|
Biddenham Pit
Biddenham Pit is a gravel pit and Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI), 0.41 hectares in size located in Biddenham, Bedfordshire. The pit was notified to Bedford Borough Council and Bedfordshire County Council under the Wildlife and Countryside Act (1981) in 1988, and is also a Geological Conservation Review site. The site is owned by Persimmon Homes and Kier Homes, with management advice given by Natural England. The pit provides an intact and visually inspectable terrace gravel, both silty and clayey, which has been laid down by the River Great Ouse. Several features of scientific interest have been identified in the deposits - interglacial mollusca and mammalian remains have been found, possible microfossil material as well as evidence of a prolific Paleolithic The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire (; abbreviated ''Beds'') is a Ceremonial County, ceremonial county in the East of England. It is bordered by Northamptonshire to the north, Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Hertfordshire to the south and the south-east, and Buckinghamshire to the west. The largest settlement is Luton (225,262), and Bedford is the county town. The county has an area of and had a population of 704,736 at the 2021 census. ''plus'' ''plus'' Its other towns include Leighton Buzzard, Dunstable, Biggleswade, Houghton Regis, and Flitwick. Much of the county is rural. For Local government in England, local government purposes, Bedfordshire comprises three Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas: Borough of Bedford, Bedford, Central Bedfordshire, and Luton. The county's highest point is on Dunstable Downs in the Chilterns. History The first recorded use of the name in 1011 was "Bedanfordscir", meaning the shire or county of Bedford, which itself means "Beda's ford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluvial Terrace
Fluvial terraces are elongated Terrace (geology), terraces that flank the sides of floodplains and fluvial valleys all over the world. They consist of a relatively level strip of land, called a "tread", separated from either an adjacent floodplain, other fluvial terraces, or uplands by distinctly steeper strips of land called "risers". These terraces lie parallel to and above the river channel and its floodplain. Because of the manner in which they form, fluvial terraces are underlain by fluvial sediments of highly variable thickness. River terraces are the remnants of earlier floodplains that existed at a time when either a stream or river was flowing at a higher elevation before its channel downcut to create a new floodplain at a lower elevation. Changes in elevation can be due to changes in the base level (elevation of the lowest point in the fluvial system, usually the drainage basin) of the fluvial system, which leads to headward erosion along the length of either a stream or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehistoric technology. It extends from the earliest known use of stone tools by Hominini, hominins, 3.3 million years ago, to the end of the Pleistocene, 11,650 Before Present#Radiocarbon calibration, cal Before Present, BP. The Paleolithic Age in Europe preceded the Mesolithic Age, although the date of the transition varies geographically by several thousand years. During the Paleolithic Age, hominins grouped together in small societies such as band society, bands and subsisted by gathering plants, fishing, and hunting or scavenging wild animals. The Paleolithic Age is characterized by the use of Knapping, knapped stone tools, although at the time humans also used wood and bone tools. Other organic commodities were adapted for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfossil
A microfossil is a fossil that is generally between 0.001 mm and 1 mm in size, the visual study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. A fossil which can be studied with the naked eye or low-powered magnification, such as a hand lens, is referred to as a macrofossil. Microfossils are a common feature of the geological record, from the Precambrian to the Holocene. They are most common in deposits of marine environments, but also occur in brackish water, fresh water and terrestrial sedimentary deposits. While every kingdom of life is represented in the microfossil record, the most abundant forms are protist skeletons or microbial cysts from the Chrysophyta, Pyrrhophyta, Sarcodina, acritarchs and chitinozoans, together with pollen and spores from the vascular plants. Overview A microfossil is a descriptive term applied to fossilized plants and animals whose size is just at or below the level at which the fossil can be analyzed by the naked e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammalian
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusca
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The number of additional fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000, and the proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine biology, marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat, as numerous groups are freshwater mollusc, freshwater and even terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial species. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class (biology), classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurobiology, neurologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interglacial
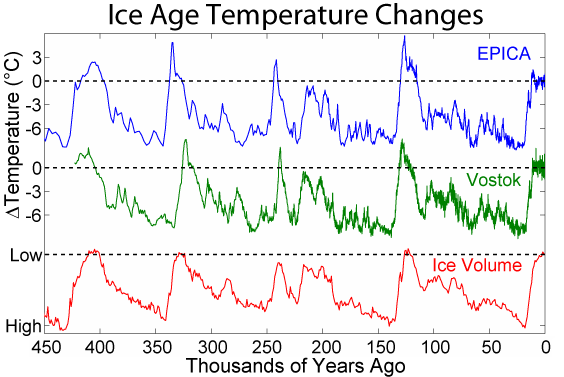
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Great Ouse
The River Great Ouse ( ) is a river in England, the longest of several British rivers called "Ouse". From Syresham in Northamptonshire, the Great Ouse flows through Buckinghamshire, Bedfordshire, Cambridgeshire and Norfolk to drain into the Wash and the North Sea near Kings Lynn. Authorities disagree both on the river's source and its length, with one quoting and another . Mostly flowing north and east, it is the fifth longest river in the United Kingdom. The Great Ouse has been historically important for commercial navigation, and for draining the low-lying region through which it flows; its best-known tributary is the Cam, which runs through Cambridge. Its lower course passes through drained wetlands and fens and has been extensively modified, or channelised, to relieve flooding and provide a better route for barge traffic. The unmodified river would have changed course regularly after floods. The name ''Ouse'' is from the Celtic or pre-Celtic *''Udso-s'', and probably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clays develop plasticity (physics), plasticity when wet but can be hardened through Pottery#Firing, firing. Clay is the longest-known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been radiocarbon dating, dated to around 14,000 BCE, and Clay tablet, clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtration, filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, often baked into brick, as an essenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension (chemistry), suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel when dry, and lacks Plasticity (physics), plasticity when wet. Silt can also be felt by the tongue as granular when placed on the front teeth (even when mixed with clay particles). Silt is a common material, making up 45% of average modern mud. It is found in many river deltas and as wind-deposited accumulations, particularly in central Asia, north China, and North America. It is produced in both very hot climates (through such processes as collisions of quartz grains in dust storms) and very cold climates (through such processes as glacial grinding of quartz grains.) Loess is soil rich in silt which makes up some of the most fertile agricultural land on Earth. However, silt is very vulnerable to erosion, and it has poo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravel
Gravel () is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally on Earth as a result of sedimentation, sedimentary and erosion, erosive geological processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone. Gravel is classified by grain size, particle size range and includes size classes from granule (geology), granule- to boulder-sized fragments. In the grain size, Udden-Wentworth scale gravel is categorized into granular gravel () and pebble gravel (). ISO 14688 grades gravels as fine, medium, and coarse, with ranges for fine and for coarse. One cubic metre of gravel typically weighs about , or one cubic yard weighs about . Gravel is an important commercial product, with a number of applications. Almost half of all gravel production is used as construction aggregate, aggregate for concrete. Much of the rest is used for road construction, either in the road base or as the road surface (with or without bitumen, asphalt or other binders.) Natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedfordshire Geology Group
Bedfordshire (; abbreviated ''Beds'') is a ceremonial county in the East of England. It is bordered by Northamptonshire to the north, Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Hertfordshire to the south and the south-east, and Buckinghamshire to the west. The largest settlement is Luton (225,262), and Bedford is the county town. The county has an area of and had a population of 704,736 at the 2021 census. ''plus'' ''plus'' Its other towns include Leighton Buzzard, Dunstable, Biggleswade, Houghton Regis, and Flitwick. Much of the county is rural. For local government purposes, Bedfordshire comprises three unitary authority areas: Bedford, Central Bedfordshire, and Luton. The county's highest point is on Dunstable Downs in the Chilterns. History The first recorded use of the name in 1011 was "Bedanfordscir", meaning the shire or county of Bedford, which itself means "Beda's ford" (river crossing). Bedfordshire was historically divided into nine hundreds: Barford, Biggleswa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |