|
Bezhetsky District
Bezhetsky District (russian: Бе́жецкий райо́н) is an administrative and municipalLaw #4-ZO district (raion), one of the thirty-six in Tver Oblast, Russia. It is located in the east of the oblast and borders with Molokovsky District in the north, Krasnokholmsky District in the northwest, Sonkovsky and Kesovogorsky Districts in the east, Kashinsky District in the southeast, Rameshkovsky District in the south, and with Maksatikhinsky District in the west. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the town of Bezhetsk. Population: 36,701 ( 2010 Census); The population of Bezhetsk accounts for 66.8% of the district's total population. Geography The whole area of the district belongs to the drainage basin of the Volga River, and much of the area belongs to the basin of the Mologa. The Mologa flows through the district, entering it from the west and turning north. The town of Bezhetsk, the district center, is located on the banks of the Mologa. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tver Oblast
Tver Oblast (russian: Тверска́я о́бласть, ''Tverskaya oblast'', ), from 1935 to 1990 known as Kalinin Oblast (), is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Tver. It was named after Mikhail Kalinin, the Soviet revolutionary. Population: 1,353,392 ( 2010 Census). Tver Oblast is a region of lakes, such as Seliger and Brosno. Much of the remaining area is occupied by the Valdai Hills, where the Volga, the Western Dvina, and the Dnieper have their source. Tver Oblast is one of the tourist regions of Russia with a modern tourist infrastructure. There are also many historic towns: Torzhok, Toropets, Zubtsov, Kashin, Vyshny Volochyok, and Kalyazin. The oldest of these is Rzhev, primarily known for the Battles of Rzhev in World War II. Staritsa was the seat of the last appanage principality in Russia. Ostashkov is a major tourist center. Geography Tver Oblast is located in the west of the middle part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment area of «Река Волга» , Russian State Water Registry which is more than twice the size of . It is also Europe's largest river in terms of average at delta – between and – and of |
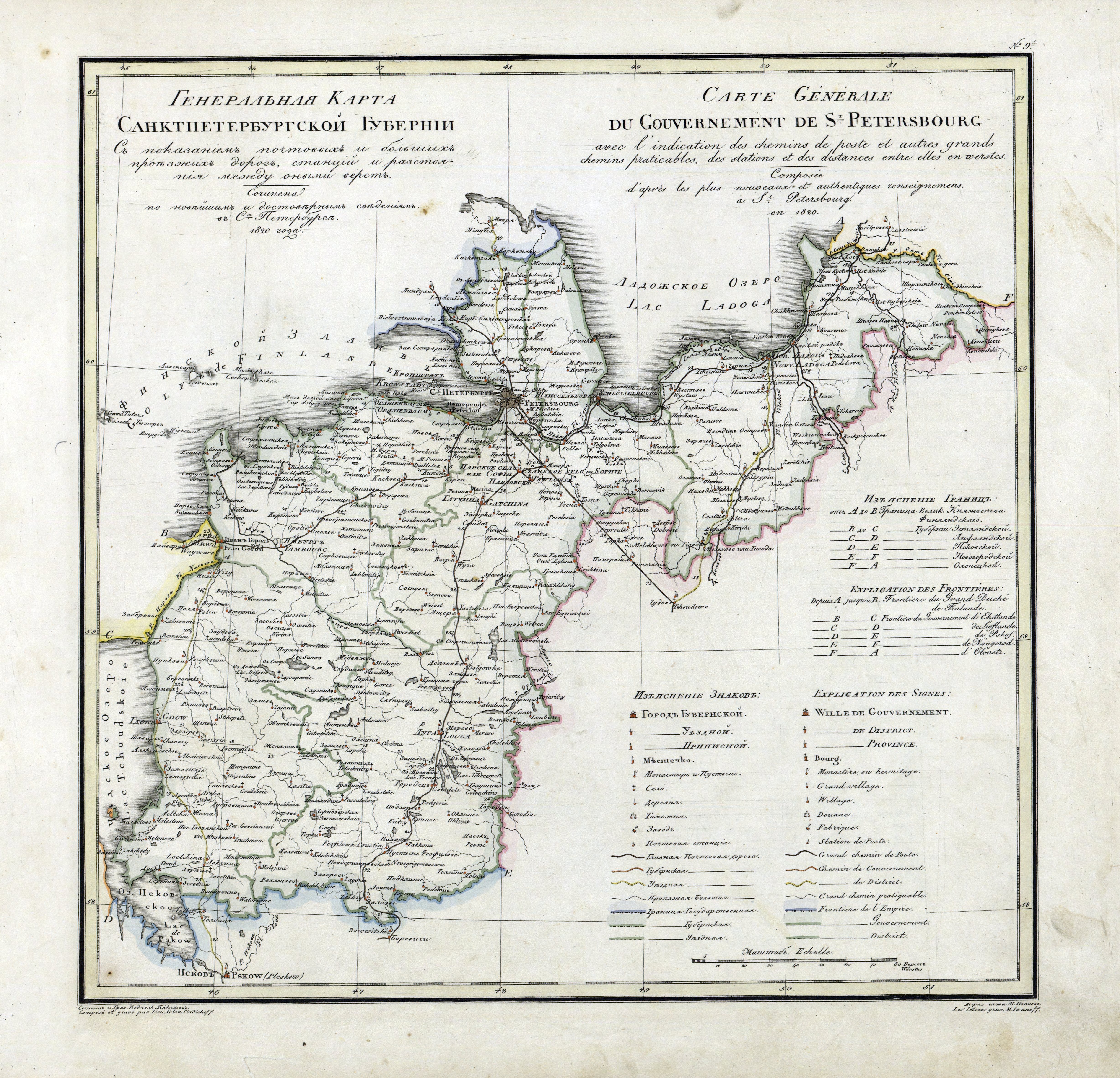
Saint Petersburg Governorate
Saint Petersburg Governorate (russian: Санкт-Петербу́ргская губе́рния, ''Sankt-Peterburgskaya guberniya''), or Government of Saint Petersburg, was an administrative division (a '' guberniya'') of the Tsardom of Russia, the Russian Empire, and the Russian SFSR, which existed during 1917–1927. Establishment Ingermanland Governorate (, ''Ingermanlandskaya guberniya'') was created from the territories reconquered from the Swedish Empire in the Great Northern War. In 1704 prince Alexander Menshikov was appointed as its first governor, and in 1706 it was first Russian region designated as a ''Governorate''. According to the Tsar Peter the Great's edict as on , 1708,Указ об учреждении губерний и � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from to 1721 and subsequently the Russian Empire until his death in 1725, jointly ruling with his elder half-brother, Ivan V until 1696. He is primarily credited with the modernisation of the country, transforming it into a European power. Through a number of successful wars, he captured ports at Azov and the Baltic Sea, laying the groundwork for the Imperial Russian Navy, ending uncontested Swedish supremacy in the Baltic and beginning the Tsardom's expansion into a much larger empire that became a major European power. He led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist and medieval social and political systems with ones that were modern, scientific, Westernised and based on the Enlightenment. Peter's reforms had a lastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Russia In 1708–1710
The administrative division reform of 1708 was carried out by Russian Tsar Peter the Great in an attempt to improve the manageability of the vast territory of Russia. Prior to the reform, the country was subdivided into uyezds and volosts, and in the 17th century the number of the uyezds was 166. Creation On , 1708, Peter issued an edict An edict is a decree or announcement of a law, often associated with monarchism, but it can be under any official authority. Synonyms include "dictum" and "pronouncement". ''Edict'' derives from the Latin edictum. Notable edicts * Telepinu Pr ... dividing Russia into eight governorates ('' guberniyas'').Указ об учреждении губерний и о росписании к ним город� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Moscow
The Grand Duchy of Moscow, Muscovite Russia, Muscovite Rus' or Grand Principality of Moscow (russian: Великое княжество Московское, Velikoye knyazhestvo Moskovskoye; also known in English simply as Muscovy from the Latin ) was a Rus' principality of the Late Middle Ages centered on Moscow, and the predecessor state of the Tsardom of Russia in the early modern period. It was ruled by the Rurik dynasty, who had ruled Rus' since the foundation of Novgorod in 862. Ivan III the Great titled himself as Sovereign and Grand Duke of All Rus' (russian: государь и великий князь всея Руси, gosudar' i velikiy knyaz' vseya Rusi). The state originated with the rule of Alexander Nevsky of the Rurik dynasty, when in 1263, his son, Daniel I, was appointed to rule the newly created Grand Principality of Moscow, which was a vassal state to the Mongol Empire (under the " Tatar Yoke"), and which eclipsed and eventually absorbed its parent du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east, including the city of Novgorod and the Lake Ladoga regions of modern Russia. The Republic prospered as the easternmost trading post of the Hanseatic League and its Slavic, Baltic and Finnic people were much influenced by the culture of the Viking-Varangians and Byzantine people. Name The state was called "Novgorod" and "Novgorod the Great" (''Veliky Novgorod'', russian: Великий Новгород) with the form "Sovereign Lord Novgorod the Great" (''Gosudar Gospodin Veliky Novgorod'', russian: Государь Господин Великий Новгород) becoming common in the 15th century. ''Novgorod Land'' and ''Novgorod volost usually referred to the land belonging to Novgorod. ''Novgorod Republic'' itself is a much later term, although the polity was described as a republic as earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medveditsa River (Volga Basin)
The Medveditsa () is a river in Spirovsky, Likhoslavlsky, Rameshkovsky, Kashinsky, and Kimrsky Districts of Tver Oblast, Russia, a left tributary of the Volga (joining the Volga at the Uglich Reservoir). The main tributaries are the Kushalka (left), the Ivitsa (right), the Drezna (left), the Rudomosh (left), and the Yakhroma (right). The length of the Medveditsa is , and the area of its drainage basin is . The source of the Medveditsa is southwest of the village of Gorma in Spirovsky District, at the southeastern outskirts of the Valdai Hills. The river flows southeast, and makes a stretch of the border between Spirovsky and Likhoslavlsky Districts. It crosses Likhoslavlsky District, enters Rameshkovsky District, and south of Rameshki turns east. The Medveditsa reaches te border with Kimrsky District and turns northeast, making the border between Rameshkovsky and Kimrsky Districts, and then east, making the border between Kashinsky and Kimrsky Districts. It enters Kashins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
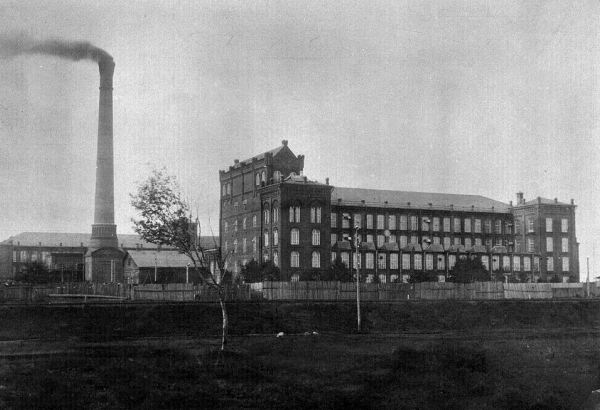
Drezna River (Tver Oblast)
Drezna (russian: Дрезна́) is a town in Orekhovo-Zuyevsky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the river Drezna (Klyazma's tributary) east of Moscow. Population: History It was founded by Ivan Zimin in 1897 as a mill town. It was named after the Drezna River. The mill utilised machinery supplied by Howard & Bullough for spinning and by Platt Brothers for weaving. Drezna was granted town status in 1940.СССР. Административно-территориальное деление союзных республик на 1 января 1980 года / Сост. В. А. Дударев, Н. А. Евсеева. — М.: Известия, 1980. — 702 с. — С. 174. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative divisions, it is incorporated within Orekhovo-Zuyevsky District as the Town A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than city, cities, though the criteria to distinguish bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashinka River
The Kashinka () is a river in Kesovogorsky and Kashinsky Districts of Tver Oblast, Russia, a left tributary of the Volga (joining the Volga at the Uglich Reservoir, near the town of Kalyazin). The length of the river is , and the area of its drainage basin is . The town of Kashin and the urban-type settlement of Kesova Gora are located along the Kashinka. The source of the Kashinka is in the swamps northwest of the village of Zadorye, at the border of Kesovogorsky and Bezhetsky Districts. It flows east, passes Kesova Gora, and in the village of Brylino turns south. It passes Kashin, where it makes a loop. The historical part of the town is located within the loop of the Kashinka. Further south, it becomes a part of the Uglich Reservoir. It joins the Volga in the village of Gorki Gorki may refer to: * Gorki Águila (b. 1968), Cuban rock musician * Gorki (band), a Belgian band of Luc De Vos * Gorki (Kazan Metro), a station of the Kazan Metro, Kazan, Russia * Gorki Ridge, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volchina River
The Volchina (russian: Волчина) is a river in Vyshnevolotsky, Udomelsky, and Maksatikhinsky Districts of Tver Oblast in Russia. It is a left tributary of the Mologa. It is long, and the area of its basin . The main tributaries are the Tifina (left) and the Vorozhba (right). The source of the Volchina is Lake Volchino, shared between Udomelsky (north) and Vyshnevolotsky (south) districts. The outflow of the Volchina is located in Udomelsky District. The river flows northwest, flows in Lake Rogozino, flows out in the southern direction and enters Vyshnevolotsky District. In the village of Ovsishche it turns east, flows to the boundary between the districts and makes a stretch of the boundary, and flows in Lake Perkhovo. From the lake, the Volchina flows east, crosses again into Udomelsky District, makes a stretch of the border between Udomelsky and Maksatikhinsky District, and continues into Maksatikhinsky District. Its mouth is downstream of the urban-type settlement of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |