|
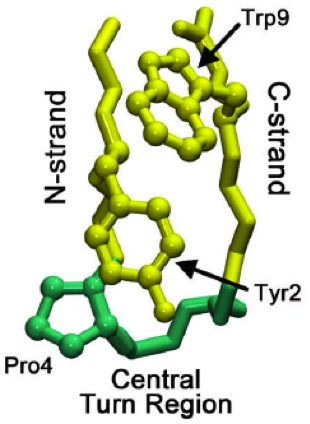
Beta Bulge Loop
Beta bulge loops are commonly occurring motifs in proteins and polypeptides consisting of five to six amino acids. There are two types: type 1, which is a pentapeptide; and type 2, with six amino acids. They are regarded as a type of beta bulge, and have the alternative name of type G1 beta bulge. Compared to other beta bulges, beta bulge loops give rise to chain reversal such that they often occur at the loop ends of beta hairpins; hairpins of this sort can be described as 3:5 (for a type 1 β bulge loop) or 4:6 (for type 2). Two websites are available for finding and examining β bulge loops in proteins, Motivated Proteins and PDBeMotif Type I beta bulge loops have two characteristic inter-main-chain hydrogen bonds. One is between the CO of residue i and the NH of residue i+3 (a β-turn); the other is between the CO of residue i+4 and the NH of residue i. Type 2 beta bulge loops have two characteristic inter-main-chain hydrogen bonds. One is between the CO of residue i and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypeptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Bulge
A beta bulge can be described as a localized disruption of the regular hydrogen bonding of beta sheet by inserting extra residues into one or both hydrogen bonded β-strands. Types β-bulges can be grouped according to their length of the disruption, the number of residues inserted into each strand, whether the disrupted β-strands are parallel or antiparallel and by their dihedral angles (which controls the placement of their side chains). Two types occur commonly. One, the ''classic beta bulge'', occurs within, or at the edge of, antiparallel beta-sheet; the first residue at the outwards bulge typically has the αR, rather than the normal β, conformation. The other type is the G1 ''beta bulge'', of which there are two common sorts, both mainly occurring in association with antiparallel sheet; one residue has the αL conformation and is usually a glycine. In one sort, the beta bulge loop, one of the hydrogen bonds of the beta-bulge also forms a beta turn or alpha turn, such that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Hairpin
The beta hairpin (sometimes also called beta-ribbon or beta-beta unit) is a simple protein structural motif involving two beta strands that look like a Hairpin (fashion), hairpin. The motif consists of two strands that are adjacent in primary structure, oriented in an Antiparallel (biochemistry), antiparallel direction (the N-terminus of one sheet is adjacent to the C-terminus of the next), and linked by a short loop of two to five amino acids. Beta hairpins can occur in isolation or as part of a series of hydrogen bonded strands that collectively comprise a beta sheet. Researchers such as Francisco J. Blanco, Francisco Blanco ''et al.'' have used protein NMR to show that beta-hairpins can be formed from isolated short peptides in aqueous solution, suggesting that hairpins could form nucleation sites for protein folding. Classification Beta hairpins were originally categorized solely by the number of amino acid residues in their loop sequences, such that they were named one-resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 1 Beta Bulge Loop
Type may refer to: Science and technology Computing * Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc. * Data type, collection of values used for computations. * File type * TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file. * Type (Unix), a command in POSIX shells that gives information about commands. * Type safety, the extent to which a programming language discourages or prevents type errors. * Type system, defines a programming language's response to data types. Mathematics * Type (model theory) * Type theory, basis for the study of type systems * Arity or type, the number of operands a function takes * Type, any proposition or set in the intuitionistic type theory * Type, of an entire function ** Exponential type Biology * Type (biology), which fixes a scientific name to a taxon * Dog type, categorization by use or function of domestic dogs Lettering * Type is a design concept for lettering used in typography which helped bring about modern textual printi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently bonded to a more Electronegativity, electronegative donor atom or group (Dn), interacts with another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Unlike simple Dipole–dipole attraction, dipole–dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding arises from charge transfer (nB → σ*AH), Atomic orbital, orbital interactions, and quantum mechanical Delocalized electron, delocalization, making it a resonance-assisted interaction rather than a mere electrostatic attraction. The general notation for hydrogen bonding is Dn−H···Ac, where the solid line represents a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are nitrogen (N), oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of proteins. D-aspartic acid is one of two D-amino acids commonly found in mammals. Apart from a few rare exceptions, D-aspartic acid is not used for protein synthesis but is incorporated into some peptides and plays a role as a neurotransmitter/ neuromodulator. Like all other amino acids, aspartic acid contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the protonated –NH form under physiological conditions, while its α-carboxylic acid group is deprotonated −COO− under physiological conditions. Aspartic acid has an acidic side chain (CH2COOH) which reacts with other amino acids, enzymes and proteins in the body. Under physiological conditions (pH 7.4) in proteins the side chain usually occurs as the negatively charged as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain carboxamide, classifying it as a polar (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it. It is encoded by the codons AAU and AAC. The one-letter symbol N for asparagine was assigned arbitrarily, with the proposed mnemonic asparagi''N''e; History Asparagine was first isolated in 1806 in a crystalline form by French chemists Louis Nicolas Vauquelin and Pierre Jean Robiquet (then a young assistant). It was isolated from asparagus juice, in which it is abundant, hence the chosen name. It was the first amino acid to be isolated. Three years later, in 1809, Pierre Jean Robiquet identified a substance from l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L- stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, '' sericum''. Serine's structure was established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form when dissolved in water), and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as ''E. coli''. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC (ACU, ACC, ACA, and ACG). Threonine sidechains are often hydrogen bonded; the most common small motifs formed are based on interactions with serine: ST turns, ST motifs (often at the beginning of alpha helices) and ST staples (usually at the middle of alpha helices). Modifications The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttranslational modifications. The hydroxyl side-chain can und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nest (protein Structural Motif)
The Nest is a type of Structural motif, protein structural motif. It is a small recurring anion-binding feature of both proteins and peptides. Each consists of the main chain atoms of three consecutive amino acid residues. The main chain NH groups bind the anions while the side chain atoms are often not involved. Proline residues lack NH groups so are rare in nests. About one in 12 of amino acid residues in proteins, on average, belongs to a nest. Nest conformations The conformation of a nest is such that the NH groups of the first and third amino acid residues are liable to be hydrogen bonded to a negatively charged, or partially negatively charged, atom, often an oxygen atom. The NH of the second residue may also be hydrogen bonded to the same atom but usually points somewhat away. These main chain atoms form a concavity called a nest into which an anionic atom fits. Such anionic atoms are sometimes called eggs and more than one egg may occur bound to a nest. The oxyanion ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |