|
Bermontians
The West Russian Volunteer Army or Bermontians was a pro-German White Russian military formation in Latvia and Lithuania during the Russian Civil War from November 1918 to December 1919. History The , unlike the pro- Entente Volunteer Army in Southern Russia, was supported and in fact put together under German auspices. The Compiègne Armistice of November 1918, in article 12, stipulated that troops of the former German Empire would remain in the Baltic provinces of the former Russian Empire to help fight against Bolshevik advances and that such German units were to withdraw once the Allies of World War I, Allies determined that the situation was under control. The order to withdraw was given after signing of the Treaty of Versailles in June 1919. However, only a small portion of the Freikorps in the Baltic retired in response to the Allies' order; the rest remained under the leadership of the German Army General Rüdiger von der Goltz. To avoid casting blame on Germany and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavel Bermondt-Avalov
Prince Pavel Rafailovich Bermondt-Avalov () or Prince Avalov ( – 27 December 1973) was a Russian officer and Cossack adventurer-warlord. He is best known as the commander of the West Russian Volunteer Army which was active in present-day Latvia and Lithuania in the aftermath of World War I. Born into a Georgian-Russian family, Avalov received a musical education in Warsaw and joined the Russian Imperial Army's Baikal Cossacks host as a musical conductor. He participated in the Russo-Japanese War, during which he was awarded the Cross of St. George. After converting to Orthodoxy, he was transferred to the Ussuri Cossacks and was promoted to cornet. During the First World War, Avalov worked as a personal adjutant for Pavel Mishchenko, serving in Eastern Prussia and Galicia. Throughout his military career, Avalov was injured seven times. After being demobilized in 1917, Avalov became involved in the Russian Civil War as an ardent supporter of the White Army. After defen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Wars Of Independence
The Lithuanian Wars of Independence, also known as the Freedom Struggles (), refer to three wars Lithuania fought defending its independence at the end of World War I: with Bolshevik forces (December 1918 – August 1919), Bermontians (October 1919 – December 1919), and Poland (August 1920 – November 1920). The wars delayed international recognition of independent Lithuania and the formation of civil institutions. Background After the Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was annexed by the Russian Empire. The Lithuanian National Revival emerged during the 19th century and the movement to establish an independent nation-state intensified during the early 20th century. During World War I, Lithuanian territory was occupied by Germany from 1915 until the war ended in November 1918. On February 16, 1918, the Council of Lithuania declared the re-establishment of independence from all previous legal bonds with other states. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
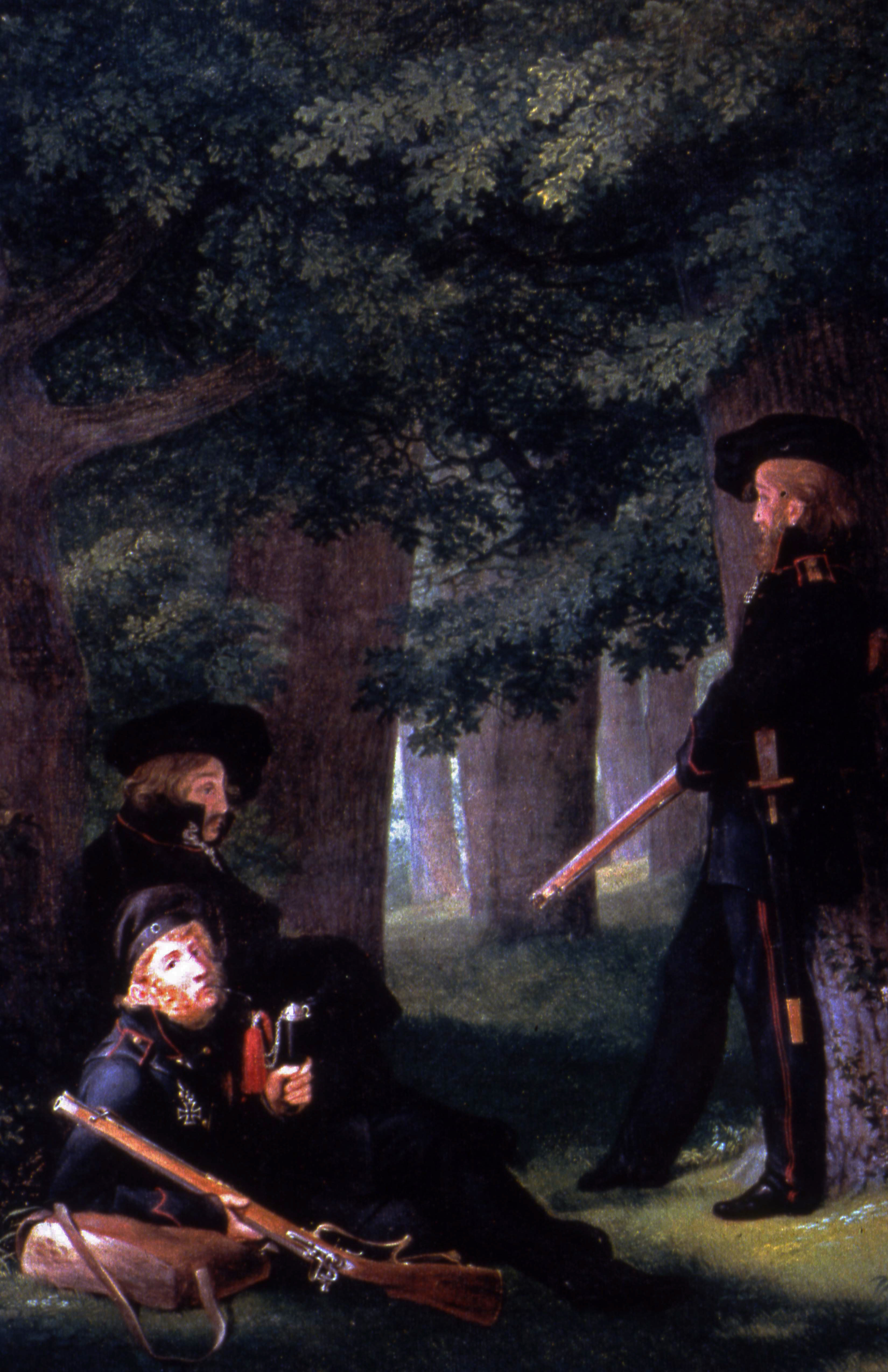
Bermontians Planes Captured By The Lithuanian Army
The West Russian Volunteer Army or Bermontians was a pro-German White Russian military formation in Latvia and Lithuania during the Russian Civil War from November 1918 to December 1919. History The , unlike the pro- Entente Volunteer Army in Southern Russia, was supported and in fact put together under German auspices. The Compiègne Armistice of November 1918, in article 12, stipulated that troops of the former German Empire would remain in the Baltic provinces of the former Russian Empire to help fight against Bolshevik advances and that such German units were to withdraw once the Allies determined that the situation was under control. The order to withdraw was given after signing of the Treaty of Versailles in June 1919. However, only a small portion of the Freikorps in the Baltic retired in response to the Allies' order; the rest remained under the leadership of the German Army General Rüdiger von der Goltz. To avoid casting blame on Germany and infuriating the Allie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and the Russian exclave, semi-exclave of Kaliningrad Oblast to the southwest, with a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Sweden to the west. Lithuania covers an area of , with a population of 2.89 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius; other major cities include Kaunas, Klaipėda, Šiauliai and Panevėžys. Lithuanians who are the titular nation and form the majority of the country's population, belong to the ethnolinguistic group of Balts and speak Lithuanian language, Lithuanian. For millennia, the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Balts, Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united for the first time by Mindaugas, who formed the Kingdom of Lithuania on 6 July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian State (1918–1920)
The Russian State () was a White Army anti-Bolshevik state proclaimed by the Act of the Ufa State Conference of September 23, 1918 (the Constitution of the Provisional All-Russian Government), “On the formation of the all-Russian supreme power” in the name of “restoring state unity and independence of Russia” affected by the Russian Revolution, revolutionary events of 1917, the October Revolution and the signing of the treaty of Brest-Litovsk with German Empire, Germany. Ufa State Conference act The delegations from Committee of Members of the Constituent Assembly, the Provisional Siberian Government (Omsk), Provisional Siberian Government, the Provisional Regional Government of the Urals, Cossack Troops governments, governments of a number of national-state entities, several all-Russian political parties that were present at the meeting formed the Provisional All-Russian Government (the so-called “Ufa Directory”), which was headed by Nikolai Avksentiev. It was fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuršėnai
Kuršėnai (; Samogitian dialect, Samogitian: ''Koršienā'') is a city in northwestern Lithuania, Šiauliai County, Šiauliai district municipality. It is the twenty-fifth largest city in Lithuania. According to the 2023 estimate, it had 10,651 residents. Etymology The city's name was first documented in the 16th century. According to historian , its name is derived from the word ''kuršis'' (Curonians, Curonian). However, according to folk etymology, folk legend, the city didn't have a name for a long time. But, one summer day the river Venta (river), Venta flooded and washed all hay bales which were standing at the river banks. People started questioning each other: where is the hay? where is the hay? („Kur šienai? Kur šienai?“). Since then, the city name stayed as Kuršėnai. In other languages the town is referred to as: ''Kurshon''; ; ; . History Early history The town and its surroundings fall within the boundaries of the territory inhabited by the ancient Samogi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leadership
Leadership, is defined as the ability of an individual, group, or organization to "", influence, or guide other individuals, teams, or organizations. "Leadership" is a contested term. Specialist literature debates various viewpoints on the concept, sometimes contrasting Eastern world, Eastern and Western world, Western approaches to leadership, and also (within the West) North American versus European approaches. Some U.S. academic environments define leadership as "a process of social influence in which a person can enlist the aid and Peer support, support of others in the accomplishment of a common and Ethics, ethical task (project management), task". In other words, leadership is an influential Power (social and political), power-relationship in which the power of one party (the "leader") promotes movement/change in others (the "followers"). Some have challenged the more traditional managerial views of leadership (which portray leadership as something possessed or owned by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jelgava
Jelgava () is a state city in central Latvia. It is located about southwest of Riga. It is the largest town in the Semigallia region of Latvia. Jelgava was the capital of the united Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (1578–1795) and was the administrative center of the Courland Governorate (1795–1918). Jelgava is situated on a fertile plain rising only above mean sea level on the right bank of the river Lielupe. At high water, the plain and sometimes the town as well can be flooded. It is a railway center, and is also a host to the Jelgava Air Base. Its importance as a railway centre can be seen by the fact that it lies at the junction of over 6 railway lines connecting Riga to Lithuania, eastern and western Latvia, and Lithuania to the Baltic Sea. Name Until 1917, the city was officially referred to as Mitau. The name of Jelgava is believed to be derived from the Livonian word ''jālgab'', meaning "town on the river." The origin of the German name ''Mitau'' is unclea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krupp
Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp (formerly Fried. Krupp AG and Friedrich Krupp GmbH), trade name, trading as Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century as well as Germany's premier weapons manufacturer during both world war, world wars. It produced battleship, battleships, U-boats, tanks, howitzers, guns, utilities, and hundreds of other commodities. The company also produced steel used to build railroads in the United States and to cap the Chrysler Building. After the Nazi Germany, Nazis seized power in Germany, Krupp supported the regime and was one of many German businesses that profited from forced labour under German rule during World War II, slave labor during World War II. Upon the war's end, the head of the company, Alfried Krupp, was tried and convicted as a war criminal for employing prisoners of war, foreign civilians and concentration camp inmates under inhumane conditions in support of the Nazi war effort. Despite being senten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Germans
Baltic Germans ( or , later ) are ethnic German inhabitants of the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, in what today are Estonia and Latvia. Since their resettlement in 1945 after the end of World War II, Baltic Germans have drastically declined as a geographically determined ethnic group in the region, with diaspora generally relocating to Germany proper and beyond. Since the late Middle Ages, native German-speakers formed the majority of merchants and clergy, and the large majority of the local landowning nobility who effectively constituted a ruling class over indigenous Latvian and Estonian non-nobles. By the time a distinct Baltic German ethnic identity began emerging in the 19th century, the majority of self-identifying Baltic Germans were non-nobles belonging mostly to the urban and professional middle class. In the 12th and 13th centuries, Catholic German traders and crusaders (''see '') began settling in the eastern Baltic territories. With the decline of Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossack
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borders of Ukraine and Russia, countering the Crimean-Nogai raids, alongside economically developing steppe regions north of the Black Sea and around the Azov Sea. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic–speaking Orthodox Christians. The rulers of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire endowed Cossacks with certain special privileges in return for the military duty to serve in the irregular troops: Zaporozhian Cossac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freikorp
(, "Free Corps" or "Volunteer Corps") were irregular German and other European paramilitary volunteer units that existed from the 18th to the early 20th centuries. They effectively fought as mercenaries or private military companies, regardless of their own nationality. In German-speaking countries, the first so-called ("free regiments", ''Freie Regimenter'') were formed in the 18th century from native volunteers, enemy renegades, and deserters. These sometimes exotically equipped units served as infantry and cavalry (or, more rarely, as artillery); sometimes in just company strength and sometimes in formations of up to several thousand strong. There were also various mixed formations or legions. The Prussian included infantry, jäger, dragoons and hussars. The French '' Volontaires de Saxe'' combined uhlans and dragoons. In the aftermath of World War I and during the German Revolution of 1918–19, , consisting partially of World War I veterans, were raised as paramili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |