin, and some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the Early Middle Ages, early medieval history of Northern Europe, northern and Eastern Europe, including the political and social development of England (and the English language) and parts of France, and established the embryo of Russia in Kievan Rus'. Expert sailors and navigators of their cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armor
Armour (Commonwealth English) or armor (American English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or from a potentially dangerous environment or activity (e.g. cycling, construction sites, etc.). Personal armour is used to protect soldiers and war animals. Vehicle armour is used on warships, armoured fighting vehicles, and some combat aircraft, mostly ground attack aircraft. A second use of the term ''armour'' describes Division (military)#Armoured division, armoured forces, #Armoured fighting vehicles, armoured weapons, and their role in combat. After the development of armoured warfare, tanks and mechanised infantry and their combat formations came to be referred to collectively as "armour". Etymology The word "armour" began to appear in the Middle Ages as a derivati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention. Key historical trends of the High Middle Ages include the medieval demography, rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, and the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1350, the robust population increase had greatly benefited the European economy, which had reached levels that would not be seen again in some areas until the 19th century. That trend faltered in the early 14th century, as the result of numerous events which together comprised the crisis of the late Middle Ages—most notable among them being the Black Death, in addition to various regional wars and economic stagnation. From , Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estoc
The French estoc is a type of sword, also called a tuck in English, in use from the 14th to the 17th century. It is characterized by a cruciform hilt with a grip for two-handed use and a straight, edgeless, but sharply pointed blade around in length. It is noted for its ability to pierce mail armor. Description The estoc was a variation of the longsword designed for fighting against mail armor or plate armor. It was long, straight and stiff with no cutting edge, just a point. Examples from Poland are more than long, with a blade of ; however, others show a more manageable , with a blade. Such swords average about with no specimen weighing more than . Blade cross-sections can be triangular, square, rhomboid, or flat hexagonal. This geometry leaves hardly any cutting capability as a sharpened edge could simply not be ground but allowed the weapon to be lengthy, stiff, and very acutely pointed. Early on, the estoc was hung from the saddle when on horseback and simply hung fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longsword
A longsword (also spelled as long sword or long-sword) is a type of European sword characterized as having a cruciform hilt with a grip for primarily two-handed use (around ), a straight double-edged blade of around , and weighing approximately . The "longsword" type exists in a morphological continuum with the medieval knightly sword and the Renaissance-era Zweihänder. It was prevalent during the Late Middle Ages, late medieval and Renaissance periods (approximately 1350 to 1550), with early and late use reaching into the 11th and 17th centuries. Names English The longsword has many names in the English language, which, aside from variant spellings, include terms such as "bastard sword" and "hand-and-a-half sword." Of these, "bastard sword" is the oldest, its use being contemporaneous with the weapon's heyday. The French ' and the English "bastard sword" originate in the 15th or 16th century, originally in the general sense of "irregular sword, sword of uncertain orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swords
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip. A slashing sword is more likely to be curved and to have a sharpened cutting edge on one or both sides of the blade. Many swords are designed for both thrusting and slashing. The precise definition of a sword varies by historical epoch and geographic region. Historically, the sword developed in the Bronze Age, evolving from the dagger; the earliest specimens date to about 1600 BC. The later Iron Age sword remained fairly short and without a crossguard. The spatha, as it developed in the Late Roman army, became the predecessor of the European sword of the Middle Ages, at first adopted as the Migration Period sword, and only in the High Middle Ages, developed into the classical arming sword with crossguard. The word ''sword'' contin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |