|
Black-body
A black body or blackbody is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence. The radiation emitted by a black body in thermal equilibrium with its environment is called ''black-body radiation''. The name "black body" is given because it absorbs all colors of light. In contrast, a white body is one with a "rough surface that reflects all incident rays completely and uniformly in all directions." A black body in thermal equilibrium (that is, at a constant temperature) emits electromagnetic black-body radiation. The radiation is emitted according to Planck's law, meaning that it has a spectrum that is determined by the temperature alone (see figure at right), not by the body's shape or composition. An ideal black body in thermal equilibrium has two main properties: #It is an ideal emitter: at every frequency, it emits as much or more thermal radiative energy as any other body at the same temperature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planck's Law
In physics, Planck's law (also Planck radiation law) describes the spectral density of electromagnetic radiation emitted by a black body in thermal equilibrium at a given temperature , when there is no net flow of matter or energy between the body and its environment. At the end of the 19th century, physicists were unable to explain why the observed spectrum of black-body radiation, which by then had been accurately measured, diverged significantly at higher frequencies from that predicted by existing theories. In 1900, German physicist Max Planck heuristically derived a formula for the observed spectrum by assuming that a hypothetical electrically charged oscillator in a cavity that contained black-body radiation could only change its energy in a minimal increment, , that was proportional to the frequency of its associated electromagnetic wave. While Planck originally regarded the hypothesis of dividing energy into increments as a mathematical artifice, introduced merely to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-body Radiation
Black-body radiation is the thermal radiation, thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body). It has a specific continuous spectrum that depends only on the body's temperature., Chapter 13. A perfectly-insulated enclosure which is in thermal equilibrium internally contains blackbody radiation and will emit it through a hole made in its wall, provided the hole is small enough to have a negligible effect upon the equilibrium. The thermal radiation spontaneously emitted by many ordinary objects can be approximated as blackbody radiation. Of particular importance, although planets and stars (including the Earth and Sun) are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, blackbody radiation is still a good first approximation for the energy they emit. The term ''black body'' was introduced by Gustav Kirchhoff in 1860. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Body Realization
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''Psychologie de la couleur – effets et symboliques'', pp. 105–26. Black and white have often been used to describe opposites such as good and evil, the Dark Ages versus the Age of Enlightenment, and night versus day. Since the Middle Ages, black has been the symbolic color of solemnity and authority, and for this reason it is still commonly worn by judges and magistrates. Black was one of the first colors used by artists in Neolithic cave paintings. It was used in ancient Egypt and Greece as the color of the underworld. In the Roman Empire, it became the color of mourning, and over the centuries it was frequently associated with death, evil, witches, and magic. In the 14th century, it was worn by royalty, clergy, judges, and government o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
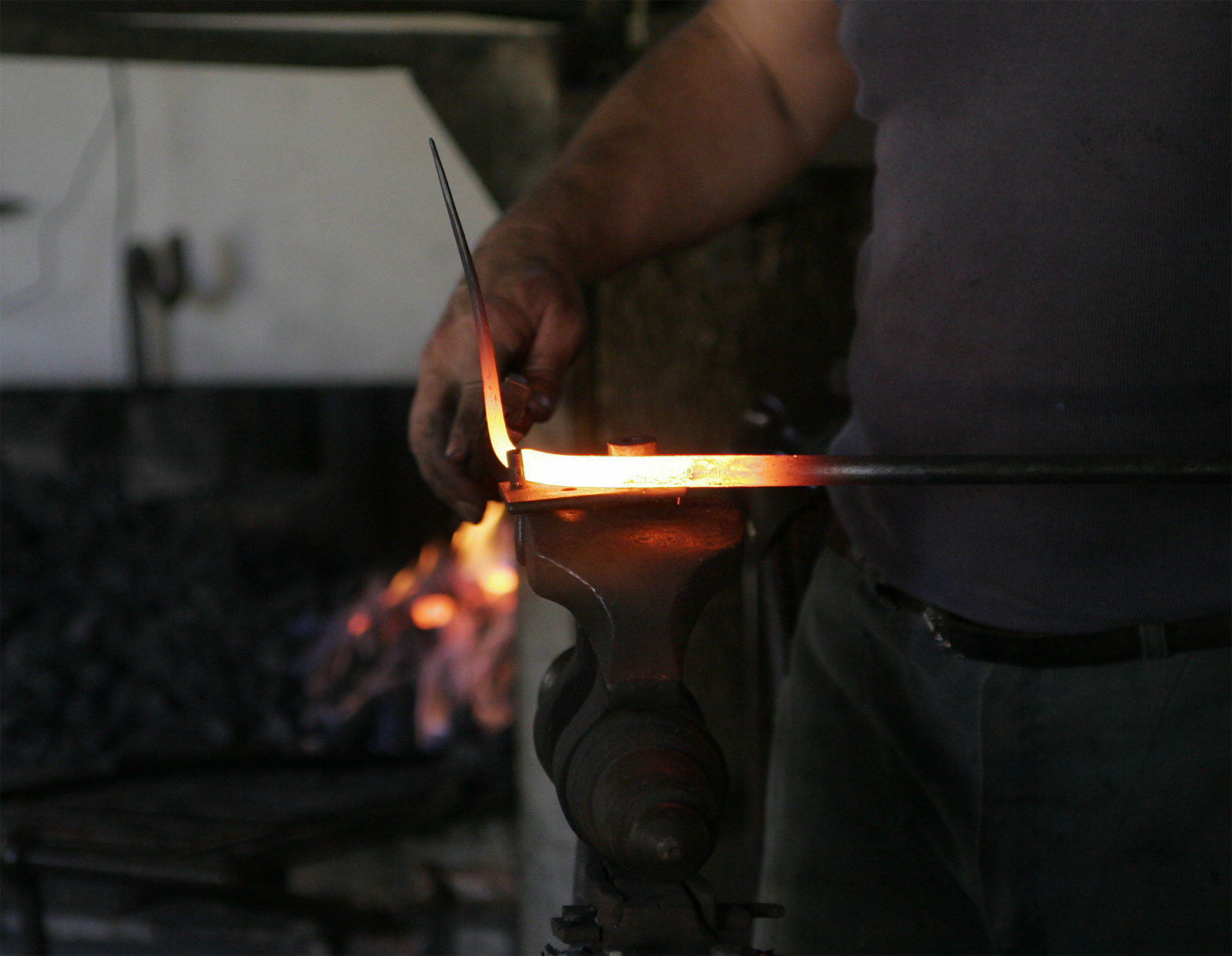
Emissivity
The emissivity of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in emitting energy as thermal radiation. Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation that most commonly includes both visible radiation (light) and infrared radiation, which is not visible to human eyes. A portion of the thermal radiation from very hot objects (see photograph) is easily visible to the eye. The emissivity of a surface depends on its chemical composition and geometrical structure. Quantitatively, it is the ratio of the thermal radiation from a surface to the radiation from an black body, ideal black surface at the same temperature as given by the Stefan–Boltzmann law. (A comparison with Planck's law is used if one is concerned with particular wavelengths of thermal radiation.) The ratio varies from 0 to 1. The surface of a perfect black body (with an emissivity of 1) emits thermal radiation at the rate of approximately 448 watts per square metre (W/m) at a room temperature of . Objects have emi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Body Radiator At CARLO Laboratory In Poland
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''Psychologie de la couleur – effets et symboliques'', pp. 105–26. Black and white have often been used to describe opposites such as good and evil, the Dark Ages versus the Age of Enlightenment, and night versus day. Since the Middle Ages, black has been the symbolic color of solemnity and authority, and for this reason it is still commonly worn by judges and magistrates. Black was one of the first colors used by artists in Neolithic cave paintings. It was used in ancient Egypt and Greece as the color of the underworld. In the Roman Empire, it became the color of mourning, and over the centuries it was frequently associated with death, evil, witches, and magic. In the 14th century, it was worn by royalty, clergy, judges, and government o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boson
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0, 1, 2, ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have half odd-integer spin (1/2, 3/2, 5/2, ...). Every observed subatomic particle is either a boson or a fermion. Paul Dirac coined the name ''boson'' to commemorate the contribution of Satyendra Nath Bose, an Indian physicist. Some bosons are elementary particles occupying a special role in particle physics, distinct from the role of fermions (which are sometimes described as the constituents of "ordinary matter"). Certain elementary bosons (e.g. gluons) act as force carriers, which give rise to forces between other particles, while one (the Higgs boson) contributes to the phenomenon of mass. Other bosons, such as mesons, are composite particles made up of smaller constituents. Outside the realm of particle physics, multiple identical composite bosons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresnel Equations
The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel coefficients) describe the reflection and transmission of light (or electromagnetic radiation in general) when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by French engineer and physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel () who was the first to understand that light is a transverse wave, when no one realized that the waves were electric and magnetic fields. For the first time, polarization could be understood quantitatively, as Fresnel's equations correctly predicted the differing behaviour of waves of the ''s'' and ''p'' polarizations incident upon a material interface. Overview When light strikes the interface between a medium with refractive index and a second medium with refractive index , both reflection and refraction of the light may occur. The Fresnel equations give the ratio of the ''reflected'' wave's electric field to the incident wave's electric field, and the ratio of the ''transmitted'' wave's electric f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler–Heisenberg Lagrangian
In physics, the Euler–Heisenberg Lagrangian describes the non-linear dynamics of electromagnetic fields in vacuum and is consequently an example of nonlinear electrodynamics. It was first obtained by Werner Heisenberg and Hans Heinrich Euler in 1936. By treating the vacuum as a medium, it predicts rates of quantum electrodynamics (QED) light interaction processes. Physics It takes into account vacuum polarization to one loop, and is valid for electromagnetic fields that change slowly compared to the inverse electron mass, :\mathcal =-\mathcal -\frac\int_^\exp\left(-m^s\right)\left es)^\frac\mathcal-\frac(es)^\mathcal - 1\rightfrac. Here is the electron mass, the electron charge, \mathcal=\frac\left(\mathbf^2 - \mathbf^2\right), and \mathcal=\mathbf\cdot\mathbf. In the weak field limit, this becomes :\mathcal = \frac\left(\mathbf^-\mathbf^\right)+\frac\left left(\mathbf^2 - \mathbf^2\right)^ + 7 \left(\mathbf\cdot\mathbf\right)^\right It describes photon–photon scatte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opticks
''Opticks: or, A Treatise of the Reflexions, Refractions, Inflexions and Colours of Light'' is a collection of three books by Isaac Newton that was published in English language, English in 1704 (a scholarly Latin translation appeared in 1706). (''Opticks'' was originally published in 1704). The treatise analyzes the fundamental nature of light by means of the refraction of light with prisms and lenses, the diffraction of light by closely spaced sheets of glass, and the behaviour of color mixtures with spectral lights or pigment powders. ''Opticks'' was Newton's second major work on physical science and it is considered one of the three major works on optics during the Scientific Revolution (alongside Johannes Kepler's ''Astronomiae Pars Optica'' and Christiaan Huygens' ''Treatise on Light''). Overview The publication of ''Opticks'' represented a major contribution to science, different from but in some ways rivalling the ''Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, Principia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-theorem
In classical statistical mechanics, the ''H''-theorem, introduced by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872, describes the tendency of the quantity ''H'' (defined below) to decrease in a nearly-ideal gas of molecules.L. Boltzmann,Weitere Studien über das Wärmegleichgewicht unter Gasmolekülen." Sitzungsberichte Akademie der Wissenschaften 66 (1872): 275-370. English translation: As this quantity ''H'' was meant to represent the entropy of thermodynamics, the ''H''-theorem was an early demonstration of the power of statistical mechanics as it claimed to derive the second law of thermodynamics—a statement about fundamentally irreversible processes—from reversible microscopic mechanics. It is thought to prove the second law of thermodynamics, albeit under the assumption of low-entropy initial conditions. The ''H''-theorem is a natural consequence of the kinetic equation derived by Boltzmann that has come to be known as Boltzmann's equation. The ''H''-theorem has led to considerable discuss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laws Of Thermodynamics
The laws of thermodynamics are a set of scientific laws which define a group of physical quantities, such as temperature, energy, and entropy, that characterize thermodynamic systems in thermodynamic equilibrium. The laws also use various parameters for thermodynamic processes, such as thermodynamic work and heat, and establish relationships between them. They state empirical facts that form a basis of precluding the possibility of certain phenomena, such as perpetual motion. In addition to their use in thermodynamics, they are important fundamental laws of physics in general and are applicable in other natural sciences. Traditionally, thermodynamics has recognized three fundamental laws, simply named by an ordinal identification, the first law, the second law, and the third law.Guggenheim, E.A. (1985). ''Thermodynamics. An Advanced Treatment for Chemists and Physicists'', seventh edition, North Holland, Amsterdam, .Kittel, C. Kroemer, H. (1980). ''Thermal Physics'', second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planck Constant
The Planck constant, or Planck's constant, denoted by h, is a fundamental physical constant of foundational importance in quantum mechanics: a photon's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant, and the wavelength of a matter wave equals the Planck constant divided by the associated particle momentum. The constant was postulated by Max Planck in 1900 as a proportionality constant needed to explain experimental black-body radiation. Planck later referred to the constant as the "quantum of Action (physics), action". In 1905, Albert Einstein associated the "quantum" or minimal element of the energy to the electromagnetic wave itself. Max Planck received the 1918 Nobel Prize in Physics "in recognition of the services he rendered to the advancement of Physics by his discovery of energy quanta". In metrology, the Planck constant is used, together with other constants, to define the kilogram, the SI unit of mass. The SI units are defined in such a way that, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |