|
Benson, Oxfordshire
Benson is a village and Civil parishes in England, civil parish in South Oxfordshire, England. The United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 Census gave the parish population as 4,754. It lies about a mile and a half (2.4 km) north of Wallingford, Oxfordshire, Wallingford at the foot of the Chiltern Hills, where a chalk stream, Ewelme Brook, joins the River Thames next to Benson Lock. Geography Benson, on the north and east banks of the Thames, was unaffected by the Local Government Act 1972, 1974 boundary changes between Berkshire and Oxfordshire. It rests on river silts and gravel, just above surrounding marshy land named in the nearby settlements of Preston Crowmarsh, Crowmarsh Gifford, and Rokemarsh. The fertile land surrounding Benson meant that farming was the main source of employment until the 20th century. The brook through the village is home to trout and to the invasive American signal crayfish. Climate The village lies in a well-known frost-pocket, sometimes recording the low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department formed in 2008 and which reports directly to Parliament. ONS is the UK Government's single largest statistical producer of independent statistics on the UK's economy and society, used to assist the planning and allocation of resources, policy-making and decision-making. ONS designs, manages and runs the census in England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Met Office
The Met Office, until November 2000 officially the Meteorological Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather and climate service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology and is led by CEO Penelope Endersby, who took on the role as Chief Executive in December 2018 and is the first woman to do so. The Met Office makes meteorological predictions across all timescales from weather forecasts to climate change. Although an executive agency of the UK Government, the Met Office supports the Scottish Government, Welsh Government and Northern Ireland Executive in their functions and preparations ahead of intense weather and planning for extreme weather alerts. Met Office policies can be used by each government to inform their planning and decision making processes. The Met Office has an office located in the Scottish capital, Edinburgh, and a forecasting centre in Aberdeen in the north–east of Scotland, which are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bensington
The Battle of Bensington was a major battle fought between Mercia, led by King Offa, and the West Saxons led by Cynewulf of Wessex. It ended with a victory for the Mercians. The battle and its consequences Nearly nothing is known about the battle itself: the only evidence is a brief annal in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' for 779 (777 in the manuscripts, whose dating is at this point dislocated by two years) reading: "Her Cynewulf & Offa gefuhton ymb Benesingtun & Offa nam þone tuun" ("This year Cynewulf and Offa fought near Bensington and Offa took the town"). Patrick Sims-Williams viewed the battle as being echoed in a territorial dispute between the Archbishop of Canterbury and the abbess of Cookham Abbey (named Cynethryth, probably the widow of Offa): Offa had taken the abbey and its lands, apparently by winning the Battle of Bensington, including land claimed not by the West-Saxon kings but by Christ Church, Canterbury Canterbury Cathedral is the cathedral of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
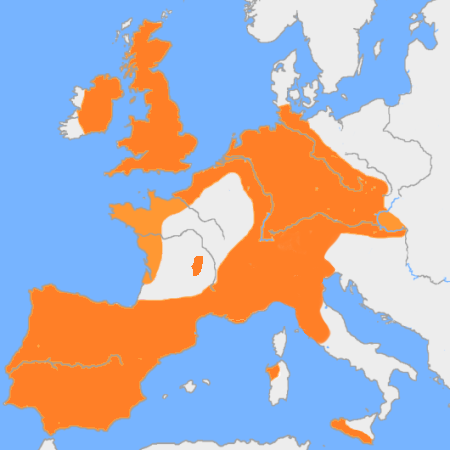
Offa Of Mercia
Offa ( 29 July 796 AD) was King of Mercia, a kingdom of Anglo-Saxon England, from 757 until his death in 796. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æthelbald. Offa defeated the other claimant, Beornred. In the early years of Offa's reign, it is likely that he consolidated his control of Midland peoples such as the Hwicce and the Magonsæte. Taking advantage of instability in the kingdom of Kent to establish himself as overlord, Offa also controlled Sussex by 771, though his authority did not remain unchallenged in either territory. In the 780s he extended Mercian Supremacy over most of southern England, allying with Beorhtric of Wessex, who married Offa's daughter Eadburh, and regained complete control of the southeast. He also became the overlord of East Anglia and had King Æthelberht II of East Anglia beheaded in 794, perhaps for rebelling against him. Offa was a Christia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wessex
The Kingdom of the West Saxons, also known as the Kingdom of Wessex, was an Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy, kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from around 519 until Alfred the Great declared himself as King of the Anglo-Saxons in 886. The Anglo-Saxons believed that Wessex was founded by Cerdic and Cynric of the Gewisse, though this is considered by some to be a legend. The two main sources for the history of Wessex are the West Saxon Genealogical Regnal List and the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' (the latter of which drew on and adapted an early version of the List), which sometimes conflict. Wessex became a Christianity, Christian kingdom after Cenwalh () was baptised and was expanded under his rule. Cædwalla later conquered Kingdom of Sussex, Sussex, Kingdom of Kent, Kent and the Isle of Wight. His successor, Ine of Wessex, Ine (), issued one of the oldest surviving English law codes and established a second West Saxon bishopric. The throne subsequently passed to a series of kings wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxoniensia
The Oxfordshire Architectural and Historical Society (OAHS) has existed in one form or another since at least 1839, although with its current name only since 1972. , , United Kingdom. Its annual publication, ''Oxoniensia'', has been produced since 1936. Overview The Society was founded in 1839 as the Society for Promoting the Study of Gothic Architecture. In 1848, it was renamed to become the Oxford Architectural Society and in 1860 it was re-founded as the Oxford Architectural and Historical Society. In 1972, the society ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Archaeology
Oxford Archaeology (OA, trading name of Oxford Archaeology Limited) is one of the largest and longest-established independent archaeology and heritage practices in Europe, operating from three permanent offices in Oxford, Lancaster and Cambridge, and working across the UK. OA is a Registered Organisation with the Chartered Institute for Archaeologists (CIfA), and carries out commercial archaeological fieldwork in advance of development, as well as a range of other heritage related services. Oxford Archaeology primarily operates in the UK, but has also carried out contracts around the world, including Sudan, Qatar, Central Asia, China and the Caribbean. Numbers of employees vary owing to the project-based nature of the work, but in 2023 OA employed over 350 people. The registered head office is in Osney Mead, Oxford, southern England; this address is also the base for OA's Oxford office. Other offices are in Lancaster, northern England, and Cambridge, based at Bar Hill, Cambri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Settlement Of Britain
The settlement of Great Britain by Germanic peoples from continental Europe led to the development of an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon cultural identity and a shared Germanic language—Old English—whose closest known relative is Old Frisian, spoken on the other side of the North Sea. The first Germanic speakers to settle Britain permanently are likely to have been soldiers recruited by the Roman administration in the 4th century AD, or even earlier. In the early 5th century, during the end of Roman rule in Britain and the breakdown of the Roman economy, larger numbers arrived, and their impact upon local culture and politics increased. There is Historiography of the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, ongoing debate about the scale, timing and nature of the Anglo-Saxon settlements and also about what happened to the existing populations of the regions where the migrants settled. The available evidence includes a small number of medieval texts which emphasize Saxons, Saxon settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Iron Age
The British Iron Age is a conventional name used in the archaeology of Great Britain, referring to the prehistoric and protohistoric phases of the Iron Age culture of the main island and the smaller islands, typically excluding prehistoric Ireland, which had an Iron Age Ireland, independent Iron Age culture of its own. The Iron Age is not an archaeological horizon of common artefacts but is rather a locally-diverse cultural phase. The British Iron Age followed the Bronze Age Britain, British Bronze Age and lasted in theory from the first significant use of iron for tools and weapons in Britain to the Romano-British culture, Romanisation of the southern half of the island. The Romanised culture is termed Roman Britain and is considered to supplant the British Iron Age. The tribes living in Britain during this time are often popularly considered to be part of a broadly-Celts, Celtic culture, but in recent years, that has been disputed. At a minimum, "Celtic" is a linguistic ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Britain
Bronze Age Britain is an era of British history that spanned from until . Lasting for approximately 1,700 years, it was preceded by the era of Neolithic Britain and was in turn followed by the period of Iron Age Britain. Being categorised as the Bronze Age, it was marked by the use of copper and then bronze by the prehistoric Britons, who used such metals to fashion tools. Great Britain in the Bronze Age also saw the widespread adoption of agriculture. During the British Bronze Age, large megalithic monuments similar to those from the Late Neolithic continued to be constructed or modified, including such sites as Avebury, Stonehenge, Silbury Hill and Must Farm. That has been described as a time "when elaborate ceremonial practices emerged among some communities of subsistence agriculturalists of western Europe". History Early Bronze Age (EBA), c. 2500–1500 BC There is no clear consensus on the date for the beginning of the Bronze Age in Great Britain and Ireland. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Britain
Several species of humans have intermittently occupied Great Britain for almost a million years. The earliest evidence of human occupation around 900,000 years ago is at Happisburgh on the Norfolk coast, with stone tools and footprints probably made by ''Homo antecessor''. The oldest human fossils, around 500,000 years old, are of ''Homo heidelbergensis'' at Boxgrove in Sussex. Until this time Britain had been permanently connected to the Continent by a chalk ridge between South East England and northern France called the Weald-Artois Anticline, but during the Anglian Glaciation around 425,000 years ago a megaflood broke through the ridge, and Britain became an island when sea levels rose during the following Hoxnian interglacial. Fossils of very early Neanderthals dating to around 400,000 years ago have been found at Swanscombe in Kent, and of classic Neanderthals about 225,000 years old at Pontnewydd in Wales. Britain was unoccupied by humans between 180,000 and 60,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Name
A personal name, full name or prosoponym (from Ancient Greek ''prósōpon'' – person, and ''onoma'' –name) is the set of names by which an individual person or animal is known. When taken together as a word-group, they all relate to that one individual. In many cultures, the term is synonymous with the ''birth name'' or ''legal name'' of the individual. In linguistic classification, personal names are studied within a specific onomastic discipline, called anthroponymy. In Western culture, nearly all individuals possess at least one ''given name'' (also known as a ''first name'', ''forename'', or ''Christian name''), together with a ''surname'' (also known as a ''last name'' or ''family name''). In the name "James Smith", for example, ''James'' is the first name and ''Smith'' is the surname. Surnames in the West generally indicate that the individual belongs to a family, a tribe, or a clan, although the exact relationships vary: they may be given at birth, taken upon adoption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |