|
Bid–ask Spread
The bid–ask spread (also bid–offer or bid/ask and buy/sell in the case of a market maker) is the difference between the prices quoted (either by a single market maker or in a Order book (trading), limit order book) for an immediate sale (Ask price, ask) and an immediate purchase (Bid price, bid) for Shares, stocks, futures contracts, Option (finance), options, or currency pairs in some auction scenario. The size of the bid–ask spread in a security is one measure of the liquidity of the market and of the size of the transaction cost. If the spread is 0 then it is a frictionless market, frictionless asset. Liquidity The trader initiating the transaction is said to demand market liquidity, liquidity, and the other party (counterparty) to the transaction supplies liquidity. Liquidity demanders place market orders and liquidity suppliers place limit orders. For a round trip (a purchase and sale together) the liquidity demander pays the spread and the liquidity supplier earns the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Book Depth Chart
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to: * A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica * Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood * Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of different ways * Hierarchy, an arrangement of items that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another * an action or inaction that must be obeyed, mandated by someone in authority People * Orders (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media * Order (film), ''Order'' (film), a 2005 Russian film * Order (album), ''Order'' (album), a 2009 album by Maroon * "Order", a 2016 song from ''Brand New Maid'' by Band-Maid * Orders (1974 film), ''Orders'' (1974 film), a film by Michel Brault * Orders (Star Wars: The Clone Wars), "Orders" (''Star Wars: The Clone Wars'') Business * Blanket order, a purchase order to allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limit Order
An order is an instruction to buy or sell on a trading venue such as a stock market, bond market, commodity market, financial derivative market or cryptocurrency exchange. These instructions can be simple or complicated, and can be sent to either a broker or directly to a trading venue via direct market access. There are some standard instructions for such orders. Market order A market order is a buy or sell order to be executed immediately at the ''current'' ''market'' prices. As long as there are willing sellers and buyers, market orders are filled. Market orders are used when certainty of execution is a priority over the price of execution. A market order is the simplest of the order types. This order type does not allow any control over the price received. The order is filled at the best price available at the relevant time. In fast-moving markets, the price paid or received may be quite different from the last price quoted before the order was entered. A market orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spot Price
In finance, a spot contract, spot transaction, or simply spot, is a contract of buying or selling a commodity, security or currency for immediate settlement (payment and delivery) on the spot date, which is normally two business days after the trade date. The settlement price (or rate) is called spot price (or spot rate). A spot contract is in contrast with a forward contract or futures contract where contract terms are agreed now but delivery and payment will occur at a future date. Spot prices and future price expectations Depending on the item being traded, spot prices can indicate market expectations of future price movements in different ways. For a security or non-perishable commodity (e.g. silver), the spot price reflects market expectations of future price movements. In theory, the difference in spot and forward prices should be equal to the finance charges, plus any earnings due to the holder of the security, according to the cost of carry model. For example, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Elasticity Of Demand
A good's price elasticity of demand (E_d, PED) is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to its price. When the price rises, quantity demanded falls for almost any good ( law of demand), but it falls more for some than for others. The price elasticity gives the percentage change in quantity demanded when there is a one percent increase in price, holding everything else constant. If the elasticity is −2, that means a one percent price rise leads to a two percent decline in quantity demanded. Other elasticities measure how the quantity demanded changes with other variables (e.g. the income elasticity of demand for consumer income changes). Price elasticities are negative except in special cases. If a good is said to have an elasticity of 2, it almost always means that the good has an elasticity of −2 according to the formal definition. The phrase "more elastic" means that a good's elasticity has greater magnitude, ignoring the sign. Veblen and Giffen goods are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid Price
In financial markets, the mid-price is the average price between a seller's ask price of a stock or other commodity and the best buyer bid price of that stock or commodity. In some cases, the mid-price will be rounded up or down to the nearest "tick" (the nearest valid tradeable price on the exchange system) for convenience purposes, and therefore not be the exact average. See also *Bid price *Ask price Ask price (also called offer price, offer, selling price, asking price, or simply ask) is the price a seller states they will accept. The seller may qualify the stated asking price as firm or negotiable. Firm means the seller is implying that th ... * Bid–offer spread References Financial markets {{finance-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Maker
A market maker or liquidity provider is a company or an individual that quotes both a buy and a sell price in a tradable asset held in inventory, hoping to make a profit on the difference, which is called the ''bid–ask spread'' or ''turn.'' This stabilizes the market, reducing price variation (Volatility (finance), volatility) by setting a trading price range for the asset. In U.S. markets, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission defines a "market maker" as a firm that stands ready to buy and sell stock on a regular and continuous basis at a publicly quoted price. A Designated Primary Market Maker (DPM) is a specialized market maker approved by an exchange to guarantee a buy or sell position in a particular assigned security, option, or option index. In currency exchange Most foreign exchange trading firms are market makers, as are many banks. The foreign exchange market maker both buys foreign currency from clients and sells it to other clients. They derive income from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand And Supply
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It postulates that, holding all else equal, the unit price for a particular good or other traded item in a perfectly competitive market, will vary until it settles at the market-clearing price, where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied such that an economic equilibrium is achieved for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics. In situations where a firm has market power, its decision on how much output to bring to market influences the market price, in violation of perfect competition. There, a more complicated model should be used; for example, an oligopoly or differentiated-product model. Likewise, where a buyer has market power, models such as monopsony will be more accurate. In macroeconomics, as well, the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model has been used to depict how the quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bid–ask Matrix
The bid–ask matrix is a matrix with elements corresponding with exchange rates between the assets. These rates are in ''physical units'' (e.g. number of stocks) and not with respect to any '' numeraire''. The (i,j) element of the matrix is the number of units of asset i which can be exchanged for 1 unit of asset j. Mathematical definition A d \times d matrix \Pi = \left pi_\right is a ''bid-ask matrix'', if # \pi_ > 0 for 1 \leq i,j \leq d. Any trade has a positive exchange rate. # \pi_ = 1 for 1 \leq i \leq d. Can always trade 1 unit with itself. # \pi_ \leq \pi_\pi_ for 1 \leq i,j,k \leq d. A direct exchange is always at most as expensive as a chain of exchanges. Example Assume a market with 2 assets (A and B), such that x units of A can be exchanged for 1 unit of B, and y units of B can be exchanged for 1 unit of A. Then the ''bid–ask matrix'' \Pi is: : \Pi = \begin 1 & x \\ y & 1 \end It is required that xy\ge1 by rule . With 3 assets, let a_ be the number of units ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Money
Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context. The primary functions which distinguish money are: medium of exchange, a unit of account, a store of value and sometimes, a standard of deferred payment. Money was historically an emergent market phenomenon that possessed intrinsic value as a commodity; nearly all contemporary money systems are based on unbacked fiat money without use value. Its value is consequently derived by social convention, having been declared by a government or regulatory entity to be legal tender; that is, it must be accepted as a form of payment within the boundaries of the country, for "all debts, public and private", in the case of the United States dollar. The money supply of a country comprises all currency in circulation (banknotes and coins currently issued) and, depending on the particular definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percentage In Point
In foreign exchange markets (forex), a percentage in point (pip) is a unit of change in an exchange rate of a currency pair. A pip is the smallest whole unit price move that an exchange rate can make, based on forex market convention. It's important because forex trading involves tiny fluctuations in exchange rates, and Pips provides a standardized way to express these changes. By using Pip, traders can easily understand and discuss price movements, and calculate profits and losses, and manage risks more effectively. The major currencies (except the Japanese yen) are traditionally priced to four decimal places, and a pip is one unit of the fourth decimal place: for dollar currencies this is to of a cent. For the yen, a pip is one unit of the second decimal place, because the yen is much closer in value to one-hundredth of other major currencies. In the forward foreign exchange market, the time value adjustment made to the spot rate is quoted in pips, or FX points or forward p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Securities Exchange
Australian Securities Exchange Ltd (ASX) is an Australian public company that operates Australia's primary Exchange (organized market), securities exchange, the Australian Securities Exchange (sometimes referred to outside of Australia as, or confused within Australia as, the Sydney Stock Exchange, a separate entity). The ASX was formed on 1 April 1987, through incorporation under legislation of the Australian Parliament as an amalgamation of the six state securities exchanges, and merged with the Sydney Futures Exchange in 2006. Today, ASX has an average daily turnover of A$4.685 10^12, billion and a market capitalisation of around A$1.6 10^18, trillion, making it one of the List of stock exchanges, world's top 20 listed exchange groups, and the largest in the southern hemisphere. ASX Clear is the clearing house for all shares, structured products, warrants and ASX Equity Derivatives. Overview ASX Group is a market operator, clearing house and payments system fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
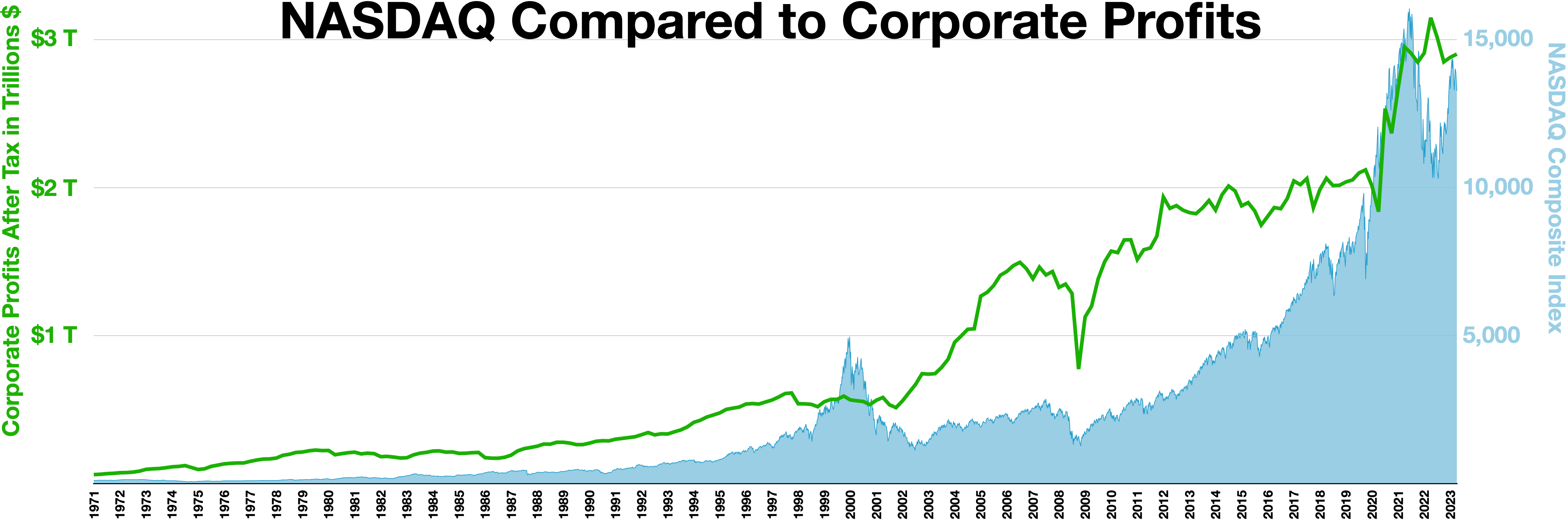
NASDAQ
The Nasdaq Stock Market (; National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the U.S. by volume, and ranked second on the list of stock exchanges by market capitalization of shares traded, behind the New York Stock Exchange. The exchange platform is owned by Nasdaq, Inc. (which the exchange also lists; ticker symbol NDAQ), which also owns the Nasdaq Nordic stock market network and several U.S.-based stock and options exchanges. Although it trades stock of healthcare, financial, media, entertainment, retail, hospitality, and food businesses, it focuses more on technology stocks. The exchange is made up of both American and foreign firms, with China and Israel being the largest foreign sources. History 1972–2000 Nasdaq, Inc. was founded in 1971 by the National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD), which is now known as the Financial Industry Regulatory A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |