|
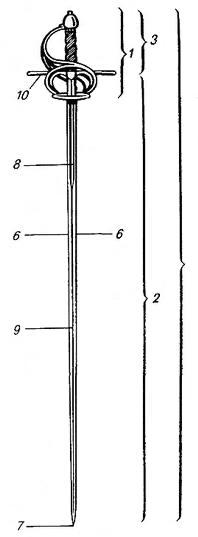
Bilbo (sword)
''For the fictional dagger wielded by Bilbo and Frodo, see Sting_(Middle-earth), Sting. The bilbo is a type of 16th century, cut-and-thrust sword or small rapier formerly popular in America. They have well-tempering (metallurgy), tempered and flexible blades and were very popular aboard ships, where they were used similarly to a cutlass. The term comes from the Basque city of Bilbao, :eu:Bilbo, Bilbo in Basque, where the metal (bilbo steel) was extracted and later sent to Toledo, a city in the center of Spain, where these swords were forged and exported to the New World. These swords were also sold to merchants of every European nation, including England. Etymology Bilbo (, ) is an English catch-all word used to very generally refer to the "utilitarian" cup-hilt swords, found all over America. They usually had a wide, relatively short sturdy and well-tempered blade, were comparatively unadorned, and were considered practical and utilitarian. The grip was often covered with wire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadsword By Heinrich Col, German (Solingen) Blade And Spanish Hilt, 1600-1650 - Higgins Armory Museum - DSC05620
The basket-hilted sword is a sword type of the early modern era characterised by a basket-shaped Hilt#Guard, guard that protects the hand. The basket hilt is a development of the quillons added to swords' crossguards since the Late Middle Ages. This variety of sword is also sometimes referred to as the broadsword, though this term may also be applied loosely and imprecisely to other swords. The basket-hilted sword was generally in use as a military sword. A true broadsword possesses a double-edged blade, while similar wide-bladed swords with a single sharpened edge and a thickened back are called backswords. Various forms of basket-hilt were mounted on both broadsword and backsword blades. One of the weapon types in the modern German dueling sport of ("academic fencing") is the basket-hilted . Nomenclature The designation "broadsword" is ambiguous, and can refer to many different types of sword. Though attestations of "broad swords" date from the 11th century, these simply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sting (Middle-earth)
The weapons and armour of Middle-earth are all those mentioned J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fantasy writings, such as ''The Hobbit'', ''The Lord of the Rings'' and ''The Silmarillion''. Tolkien modelled his fictional warfare on the Ancient and Early Medieval periods of history. His depiction of weapons and armour particularly reflect Northern European culture as seen in ''Beowulf'' and the Norse sagas. Tolkien established this relationship in '' The Fall of Gondolin'', the first story in '' his legendarium'' to be written. In this story, the Elves of Gondolin use the mail armour, swords, shields, spears, axes and bows of Northern European warfare. In Tolkien's writings, such Medieval weapons and armour are used by his fictional races, including Elves, Dwarves, Men, Hobbits, and Orcs. As in his sources, Tolkien's characters often gave names to their weapons, sometimes with runic inscriptions to show they are magical and have their own history and power. Terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip. A slashing sword is more likely to be curved and to have a sharpened cutting edge on one or both sides of the blade. Many swords are designed for both thrusting and slashing. The precise definition of a sword varies by historical epoch and geographic region. Historically, the sword developed in the Bronze Age, evolving from the dagger; the Bronze Age sword, earliest specimens date to about 1600 BC. The later Iron Age sword remained fairly short and without a crossguard. The spatha, as it developed in the Late Roman army, became the predecessor of the European sword of the Middle Ages, at first adopted as the Migration Period sword, and only in the High Middle Ages, developed into the classical Knightly sword, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapier
A rapier () is a type of sword originally used in Spain (known as ' -) and Italy (known as '' spada da lato a striscia''). The name designates a sword with a straight, slender and sharply pointed two-edged long blade wielded in one hand. It was widely popular in Western Europe throughout the 16th and 17th centuries as a symbol of nobility or gentleman status. It is called because it was carried as an accessory to clothing, generally used for fashion and as a weapon for dueling, self-defense and as a military side arm. Its name is of Spanish origin and appears recorded for the first time in the '' Coplas de la panadera'', by Juan de Mena, written approximately between 1445 and 1450: As fencing spread throughout Western Europe, important sources for rapier fencing arose in Spain, known under the term ("dexterity"), in Italy and France. The French small sword or court sword of the 18th century was a direct continuation of this tradition of fencing. Rapier fencing form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempering (metallurgy)
Tempering is a process of heat treating, which is used to increase the toughness of iron-based alloys. Tempering is usually performed after Hardening (metallurgy), hardening, to reduce some of the excess hardness, and is done by heating the metal to some temperature below the critical point (thermodynamics), critical point for a certain period of time, then allowing it to cool in still air. The exact temperature determines the amount of hardness removed, and depends on both the specific composition of the alloy and on the desired properties in the finished product. For instance, very hard tools are often tempered at low temperatures, while spring (device), springs are tempered at much higher temperatures. Introduction Tempering is a heat treatment technique applied to ferrous alloys, such as steel or cast iron, to achieve greater toughness by decreasing the hardness of the alloy. The reduction in hardness is usually accompanied by an increase in ductility, thereby decreasing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blade
A blade is the Sharpness (cutting), sharp, cutting portion of a tool, weapon, or machine, specifically designed to puncture, chop, slice, or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are intended to cut. This includes early examples made from flaked stones like flint or obsidian, evolving through the ages into metal forms like copper, bronze, and iron, and culminating in modern versions made from steel or ceramics. Serving as one of humanity's oldest tools, blades continue to have wide-ranging applications, including in combat, cooking, and various other everyday and specialized tasks. Blades function by concentrating force at the cutting edge. Design variations, such as serrated edges found on bread knives and saws, serve to enhance this force concentration, adapting blades for specific functions and materials. Blades thus hold a significant place both historically and in contemporary society, reflecting an evolution i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutlass
A cutlass is a short, broad sabre or slashing sword with a straight or slightly curved blade sharpened on the cutting edge and a hilt often featuring a solid cupped or basket-shaped guard. It was a common naval weapon during the early Age of Sail. Etymology The word "cutlass" developed from the 17th-century English use of ''coutelas'', a 16th-century French word for a machete-like mid-length single-edged blade (the modern French for "knife", in general, is ''couteau''; in 17th- and 18th-century English the word was often spelled "cuttoe"). The French word ''coutelas'' may be a convergent development from a Latin root, along with the Italian ''coltellaccio'' or ''cortelazo'', meaning "large knife". In Italy, the ''cortelazo'' was a similar short, broad-bladed sabre popular during the 16th century.Ossian, RobThe Cutlass(accessed Jan. 25, 2015) The root ''coltello'', for "knife", derived ultimately from the Latin ''cultellus'' meaning "smaller knife", which is the common Latin r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilbao
Bilbao is a city in northern Spain, the largest city in the Provinces of Spain, province of Biscay and in the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country as a whole. It is also the largest city proper in northern Spain. Bilbao is the List of cities in Spain by population, tenth largest city in Spain, with a population of more than 347,000 as of 2023. The Bilbao metropolitan area has 1,037,847 inhabitants,Proyecto Audes making it the most populous metropolitan area in northern Spain. The Comarcas of the Basque Country, comarca of Greater Bilbao is the fifth-largest urban area in Spain. Bilbao is also the main urban area in what is defined as the Basque Country (greater region), Greater Basque region. Bilbao is located in the north-central part of Spain, some south of the Bay of Biscay, where the economic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirk
A dirk is a long-bladed thrusting dagger.Chisholm, Hugh (ed.); "Dagger", ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 11th ed., Vol. VII, New York, NY: Cambridge University Press (1910), p. 729. Historically, it gained its name from the Highland dirk (Scottish Gaelic ) where it was a personal weapon of officers engaged in naval hand-to-hand combat during the Age of SailO'Brian, Patrick; ''Men-of-War: Life in Nelson's Navy'', New York: W. W. Norton & Co., (1974), p. 35. as well as the personal sidearm of Highlanders. It was also the traditional sidearm of the Highland Clansman and later used by the officers, pipers, and drummers of Scottish Highland regiments around 1725 to 1800 and by Japanese naval officers. Etymology The term is associated with Scotland in the Early Modern Era, being attested from about 1600. The term was spelled ''dork'' or ''dirk'' during the 17th century,Head, T. F.; ''The Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology'' Oxford University Press (1996) . presumed relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falchion
A falchion (; Old French: ''fauchon''; Latin: ''falx'', "sickle") is a one-handed, backsword, single-edged sword of European origin. Falchions are found in different forms from around the 13th century up to and including the 16th century. In some versions, the falchion looks rather like the seax and later the sabre, and in other versions more like a machete with a crossguard. Types The blade designs of falchions varied widely across the continent and over time. They almost always included a single edge with a slight curve on the blade towards the point on the end and most were also affixed with a quilloned crossguard for the hilt in the manner of the contemporary arming swords. Unlike the double-edged swords of Europe, few actual swords of this type have survived to the present day; fewer than a dozen specimens are currently known. A number of weapons similar to the falchion existed in Western Europe, including the Messer (weapon), Messer, hanger (weapon), hanger and the backs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutlass
A cutlass is a short, broad sabre or slashing sword with a straight or slightly curved blade sharpened on the cutting edge and a hilt often featuring a solid cupped or basket-shaped guard. It was a common naval weapon during the early Age of Sail. Etymology The word "cutlass" developed from the 17th-century English use of ''coutelas'', a 16th-century French word for a machete-like mid-length single-edged blade (the modern French for "knife", in general, is ''couteau''; in 17th- and 18th-century English the word was often spelled "cuttoe"). The French word ''coutelas'' may be a convergent development from a Latin root, along with the Italian ''coltellaccio'' or ''cortelazo'', meaning "large knife". In Italy, the ''cortelazo'' was a similar short, broad-bladed sabre popular during the 16th century.Ossian, RobThe Cutlass(accessed Jan. 25, 2015) The root ''coltello'', for "knife", derived ultimately from the Latin ''cultellus'' meaning "smaller knife", which is the common Latin r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |