|
Bielsko-Biała Museum And Castle
The Bielsko-Biała Museum, also known as the Castle of the Sułkowski Princes (Polish: ''Zamek książąt Sułkowskich'') is a museum for the city of Bielsko-Biała, Poland located in the historical Bielsko Castle. Three local branches of the museum have been established since the 1970s: the Julian Fałat Museum, the Museum of Technology and Textile Industry, and the Weaver's House Museum. History of the Museum The Bielsko-Biała Museum, with its main location in the historical Bielsko Castle has maintained museum traditions conceived at the beginning of the 20th century, when the local government of Silesian Bielsko and Galician Biała founded two separate museums. The older Biała Municipal Museum was set up upon the initiative of Bielsko Gymnasium (lower secondary school) teacher Erwin Hanslik by virtue of the City Council Resolution of 19 December 1902. At the same time, in a forum of the City Council of neighbouring Bielsko, similar initiative was taken by Arthur Schmidt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zamek Sulkowskich 2020
Zamek (the Polish word for "castle") may refer to: *Zamek, popular name for the palace called the Imperial Castle in Poznań *Zamek, Pomeranian Voivodeship Zamek is a settlement in the administrative district of Gmina Stary Dzierzgoń, within Sztum County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies approximately north of Stary Dzierzgoń, east of Sztum, and south-east of the regiona ..., a village in northern Poland * Zamek, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, a village in north-western Poland See also * {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bielsko-Biała City Hall
The Bielsko-Biała City Hall is a Renaissance Revival architecture, Neo-Renaissance, historic Town hall, city hall located at in Bielsko-Biała, administratively within the boundaries of the Biała Śródmieście district and within the registration area of Biała Miasto. It was built between 1895 and 1897 according to the design by . Originally, it housed the city hall of , the Communal Savings Bank, as well as several other institutions and apartments for officials. Since 1951, it has been the seat of the Mayor, the City Council, and some departments of the Municipal Office in Bielsko-Biała. History In the 1890s, the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian authorities in Biała recognized that the city hall, built in 1827 and situated in the market square (nowadays ), was insufficient for the rapidly developing city. It was decided to construct a new building, with sponsorship secured from the Communal Savings Bank, a local bank founded in 1883. In February 1894, the management o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Lands
The Czech lands or the Bohemian lands (, ) is a historical-geographical term which denotes the three historical regions of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia out of which Czechoslovakia, and later the Czech Republic and Slovakia, were formed. Together the three have formed the Czech part of Czechoslovakia since 1919, and the Czech Republic since 1 January 1993. In a historical context, Czech texts use the term to refer to any territory ruled by the Kings of Bohemia, i.e., the lands of the Bohemian Crown (') as established by Emperor Charles IV in the 14th century. This includes territories like the Lusatias (which in 1635 fell to Saxony) and the whole of Silesia, which at the time were all ruled from Prague Castle. Since the conquest of Silesia by the Prussian king Frederick the Great in the First Silesian War in 1742, the remaining lands of the Bohemian Crown—Bohemia, Moravia and Austrian Silesia—have been more or less co-extensive with the territory of the mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
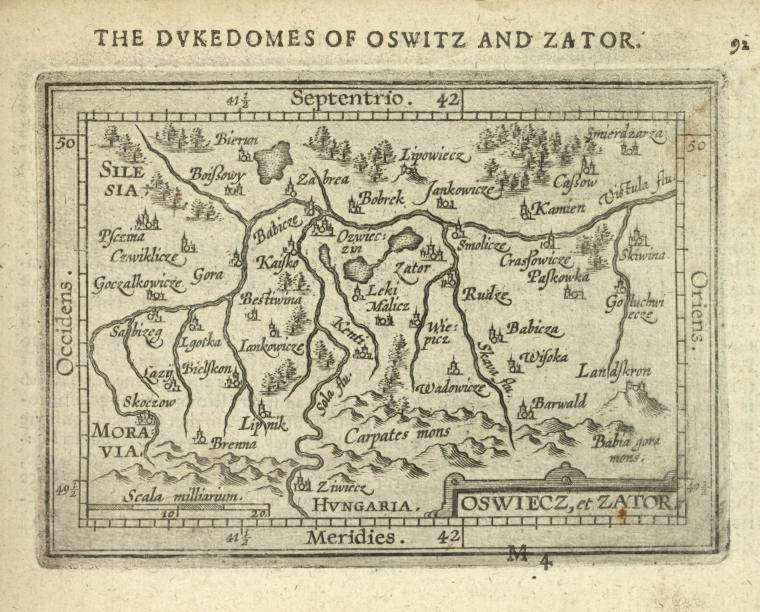
Oświęcim
Oświęcim (; ; ; ) is a town in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship in southern Poland, situated southeast of Katowice, near the confluence of the Vistula (''Wisła'') and Soła rivers. Oświęcim dates back to the 12th century, when it was an important castellan seat. From 1315 to 1457 it was the seat of a local line of the Piast dynasty, and from 1564 to 1772 it was a royal city of the Kingdom of Poland, with the Oświęcim Castle, Ducal and Royal Castle and several Middle Ages, medieval Gothic architecture, Gothic churches among the city's landmarks. Located on the east-west trade route, it was an important hub for trade, especially in salt from Wieliczka Salt Mine, Wieliczka. In the interwar period, Oświęcim was a garrison town for the Polish Army, and during the Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), German occupation of Poland in World War II, the former barracks were expanded to host the infamous German Nazi Auschwitz concentration camp (also known as KL or KZ Auschwitz Birke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cieszyn
Cieszyn ( , ; ; ) is a border town in southern Poland on the east bank of the Olza River, and the administrative seat of Cieszyn County, Silesian Voivodeship. The town has 33,500 inhabitants ( and lies opposite Český Těšín in the Czech Republic. Both towns belong to the historical region of Cieszyn Silesia, and formerly constituted the capital of the Duchy of Cieszyn as a single town. Geography The town is situated on the Olza (river), Olza river, a tributary of the Oder River, which forms the border with the Czech Republic. It is located within the western Silesian Foothills north of the Silesian Beskids and Mt. Czantoria Wielka, a popular ski resort. Cieszyn is the heart of the historical region of Cieszyn Silesia, the southeasternmost part of Upper Silesia. Until the end of World War I in 1918 it was a seat of the Duchy of Cieszyn, Dukes of Cieszyn. In 1920 Cieszyn Silesia was divided between the two newly created states of Second Polish Republic, Poland and First Czec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortification
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ("strong") and ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large cyclopean stone walls fitted without mortar had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae. A Greek ''Towns of ancient Greece#Military settlements, phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the ancient Roman, Roman castellum or fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortifications
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ("strong") and ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large cyclopean stone walls fitted without mortar had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae. A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they acted as a bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of King Casimir III the Great. Branches of the Piast dynasty continued to rule in the Duchy of Masovia (until 1526) and in the Duchies of Silesia until the last male Silesian Piast died in 1675. The Piasts intermarried with several noble lines of Europe, and possessed numerous titles, some within the Holy Roman Empire. The Jagiellonian kings ruling after the death of Casimir IV of Poland were also descended in the female line from Casimir III's daughter. Origin of the name The early dukes and kings of Poland are said to have regarded themselves as descendants of the semi-legendary Piast the Wheelwright (''Piast Kołodziej''), first mentioned in the '' Cronicae et gesta ducum sive principum Polonorum'' (''Deeds of the Princes of the Poles''), written c. 1113 by Gallus Anonym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merchant
A merchant is a person who trades in goods produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Merchants have been known for as long as humans have engaged in trade and commerce. Merchants and merchant networks operated in ancient Babylonia, Assyria, China, Egypt, Greece, India, Persia, Phoenicia and Rome. During the European medieval period, a rapid expansion in trade and commerce led to the rise of a wealthy and powerful merchant class. The European Age of Discovery opened up new trading routes and gave European consumers access to a much broader range of goods. By the 18th century, a new type of manufacturer-merchant had started to emerge and modern business practices were becoming evident. The status of the merchant has varied during different periods of history and among different societies. In modern times, the term ''merchant'' has occasionally been used to refer to a businessperson or someone undertaking activities (commercial or industrial) for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular territory. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradespeople belonging to a professional association. They sometimes depended on grants of letters patent from a monarch or other ruler to enforce the flow of trade to their self-employed members, and to retain ownership of tools and the supply of materials, but most were regulated by the local government. Guild members found guilty of cheating the public would be fined or banned from the guild. A lasting legacy of traditional guilds are the guildhalls constructed and used as guild meeting-places. Typically the key "privilege" was that only guild members were allowed to sell their goods or practice their skill within the city. There might be controls on minimum or maximum prices, hours of trading, numbers of apprentices, and many other things. Critics argued that these rules reduced Free market, fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During Hitler's rise to power, it was frequently referred to as Hitler Fascism () and Hitlerism (). The term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideology, which formed after World War II, and after Nazi Germany collapsed. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. Its beliefs include support for dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, anti-Slavism, anti-Romani sentiment, scientific racism, white supremacy, Nordicism, social Darwinism, homophobia, ableism, and the use of eugenics. The ultranationalism of the Nazis originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist ''Völkisch movement, Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katowice
Katowice (, ) is the capital city of the Silesian Voivodeship in southern Poland and the central city of the Katowice urban area. As of 2021, Katowice has an official population of 286,960, and a resident population estimate of around 315,000. Katowice is a central part of the Metropolis GZM, with a population of 2.3 million, and a part of a larger Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan area that extends into the Czech Republic and has a population of around 5 million people, making it List of metropolitan areas in Europe#Polycentric metropolitan areas in the European Union, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the European Union."''Study on Urban Functions (Project 1.4.3)''" – European Observation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |