|
Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany. Before the Roman province came into existence in about 50 BC, the region was conquered by Julius Caesar during his Gallic Wars. His report, the ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'', described Belgic Gaul as one of the three parts of Gaul (Tres Galliæ), the other two being Gallia Aquitania and Gallia Lugdunensis. Belgica stretched from the Marne River, Marne and Seine rivers, which Caesar described as a cultural boundary between the Belgae and the Celts, Celtic Gauls. In the north and east it stretched all the way to the Rhine. The official Roman province of this name was later created by emperor Augustus in 22 BC, and named after the Belgae, as the largest tribal confederation in the area. However, it also included the territories of the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgae
The Belgae ( , ) were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by Julius Caesar in his Commentarii de Bello Gallico, account of his wars in Gaul. Some peoples in southern Roman Britain, Britain were also called Belgae and had apparently moved from the continent. T. F. O'Rahilly believed that some had moved further west and he equated them with the Fir Bolg in Ireland. The Roman province of Gallia Belgica was named after the continental Belgae. The term continued to be used in the region until the present day and is reflected in the name of the modern country of Belgium. Etymology The consensus among linguists is that the ethnic name ''Belgae'' probably comes from the Proto-Celtic root ''*belg-'' or ''*bolg-'' meaning "to swell (particularly with anger/battle fury/etc.)", cognate with the Dutch language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
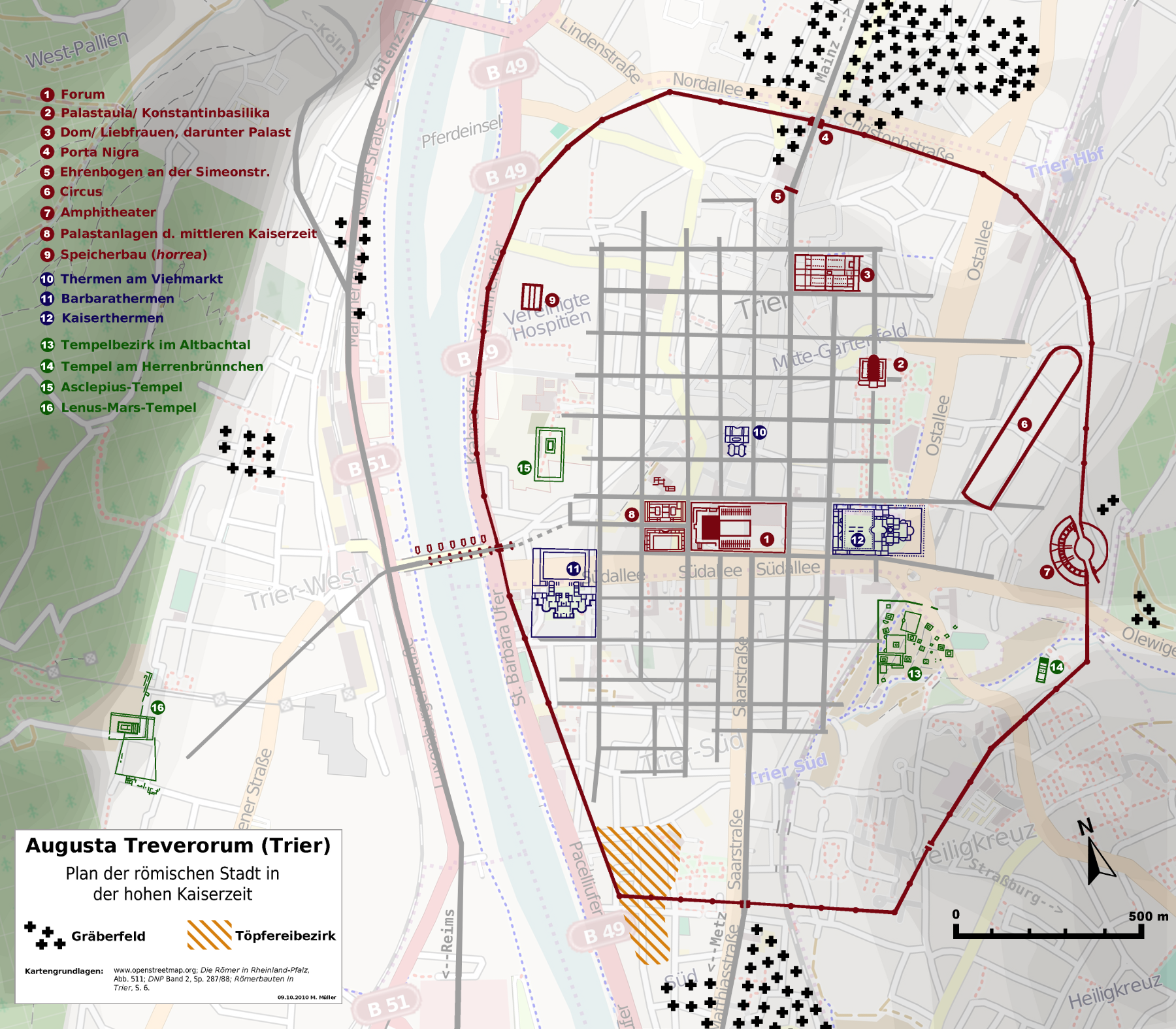
Augusta Treverorum
Augusta Treverorum (Latin for "City of Augustus in the Land of the Treveri") was a Ancient Rome, Roman city on the Moselle River, from which modern Trier emerged. The date of the city's founding is placed between the construction of the first Roman bridge, Roman bridge in Trier (18/17 BC) and the late reign of Augustus († 14 AD). In the Roman Empire, Trier formed the main town of the ''civitas'' of the Treverians, where several ten thousand people lived, and belonged to the province of Gallia Belgica. Roman Trier gained particular importance in late antiquity: between the late 3rd and late 4th centuries several rulers, including Constantine the Great, used the city as one of the western imperial residences, sponsoring monumental buildings such as the Trier Imperial Baths and the Aula Palatina, Basilica of Constantine. With a high five-digit population in 300, Augusta Treverorum, now sometimes called Treveris, was the largest city north of the Alps and thus had the status of a glo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the south, and the North Sea to the west. Belgium covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.8 million; its population density of ranks List of countries and dependencies by population density, 22nd in the world and Area and population of European countries, sixth in Europe. The capital and Metropolitan areas in Belgium, largest metropolitan region is City of Brussels, Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven. Belgium is a parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy with a complex Federation, federal system structured on regional and linguistic grounds. The country is divided into three highly autonomous Communities, regions and language areas o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durocortorum
Durocortorum was the name of the city of Reims during the Roman era. It was the capital of the Remi tribe and the second largest city in Roman Gaul. Before the Roman conquest of northern Gaul, the city was founded circa 80 BC and was the capital of the tribe of the Remi. In the course of Julius Caesar's conquest of Gaul (58–51 BC), the Remi allied themselves with the Romans, and, by their fidelity throughout the various Gallic insurrections, secured the special favour of imperial power. At its height in Roman times the city had a population in the range of 30,000 – 50,000 or perhaps up to 100,000, and was an important node in the road system of Gallia Belgica. After the installation of Magnus Maximus in Augusta Treverorum, Durocortorum was renamed ''Metropolis Civitas Remorum'', and no longer served as the capital of Gallia Belgica although it remained the capital of Belgica Secunda. Etymology and historical mentions The Latin Durocortōrum comes from the Celtic "Duroco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civitas Tungrorum
The ''Civitas Tungrorum'' was a large Roman administrative district dominating what is now eastern Belgium and the southern Netherlands. In the early days of the Roman Empire it was in the province of Gallia Belgica, but it later joined the neighbouring lower Rhine River border districts, within the province of Germania Inferior. Its capital was ''Aduatuca Tungrorum'', now Tongeren. Like many other Roman administrative districts, it was named after the tribal grouping that lived there, the Tungri, although that name is not known from the area before it became part of the Roman Empire. Also like other such districts, it became the basis for a medieval bishopric, but the bishops of Tongeren moved first to nearby Maastricht and then to Liège. Location The geographical boundaries of the ''civitas'' probably corresponded at least roughly to the area of the large medieval Catholic diocese of Liège, which was reduced in 1559. In modern terms this large diocese contained approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treveri
The Treveri (Gaulish language, Gaulish: *''Treweroi'') were a Germanic peoples, Germanic or Celts, Celtic tribe of the Belgae group who inhabited the lower valley of the Moselle (river), Moselle in modern day Germany from around 150 BCE, if not earlier, until their displacement by the Franks. Their domain lay within the southern fringes of the ''Silva Arduenna'' (Ardennes Forest), a part of the vast Silva Carbonaria, in what are now Luxembourg, southeastern Belgium and western Germany; its centre was the city of Trier (''History of Trier, Augusta Treverorum''), to which the Treveri give their name. Celtic languages, Celtic in language, according to Tacitus they claimed Germanic descent.Tacitus writes, "The Treveri and Nervii are even eager in their claims of a German origin, thinking that the glory of this descent distinguishes them from the uniform level of Gallic effeminacy." ''#Germania, Germania'' s:Germania#XXVIII, XXVIII. They contained both Gauls, Gallic and Germanic influenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Gaul
Roman Gaul refers to GaulThe territory of Gaul roughly corresponds to modern-day France, Belgium and Luxembourg, and adjacent parts of the Netherlands, Switzerland and Germany. under provincial rule in the Roman Empire from the 1st century BC to the 5th century AD. History During the Republic The Roman Republic's influence began in southern Gaul. By the mid-2nd century BC, Rome was trading heavily with the Greek colony of Massalia, Massilia (modern Marseille) and entered into an alliance with them, by which Rome agreed to protect the town from local Gauls, including the nearby Aquitani and from sea-borne Carthaginians and other rivals, in exchange for land that the Romans wanted in order to build a road to Hispania to improve troop movements to its provinces there. The Mediterranean settlements on the coast continued to be threatened by the powerful Gallic tribes to the north and in 122 BC the Roman general Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus (consul 122 BC), Gnaeus Domitius Ahe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century BC, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . "[T]he Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe." in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic languages and other cultural similarities.. "C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallia Aquitania
Gallia Aquitania (, ), also known as Aquitaine or Aquitaine Gaul, was a list of Roman provinces, province of the Roman Empire. It lies in present-day southwest France and the Comarques of Catalonia, comarca of Val d'Aran in northeast Spain, where it gives its name to the modern Regions of France, region of Aquitaine. It was bordered by the provinces of Gallia Lugdunensis, Gallia Narbonensis, and Hispania Tarraconensis.John Frederick Drinkwater (1998). "Gaul (Transalpine)". ''The Oxford Companion to Classical Civilization.'' Ed. Simon Hornblower and Antony Spawforth. Oxford University PressOxford Reference Online Tribes of Aquitania Fourteen Celtic tribes and over twenty Aquitanian tribes occupied the area from the northern slopes of the Pyrenees in the south to the ''Liger'' (Loire) river in the north. The major tribes are listed at the end of this section.''Strabo: The Geography''The Aquitani There were more than twenty tribes of Aquitani, but they were small and lacking in repu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trier
Trier ( , ; ), formerly and traditionally known in English as Trèves ( , ) and Triers (see also Names of Trier in different languages, names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle (river), Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the west of the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, near the border with Luxembourg and within the important Mosel (wine region), Moselle wine region. Founded by the Ancient Romans, Romans in the late 1st century BC as ''Augusta Treverorum'' ("The City of Augustus among the Treveri"), Trier is considered Germany's oldest city. It is also the oldest cathedral, seat of a bishop north of the Alps. Trier was one of the four capitals of the Roman Empire during the Tetrarchy period in the late 3rd and early 4th centuries. In the Middle Ages, the archbishop-elector of Trier was an important prince of the Church who controlled land from the French border to the Rhine. The archbishop-elector of Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediomatrici
The Mediomatrici (Gaulish: ''*Medio-māteres'') were according to Caesar a Gaulish tribe at the frontier to the Belgicae dwelling in the present-day regions Lorraine, Upper Moselle during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Name They are mentioned as ''Mediomatricorum'' and ''Mediomatricis'' (dat.) by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), ''Mediomatrikoì'' (Μεδιοματρικοὶ ) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), ''Mediomatrici'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), ''Mediomatricos'' (acc.) by Tacitus (early 2nd c. AD), and as ''Mediomátrikes'' (Μεδιομάτρικες) by Ptolemy (2nd c. AD). The ethnonym ''Mediomatrici'' is a Latinized form of the Gaulish ''*Medio-māteres'', which literally means 'Middle-Mothers'. It is formed with the stem ''medio-'' ('in the middle, central') attached to a plural form of ''mātīr'' ('mother'). The name could be interpreted as meaning 'those who live between the Matrona (Marne) and the Matra rivers' (i.e. the mother-rivers), or possibly as the 'Mothers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankish Kingdom
The Kingdom of the Franks (), also known as the Frankish Kingdom, or just Francia, was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Frankish Merovingian and Carolingian dynasties during the Early Middle Ages. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period era. Originally, the core Frankish territories inside the former Western Roman Empire were located close to the Rhine and Meuse rivers in the north, but Frankish chiefs such as Chlodio would eventually expand their influence within Roman territory as far as the Somme river in the 5th century. Childeric I, a Salian Frankish king, was one of several military leaders commanding Roman forces of various ethnic affiliations in the northern part of what is now France. His son, Clovis I, succeeded in unifying most of Gaul under his rule in the 6th century by notably conquering Soissons in 486 and Aquitaine in 507 following the collapse of the Western Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |