|
Bell Test Experiments
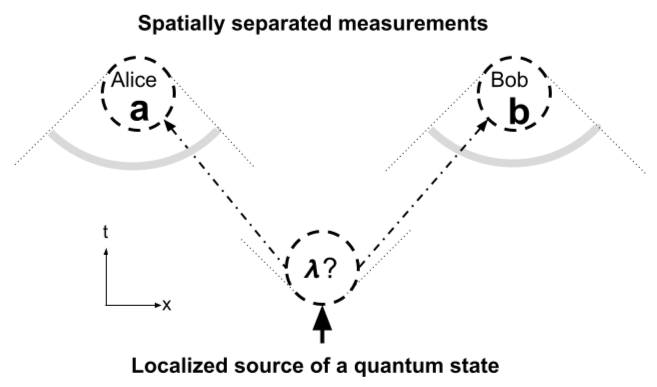
A Bell test, also known as Bell inequality test or Bell experiment, is a real-world physics experiment designed to test the theory of quantum mechanics in relation to Albert Einstein's concept of local realism. Named for John Stewart Bell, the experiments test whether or not the real world satisfies local realism, which requires the presence of some additional local variables (called "hidden" because they are not a feature of quantum theory) to explain the behavior of particles like photons and electrons. The test empirically evaluates the implications of Bell's theorem. , all Bell tests have found that the hypothesis of local hidden variables is inconsistent with the way that physical systems behave. Many types of Bell tests have been performed in physics laboratories, often with the goal of ameliorating problems of experimental design or set-up that could in principle affect the validity of the findings of earlier Bell tests. This is known as "closing loopholes in Bell tests". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathan Rosen
Nathan Rosen (; March 22, 1909 – December 18, 1995) was an American and Israeli physicist noted for his study on the structure of the hydrogen molecule and his collaboration with Albert Einstein and Boris Podolsky on entangled wave functions and the EPR paradox. He is also remembered for the Einstein–Rosen bridge, the first known kind of wormhole. Background Nathan Rosen was born into a Jewish family in Brooklyn, New York (state), New York. He attended MIT during the Great Depression, where he received a bachelor's degree in electromechanical engineering and later a master's and a doctorate in physics. As a student he published several papers of note, one being "The Neutron," which attempted to explain the structure of the atomic nucleus a year before their discovery by James Chadwick. He also developed an interest in wave functions, and later, gravitation, when he worked as a fellow at the University of Michigan and Princeton University. State of science At the beginning of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Zeilinger
Anton Zeilinger (; born 20 May 1945) is an Austrian quantum physicist and Nobel laureate in physics of 2022. Zeilinger is professor of physics emeritus at the University of Vienna and senior scientist at the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information of the Austrian Academy of Sciences. Most of his research concerns the fundamental aspects and applications of quantum entanglement. In 2007, Zeilinger received the first Inaugural Isaac Newton Medal of the Institute of Physics, London, for "his pioneering conceptual and experimental contributions to the foundations of quantum physics, which have become the cornerstone for the rapidly-evolving field of quantum information". In October 2022, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Alain Aspect and John Clauser for their work involving experiments with entangled photons, establishing the violation of Bell inequalities and pioneering quantum information science. Early life and education Anton Zeilinger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alain Aspect
Alain Aspect (; born 15 June 1947) is a French physicist noted for his experimental work on quantum entanglement. Aspect was awarded the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with John Clauser and Anton Zeilinger, "for experiments with Quantum entanglement, entangled photons, establishing the violation of Bell inequalities and pioneering quantum information science". Education Aspect is a graduate of the École Normale Supérieure de Cachan (ENS Cachan, today part of Paris-Saclay University). He passed the ''agrégation'' in physics in 1969 and received his PhD degree in 1971 from the École supérieure d'optique (later known as Institut d'Optique Graduate School) of Université d'Orsay (later known as Université Paris-Sud). He then taught for three years in Cameroon as a replacement for then compulsory military service. In the early 1980s, while working on his doctorat d'État (habilitation thesis), he performed the Bell test experiments that showed that Albert Einstein, Boris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Clauser
John Francis Clauser (; born December 1, 1942) is an American theoretical and experimental physicist known for contributions to the foundations of quantum mechanics, in particular the Clauser–Horne–Shimony–Holt inequality. Clauser was awarded the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Alain Aspect and Anton Zeilinger "for experiments with entangled photons, establishing the violation of Bell inequalities and pioneering quantum information science". In 2023, he declared himself as a climate change denier. Early life Clauser was born in Pasadena, California. His father, Francis H. Clauser, was a professor of aeronautical engineering who founded and chaired the aeronautics department at Johns Hopkins University. He later served as the Clark Blanchard Millikan Professor of Engineering at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). His mother, Catharine McMillan, was the humanities librarian at Caltech and sister of 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry laureate Edwin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHSH Inequality
In physics, the Clauser–Horne–Shimony–Holt (CHSH) inequality can be used in the proof of Bell's theorem, which states that certain consequences of entanglement in quantum mechanics cannot be reproduced by local hidden-variable theories. Experimental verification of the inequality being violated is seen as confirmation that nature cannot be described by such theories. CHSH stands for John Clauser, Michael Horne, Abner Shimony, and Richard Holt, who described it in a much-cited paper published in 1969. They derived the CHSH inequality, which, as with John Stewart Bell's original inequality, is a constraint—on the statistical occurrence of “coincidences” in a Bell test—which is necessarily true if an underlying local hidden-variable theory exists. In practice, the inequality is routinely violated by modern experiments in quantum mechanics. Statement The usual form of the CHSH inequality is where a and a' are detector settings on side A, b and b' on side B, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin (physics)
Spin is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic form of angular momentum carried by elementary particles, and thus by List of particles#Composite particles, composite particles such as hadrons, atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei, and atoms. Spin is quantized, and accurate models for the interaction with spin require relativistic quantum mechanics or quantum field theory. The existence of electron spin angular momentum is inferred from experiments, such as the Stern–Gerlach experiment, in which silver atoms were observed to possess two possible discrete angular momenta despite having no orbital angular momentum. The relativistic spin–statistics theorem connects electron spin quantization to the Pauli exclusion principle: observations of exclusion imply half-integer spin, and observations of half-integer spin imply exclusion. Spin is described mathematically as a vector for some particles such as photons, and as a spinor or bispinor for other particles such as electrons. Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Locality
In physics, the principle of locality states that an object is influenced directly only by its immediate surroundings. A theory that includes the principle of locality is said to be a "local theory". This is an alternative to the concept of instantaneous, or "non-local" action at a distance. Locality evolved out of the Classical field theory, field theories of classical physics. The idea is that for a cause at one point to have an effect at another point, something in the space between those points must mediate the action. To exert an influence, something, such as a wave or particle, must travel through the space between the two points, carrying the influence. The special relativity, special theory of relativity limits the maximum speed at which causal influence can travel to the speed of light, c. Therefore, the principle of locality implies that an event at one point cannot cause a truly simultaneous result at another point. An event at point A cannot cause a result at point B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
No-communication Theorem
In physics, the no-communication theorem (also referred to as the no-signaling principle) is a no-go theorem in quantum information theory. It asserts that during the measurement of an entangled quantum state, it is impossible for one observer to transmit information to another observer, regardless of their spatial separation. This conclusion preserves the principle of causality in quantum mechanics and ensures that information transfer does not violate special relativity by exceeding the speed of light. The theorem is significant because quantum entanglement creates correlations between distant events that might initially appear to enable faster-than-light communication. The no-communication theorem establishes conditions under which such transmission is impossible, thus resolving paradoxes like the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) paradox and addressing the violations of local realism observed in Bell's theorem. Specifically, it demonstrates that the failure of local realism doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causality (physics)
Causality is the relationship between causes and effects. While causality is also a topic studied from the perspectives of philosophy and physics, it is operationalized so that causes of an event must be in the past light cone of the event and ultimately reducible to fundamental interactions. Similarly, a cause cannot have an effect outside its future light cone. Macroscopic vs microscopic causality Causality can be defined macroscopically, at the level of human observers, or microscopically, for fundamental events at the atomic level. The strong causality principle forbids information transfer faster than the speed of light; the weak causality principle operates at the microscopic level and need not lead to information transfer. Physical models can obey the weak principle without obeying the strong version. Macroscopic causality In classical physics, an effect cannot occur ''before'' its cause which is why solutions such as the advanced time solutions of the Liénard–W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action At A Distance
Action at a distance is the concept in physics that an object's motion (physics), motion can be affected by another object without the two being in Contact mechanics, physical contact; that is, it is the concept of the non-local interaction of objects that are separated in space. Coulomb's law and Newton's law of universal gravitation are based on action at a distance. Historically, action at a distance was the earliest scientific model for gravity and electricity and it continues to be useful in many practical cases. In the 19th and 20th centuries, field models arose to explain these phenomena with more precision. The discovery of Electron, electrons and of special relativity led to new action at a distance models providing alternative to field theories. Under our modern understanding, the four fundamental interactions (gravity, electromagnetism, the strong interaction and the weak interaction) in all of physics are not described by action at a distance. Categories of action I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Cone
In special and general relativity, a light cone (or "null cone") is the path that a flash of light, emanating from a single Event (relativity), event (localized to a single point in space and a single moment in time) and traveling in all directions, would take through spacetime. Details If one imagines the light confined to a two-dimensional plane, the light from the flash spreads out in a circle after the event E occurs, and if we graph the growing circle with the vertical axis of the graph representing time, the result is a Cone (geometry), cone, known as the future light cone. The past light cone behaves like the future light cone in reverse, a circle which contracts in radius at the speed of light until it converges to a point at the exact position and time of the event E. In reality, there are three space Dimension (vector space), dimensions, so the light would actually form an expanding or contracting sphere in three-dimensional (3D) space rather than a circle in 2D, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |