|
Berdysyčran-depe
Berdysyčran-depe (turk. Berdysyçran-depe, рус. Бердысычран-депе) is an ancient Bronze Age settlement located in the former delta of Tejen River, 60 km south of Tejen (city), Turkmenistan. Archaeological research Berdysyčran-depe was surveyed in 2015 by a Turkmen-Polish archaeological expedition of the University of Warsaw, headed by Barbara Kaim General characteristics The total area of Berdysyčran-depe is about 15 hectares. The site consists of two parts. The first, the southern mound, is steeper, with an area of about 1 hectare and a height of 6 metres. The second mound, is a more flattened with a height of 7 metres and covering an area of 2.1 hectares. The area between these hills is densely covered with pottery. The analysis of all collected material allowed to date the site to the Middle, Late and Final Bronze Age (2250-1500 BC), i.e. the time corresponding to the rise, flouring and fall of the Oxus Civilization - Bactria–Margiana Archaeolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex
The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC) is the modern archaeological designation for a particular Middle Bronze Age civilisation of southern Central Asia, also known as the Oxus Civilization. The civilisation's urban phase or Integration Era was dated in 2010 by Sandro Salvatori to –1950 BC, but a different view is held by Nadezhda A. Dubova and Bertille Lyonnet, –1700 BC.Lyonnet, Bertille, and Nadezhda A. Dubova, (2020b)"Questioning the Oxus Civilization or Bactria- Margiana Archaeological Culture (BMAC): an overview" in Bertille Lyonnet and Nadezhda A. Dubova (eds.), ''The World of the Oxus Civilization'', Routledge, London and New York, p. 32.: "...Salvatori has often dated its beginning very early (ca. 2400 BC), to make it match with Shahdad where a large amount of material similar to that of the BMAC has been discovered. With the start of international cooperation and the multiplication of analyses, the dates now admitted by all place the Oxus Civilizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hari (Afghanistan)
The Hari River ( or ; ) or Herat River or Tejen River or Harirud is a river flowing from the mountains of central Afghanistan to Turkmenistan, where it forms the Tejen oasis and disappears in the Karakum Desert. In its lower course, the river forms a northern part of the border between Afghanistan and Iran, and a southeastern part of the border between Turkmenistan and Iran. The name of the river derives from the Old Persian word Harawaiah 'river rich in water'. In Turkmenistan, the Hari is known as the Tejen or Tedzhen river and passes close to the city of Tejen. To the ancient Greeks, it was known as the Arius. In Latin, it was known as the Tarius. History One theory suggests that the Rigvedic Sarayu and the Hari are the same river. A Buddhist monastery hand-carved in the bluff of the river Harirud existed in the first centuries during the prevalence of Buddhism. The artificial caves revealed testimony of daily life of the Buddhist monks. Course The river originat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
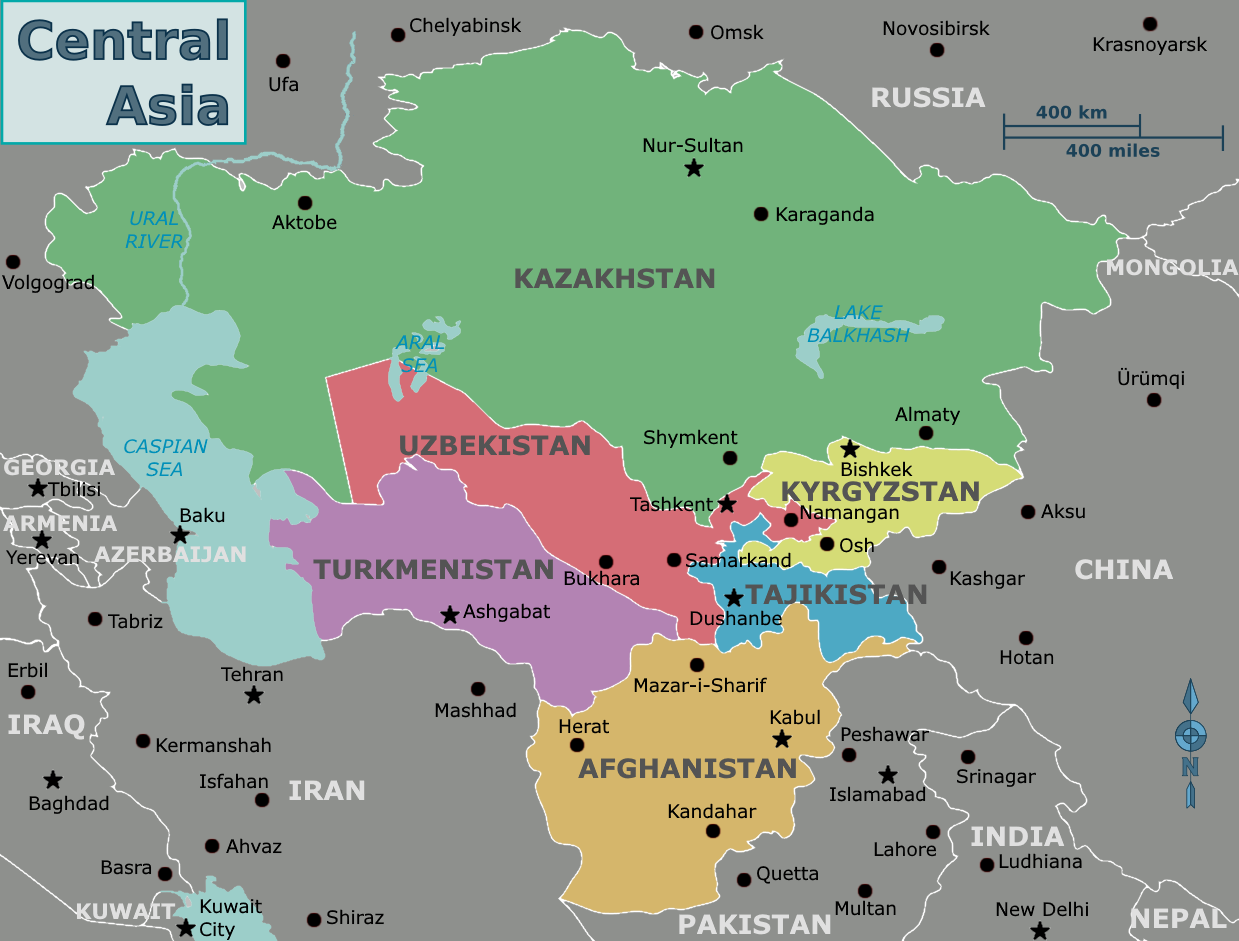
Tejen
Tejen (older spellings: Tedzhen, Tejend, Tejent) is an oasis city in the Karakum Desert, in Ahal Province of Turkmenistan. It lies along the M37 highway, between Dushak and Mary, by road southeast of Ashgabat. It has a population of approximately 67,500. To the east is the larger oasis of Mary. Khlopin suggests Tejen may have been the birthplace of Zoroaster. Etymology The meaning of ''tejen'' is unclear. Atanyyazov explained, ...The meaning of this ancient name is not clear...Barthold noted that this name was also used in the form of Tuzhen in the X-XI centuries...Vambery derived it from the words ''tei-e hend'' (''tei-e kent'', ''tei''— “down”, ''kent'' - “village”, “city”) and derived from that “downstream of the city,” “downstream of the city,” or “downstream of the river". He writes that he may have understood the meaning of the word as "city in the desert"...the name of the village along the Gerrud River is mentioned...This name also means "the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ashgabat is the capital and largest city. It is one of the six independent Turkic states. With a population over 7 million, Turkmenistan is the 35th most-populous country in Asia and has the lowest population of the Central Asian republics while being one of the most sparsely populated nations on the Asian continent. Turkmenistan has long served as a thoroughfare for several empires and cultures. Merv is one of the oldest oasis-cities in Central Asia, and was once among the biggest cities in the world. It was also one of the great cities of the Islamic world and an important stop on the Silk Road. Annexed by the Russian Empire in 1881, Turkmenistan figured prominently in the anti-Bolshevik movement in Central Asia. In 1925, Turkmenistan be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Warsaw
The University of Warsaw (, ) is a public university, public research university in Warsaw, Poland. Established on November 19, 1816, it is the largest institution of higher learning in the country, offering 37 different fields of study as well as 100 specializations in humanities, Engineering, technical, and natural sciences. The University of Warsaw consists of 126 buildings and educational complexes with over 18 faculties: biology, chemistry, medicine, journalism, political science, philosophy, sociology, physics, geography, regional studies, geology, history, applied linguistics, philology, Polish language, pedagogy, economics, law, public administration, psychology, applied social sciences, management, mathematics, computer science, and mechanics. Among the university's notable alumni are heads of state, prime ministers, Nobel Prize laureates, including Joseph Rotblat, Sir Joseph Rotblat and Olga Tokarczuk, as well as several historically important individuals in their res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Kaim
Barbara Kaim (born 1 December 1952) is a Polish archaeologist, professor at the Faculty of Archaeology University of Warsaw. Her research focuses on the Achaemenid, Parthian and Sasanian periods in Iran and Central Asia. Professional career Barbara Kaim studied at the Institute of Archaeology (now Faculty of Archaeology) (graduated in 1977). Since 1977 she worked as a Research Assistant. After completing her PhD in 1983, she began working as an assistant professor in the Department of Near Eastern Archaeology at the same institute. She did her habilitation in 2003, working on the architecture of Kushan period, and became a professor in 2005. On 18 April 2013, she was awarded the title of Professor. Excavations In 1995 Barbara Kaim began archaeological research at Old Serakhs, located in Serakhs oasis, Turkmenistan. Two years later she started excavations at Mele Hairam in the same oasis, which revealed the remains of the Zoroastrian fire temple. In 2005-2006 she was a co-dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namazga-Tepe
Namazga-Tepe or ''Namazga-depe'', is a Bronze Age ( BMAC) archaeological site in Turkmenistan, at the foot of the Kopet-Dag, near the delta of the Tejen River, some 100 km east of Aşgabat, near the border to Iran. Excavated by Vadim Mikhailovich Masson, Viktor Sarianidi, and I. N. Khlopin from the 1950s, the site set the chronology for the Bronze Age sites in Turkmenistan (Namazga III-VI). Namazga culture was preceded in the area by the Jeitun culture. Chronology It is believed that the Anau culture of Turkmenistan considerably precedes the Namazga culture in the area. Namazga I period (c. 4000–3500 BC),Vidale, Massimo, (2017)Treasures from the Oxus. p. 9, Table 1. is considered contemporary with Anau IB2 period. Namazga III (c. 3200–2800) as a village settlement in Late Chalcolithic phase, and Namazga IV (c. 2800–2400 BC) as a proto-urban site, both belong to the Late Regionalization Era. Namazga V (c. 2400–2000 BC), is in the Integration Era or the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Central Asia
The history of Central Asia concerns the history of the various peoples that have inhabited Central Asia. The lifestyle of such people has been determined primarily by the area's climate and geography of Asia, geography. The aridity of the region makes agriculture difficult and distance from the sea cut it off from much trade. Thus, few major cities developed in the region. Nomadic horse peoples of the steppe dominated the area for millennia. Relations between the steppe nomads and the settled people in and around Central Asia were marked by conflict. The nomadic lifestyle was well suited to warfare, and the steppe horse riders became some of the most militarily potent people in the world, due to the devastating techniques and ability of their horse archers. Periodically, tribal leaders or changing conditions would cause several tribes to organize themselves into a single military force, which would then often launch campaigns of conquest, especially into more 'civilized' areas. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Turkmenistan Complex Archaeological Expedition
The South Turkmenistan Complex Archaeological Expedition (STACE), also called the South Turkmenistan Archaeological Inter-disciplinary Expedition of the Academy of Sciences of the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic (YuTAKE) was endorsed by the Turkmenistan Academy of Sciences. It was initially organized by the Oriental studies, orientalist Mikhail Evgenievich Masson in 1946. The expedition had several excavations or "Brigades", based on sites and periods, and were spread over many years. The Chalcolithic settlements of southern Turkmenistan, according to Masson, date to the late 5th millennium – early 3rd millennium BC, as assessed by carbon dating and Paleomagnetism, paleomagnetic studies of the findings from the excavations carried out by STACE in the Altyndepe and Tekkendepe. The foothills of the Kopetdag mountains have revealed the earliest village cultures of Central Asia in the areas of Namazga-Tepe (more than 50 ha) and Altyndepe (26 ha), Ulug Depe (20 ha), Kara Depe (15 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |