|
Bipropellants
A liquid-propellant rocket or liquid rocket uses a rocket engine burning liquid propellants. (Alternate approaches use gaseous or solid propellants.) Liquids are desirable propellants because they have reasonably high density and their combustion products have high specific impulse (''I''sp). This allows the volume of the propellant tanks to be relatively low. Types Liquid rockets can be monopropellant rockets using a single type of propellant, or bipropellant rockets using two types of propellant. Tripropellant rockets using three types of propellant are rare. Liquid oxidizer propellants are also used in hybrid rockets, with some of the advantages of a solid rocket. Bipropellant liquid rockets use a liquid fuel such as liquid hydrogen or RP-1, and a liquid oxidizer such as liquid oxygen. The engine may be a cryogenic rocket engine, where the fuel and oxidizer, such as hydrogen and oxygen, are gases which have been liquefied at very low temperatures. Most designs of liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Engine Throttling
A rocket engine is a reaction engine, producing thrust in accordance with Newton's third law by ejecting reaction mass rearward, usually a high-speed jet of high-temperature gas produced by the combustion of rocket propellants stored inside the rocket. However, non-combusting forms such as cold gas thrusters and nuclear thermal rockets also exist. Rocket vehicles carry their own oxidiser, unlike most combustion engines, so rocket engines can be used in a vacuum, and they can achieve great speed, beyond escape velocity. Vehicles commonly propelled by rocket engines include missiles, artillery shells, ballistic missiles and rockets of any size, from tiny fireworks to man-sized weapons to huge spaceships. Compared to other types of jet engine, rocket engines are the lightest and have the highest thrust, but are the least propellant-efficient (they have the lowest specific impulse). The ideal exhaust is hydrogen, the lightest of all elements, but chemical rockets produce a mix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipropellant Rocket
A liquid-propellant rocket or liquid rocket uses a rocket engine burning liquid propellants. (Alternate approaches use gaseous or solid propellants.) Liquids are desirable propellants because they have reasonably high density and their combustion products have high specific impulse (''I''sp). This allows the volume of the propellant tanks to be relatively low. Types Liquid rockets can be monopropellant rockets using a single type of propellant, or bipropellant rockets using two types of propellant. Tripropellant rockets using three types of propellant are rare. Liquid oxidizer propellants are also used in hybrid rockets, with some of the advantages of a solid rocket. Bipropellant liquid rockets use a liquid fuel such as liquid hydrogen or RP-1, and a liquid oxidizer such as liquid oxygen. The engine may be a cryogenic rocket engine, where the fuel and oxidizer, such as hydrogen and oxygen, are gases which have been liquefied at very low temperatures. Most designs of liq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
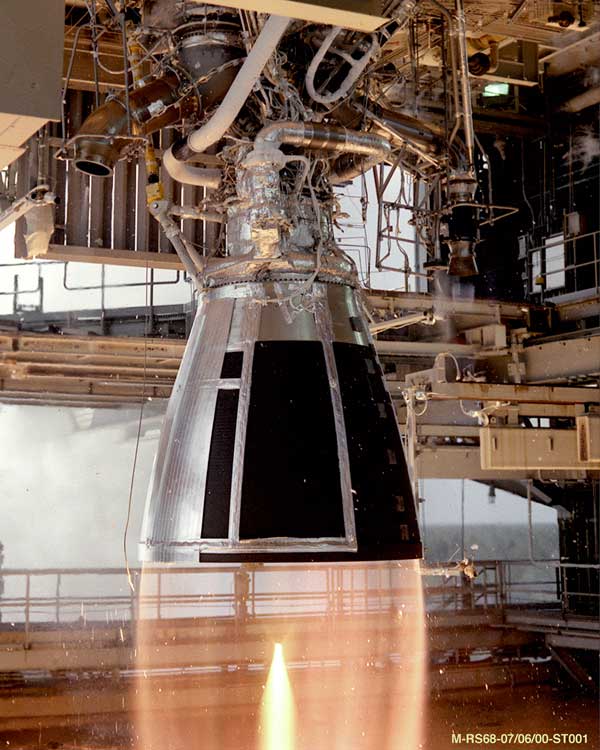
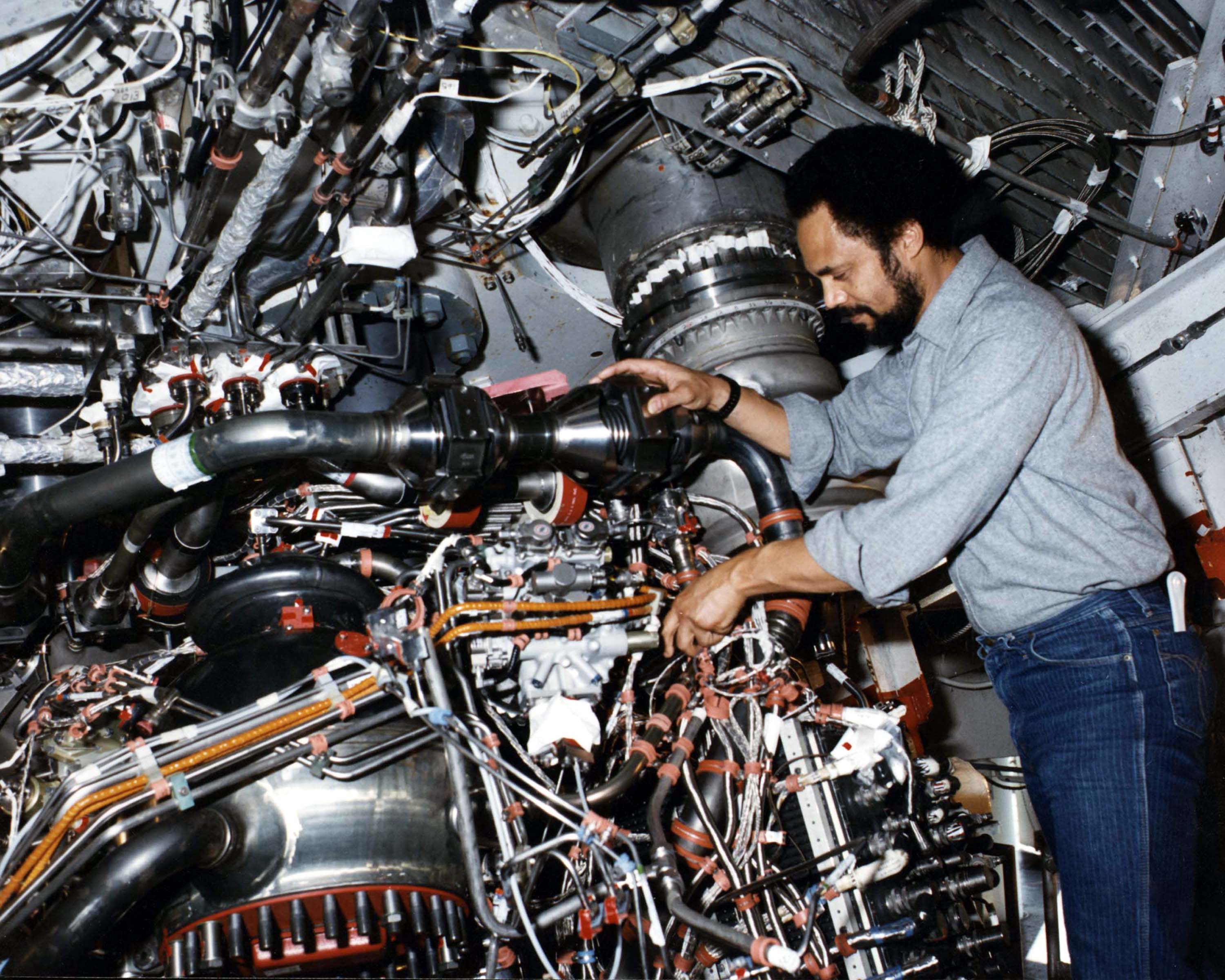
Rocket Engine
A rocket engine is a reaction engine, producing thrust in accordance with Newton's third law by ejecting reaction mass rearward, usually a high-speed Jet (fluid), jet of high-temperature gas produced by the combustion of rocket propellants stored inside the rocket. However, non-combusting forms such as cold gas thrusters and nuclear thermal rockets also exist. Rocket vehicles carry their own oxidiser, unlike most combustion engines, so rocket engines can be used in a vacuum, and they can achieve great speed, beyond escape velocity. Vehicles commonly propelled by rocket engines include missiles, Rocket-assisted projectile, artillery shells, ballistic missiles and rockets of any size, from tiny Rocket (firework), fireworks to Rocket (weapon), man-sized weapons to huge Space vehicle, spaceships. Compared to other types of jet engine, rocket engines are the lightest and have the highest thrust, but are the least propellant-efficient (they have the lowest specific impulse). The ideal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
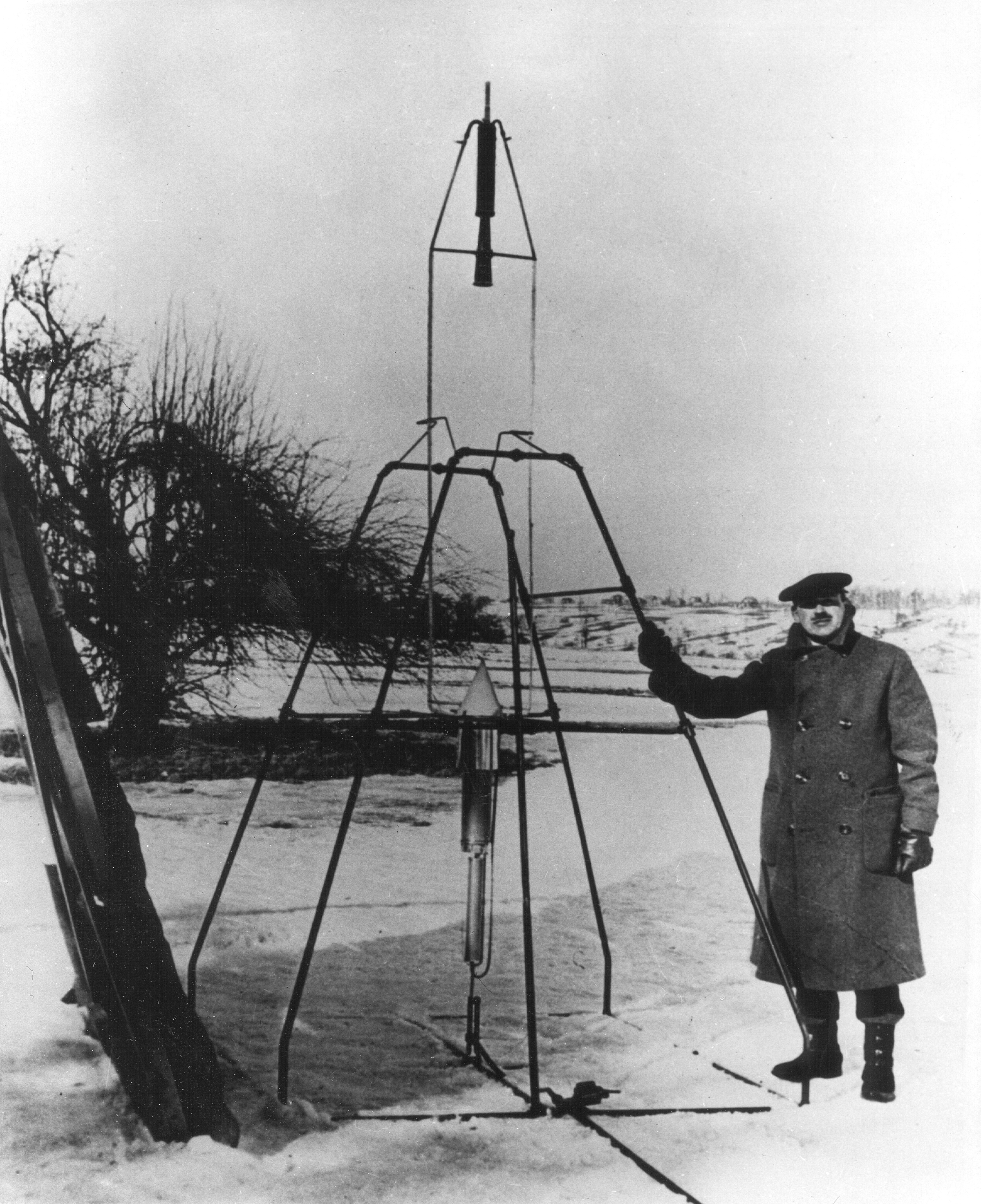
Liquid Rocket Propellant
The highest specific impulse chemical rockets use liquid propellants (liquid-propellant rockets). They can consist of a single chemical (a monopropellant) or a mix of two chemicals, called bipropellants. Bipropellants can further be divided into two categories; hypergolic propellants, which ignite when the fuel and oxidizer make contact, and non-hypergolic propellants which require an ignition source. About 170 different propellants made of liquid fuel have been tested, excluding minor changes to a specific propellant such as propellant additives, corrosion inhibitors, or stabilizers. In the U.S. alone at least 25 different propellant combinations have been flown. Many factors go into choosing a propellant for a liquid-propellant rocket engine. The primary factors include ease of operation, cost, hazards/environment and performance. History Development in early 20th century Konstantin Tsiolkovsky proposed the use of liquid propellants in 1903, in his article ''Exploration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbopumps
A turbopump is a fluid pump with two main components: a rotodynamic pump and a driving gas turbine, usually both mounted on the same shaft, or sometimes geared together. They were initially developed in Germany in the early 1940s. The most common purpose of a turbopump is to produce a high-pressure fluid for feeding a combustion chamber. While other use cases exist, they are most commonly found in liquid rocket engines. There are two common types of pumps used in turbopumps: a centrifugal pump, where the pumping is done by throwing fluid outward at high speed, or an axial-flow pump, where alternating rotating and static blades progressively raise the pressure of a fluid. Axial-flow pumps have small diameters but give relatively modest pressure increases. Although multiple compression stages are needed, axial flow pumps work well with low-density fluids. Centrifugal pumps are far more powerful for high-density fluids but require large diameters for low-density fluids. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ullage Motor
Ullage motors (also known as ullage engines or ullage rockets) are relatively small, independently fueled rocket engines that may be fired prior to main engine ignition, when the vehicle is in a zero-g situation. The resulting acceleration causes liquid in the rocket's main tanks to settle towards the aft end, ensuring uninterrupted flow to the fuel and oxidizer pumps. Description Cryogenic-liquid-fueled rockets keep their propellants in insulated tanks. These tanks are never completely filled to allow for expansion. In weightlessness, micro-gravity conditions the cryogenic liquids are without a free surface, and exist in a slushy state between solid, liquid, and gas. In this mixed state, ullage gases may be sucked into the engines, which is undesirable, as it displaces useful propellant, reduces efficiency, and may damage the engines. Small rocket engines, called "ullage motors", are sometimes used to settle the propellant before main engine ignition to allow the formation of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pogo Oscillation
Pogo oscillation is a self-excited vibration in liquid-propellant rocket engines caused by Rocket engine#Combustion instabilities, combustion instability. The unstable combustion results in variations of engine thrust, causing variations of acceleration on the vehicle's flexible structure, which in turn cause variations in propellant pressure and flow rate, closing the self-excitation cycle. The name is a metaphor comparing the Flight control surfaces#Longitudinal axis, longitudinal vibration to the bouncing of a pogo stick. Pogo oscillation places stress on the frame of the vehicle, which in severe cases can be dangerous. Origin NASA Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight George Mueller (NASA), George Mueller explained Apollo 6's pogo oscillation to a congressional hearing: In general, pogo oscillation occurs when a surge in combustion chamber pressure increases back pressure against the fuel coming into the engine. This reduces fuel flow and thus chamber pressure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Management
Total quality management, Total Quality management (TQM), ensures that an organization, product, or service consistently performs as intended, as opposed to Quality Management, which focuses on work process and procedure standards. It has four main components: quality planning, quality assurance, quality control, and quality improvement. Customers recognize that quality is an important attribute when choosing and purchasing products and services. Suppliers can recognize that quality is an important differentiator of their offerings, and endeavor to compete on the quality of their products and the service they offer. Thus, quality management is focused both on product and service quality. Advancement In earlier periods, arts and crafts were led by Master craftsman, master craftspeople or artists who supervised studios, trained apprentices, and oversaw the product development process. With the advent of the Industrial Revolution, steam engines, and mass production, the role of crafts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slosh
In fluid dynamics, slosh refers to the movement of liquid inside another object (which is, typically, also undergoing motion). Strictly speaking, the liquid must have a free surface to constitute a slosh dynamics problem, where the dynamics of the liquid can interact with the container to alter the system dynamics significantly. Important examples include propellant slosh in spacecraft tanks and rockets (especially upper stages), and the free surface effect (cargo slosh) in ships and trucks transporting liquids (for example oil and gasoline). However, it has become common to refer to liquid motion in a completely filled tank, i.e. without a free surface, as "fuel slosh". Such motion is characterized by "inertial waves" and can be an important effect in spinning spacecraft dynamics. Extensive mathematical and empirical relationships have been derived to describe liquid slosh. These types of analyses are typically undertaken using computational fluid dynamics and finite element met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
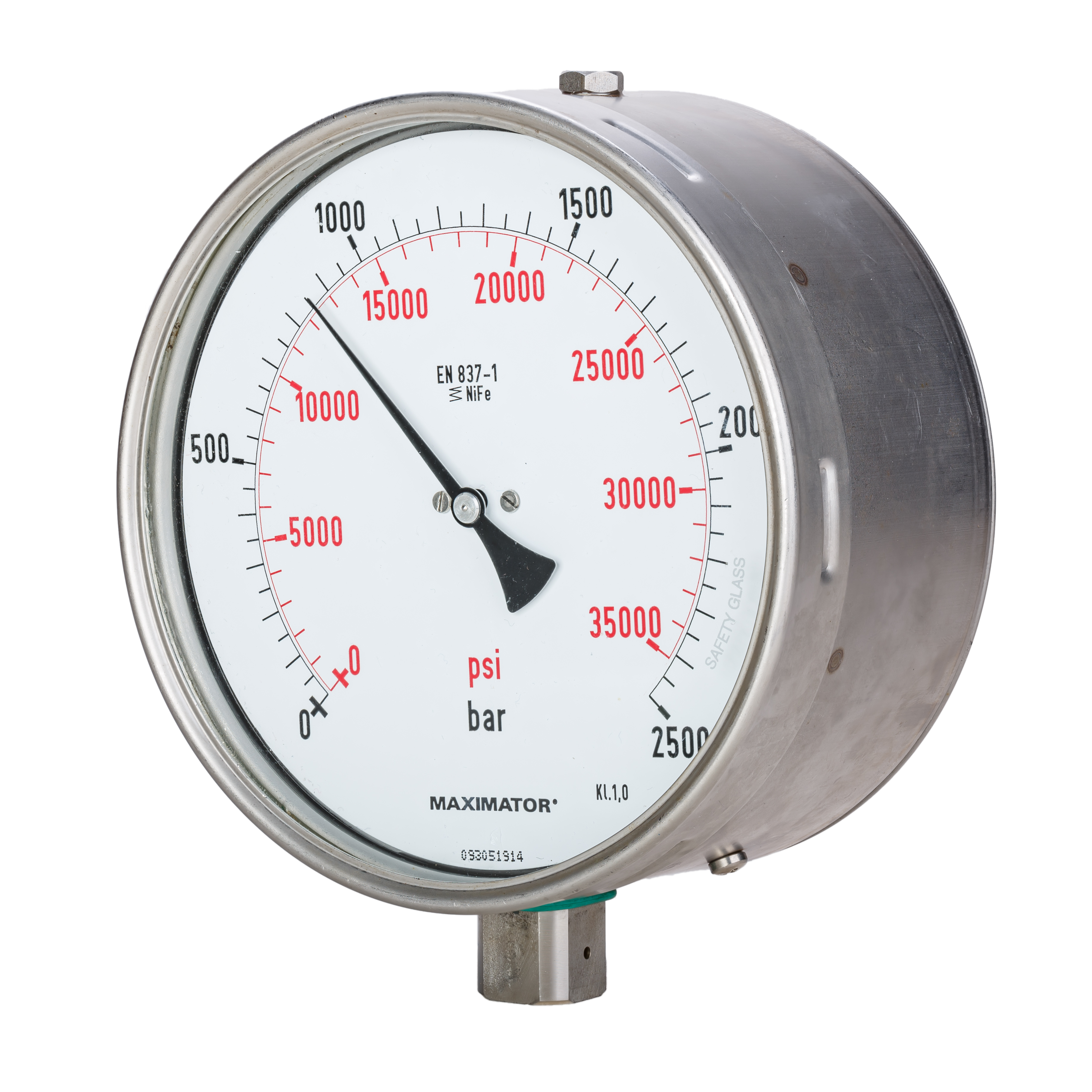
Gauge Pressure
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges, vacuum gauges or compound gauges (vacuum & pressure). The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge. A vacuum gauge is used to measure pressures lower than the ambient atmospheric pressure, which is set as the zero point, in negative values (for instance, −1 bar or −760 mmHg equals total vacuum). Most gauges measure pressure relative to atmospheric pressure as the zero point, so this form of reading is simply referred to as "gauge pressure". However, anything greater than total vacuum is technically a form of pressure. For very low pressu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of Gravity Of An Aircraft
The center of gravity (CG) of an aircraft is the point over which the aircraft would balance. Its position is calculated after supporting the aircraft on at least two sets of weighing scale A scale or balance is a device used to measure weight or mass. These are also known as mass scales, weight scales, mass balances, massometers, and weight balances. The traditional scale consists of two plates or bowls suspended at equal d ...s or load cells and noting the weight shown on each set of scales or load cells. The center of gravity affects the stability of the aircraft. To ensure the aircraft is safe to fly, the center of gravity must fall within specified limits established by the aircraft manufacturer. Terminology ;Ballast: Ballast is removable or permanently installed weight in an aircraft used to bring the center of gravity into the allowable range. ;Center-of-Gravity Limits: Center of gravity (CG) limits are specified longitudinal (forward and aft) and/or lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |